Trigeminal Neuralgia (TN) is one of the most chronic facial pain disorders that may manifest in two types Typical and Atypical Trigeminal Neuralgia. Although both have the same characteristic of facial pain that originates from the trigeminal nervous system, they are distinct in many important aspects, such as their cause as well as their characteristics and methods of treatment.
The differences shed some light on the distinct features in Typical as well as Atypical Trigeminal Neuralgia. This will allow them to gain a better knowledge of this condition as well as their treatment.
What is Typical Trigeminal Neuralgia?
Trigeminal neuralgia (TN) is a neurologic disorder that manifests as acute and severe facial pain which is usually described as stabbing, sharp, or electric shock-like tingling sensations.
The most affected area is the trigeminal nerve which is responsible for transferring sensory information through the facial area to the brain. The most common occurrence of TN is very brief, but intense, episodes of pain excruciatingly painful, which are caused by even the smallest of triggers like touching the face, chewing, or talking. The condition can severely affect the quality of life of a person and, in most cases, requires medical intervention to manage.
What is Atypical Trigeminal Neuralgia?
Atypical Trigeminal Neuralgia, also called Type 2 or Atypical Facial Pain is a neurologic condition characterized by facial pain that differs from the typical or classic appearance of Trigeminal Neuralgia (TN).
Contrary to the abrupt intense, frequent, and sporadic pain typical of TN Atypical TN is characterized by constant burning, aching, or painful facial throbbing. The pain could be less severe, but it can persist for long periods of time or become chronic.
Atypical TN typically lacks particular trigger factors, which makes it harder to identify and manage than normal TN. It may be linked to many underlying causes, such as neurological disorders or as a result of other health problems, thereby making it more difficult to diagnose and treat.
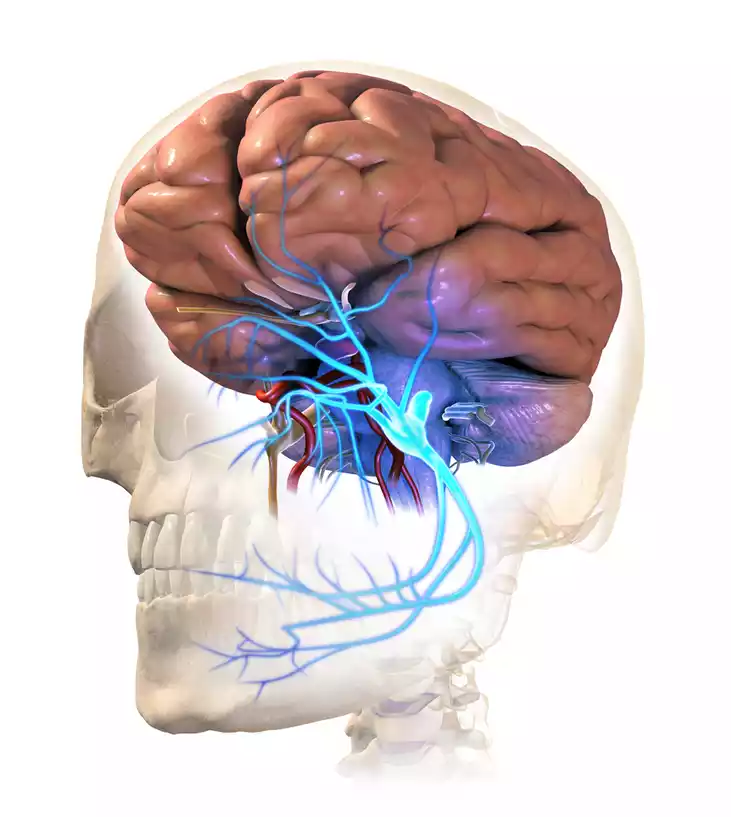
Importance of understanding TN variations
Understanding the different forms that occur in Trigeminal Neuralgia (TN), which includes both atypical and typical forms, is of vital importance for a variety of reasons:
- Accurate diagnosis: Understanding the distinctions between typical as well as atypical types of TN is essential for healthcare professionals to arrive at an appropriate diagnosis. This will ensure that patients receive the appropriate and timely treatment as the treatment methods may differ dramatically.
- Tailored Treatment: Distinguishing between the two kinds of TN allows the creation of custom treatment strategies. The typical TN generally responds well to certain surgical and medication treatments however the atypical TN might require different treatment options due to its ongoing and unpredictable nature.
- Quality of Life Quality of Life: TN, in all its types, has the potential to severely affect the quality of life of a person because of the intense pain it can cause. Knowing TN variations aids in the development of strategies to ease discomfort, manage symptoms, and improve the overall health of patients.
- Research and advancements: The knowledge of TN variations is the basis for the ongoing research and advancements in medical technology. It encourages health professionals to study the root causes as well as risk factors and the possibility of new treatments for normal and abnormal TN.
- Patient Education: Informing patients about the various forms of TN allows them to better comprehend their health condition, control their expectations of the outcome of treatment, and take part in their healthcare decisions.
- Support and Advocacy: Support and advocacy by understanding TN variations as well as advocacy groups and support networks can offer better-targeted aid and support to those who suffer from these ailments and foster a sense the community and mutual acceptance between patients.
Knowing the various variations in Trigeminal Neuralgia is crucial for an accurate diagnosis, individualized treatment and a better standard of living, advances in medical science, as well as the overall health of people suffering from this challenging neurological condition.
Comparison Table of Typical and Atypical Trigeminal Neuralgia
Here is a comparison table highlighting the key differences between Typical and Atypical Trigeminal Neuralgia:
| Aspect | Typical Trigeminal Neuralgia (TN) | Atypical Trigeminal Neuralgia (TN) |
|---|---|---|
| Pain Characteristics | Sudden, severe, electric shock-like | Constant, burning, aching, or throbbing |
| Pain Duration | Short-lived episodes | Longer-lasting, potentially chronic |
| Trigger Factors | Often triggered by specific actions | Lacks specific trigger factors |
| Pain Frequency | Episodic, with pain-free intervals | May be persistent or chronic |
| Underlying Causes | Typically compression of the trigeminal nerve | May be associated with neurological conditions or other health issues |
| Diagnosis Challenge | Relatively straightforward diagnosis | May be more challenging to diagnose |
| Response to Medications | Typically responsive to certain medications | May require different medications or approaches |
| Surgical Interventions | Microvascular decompression surgery may be considered | Surgical options may vary, often less straightforward |
| Prognosis | Generally better response to treatment | More variable outcomes, potentially more challenging to manage |
| Impact on Quality of Life | Significant, but with periods of relief | Persistent pain can have a profound impact on daily life |
| Research Focus | Well-studied, with established treatment guidelines | Ongoing research to better understand and manage atypical TN |
| Support and Awareness | Well-established support groups and awareness | Developing awareness and support networks for atypical TN |
Please note that while this table highlights the typical differences between the two forms of Trigeminal Neuralgia, individual cases can vary, and diagnosis and treatment should be tailored to each patient’s unique circumstances.
Microvascular decompression surgery
The Microvascular Decompression (MVD) procedure is a surgical treatment that is utilized for treating Trigeminal Neuralgia (TN) and various other neurological disorders. This procedure aims to relieve the pressure on the trigeminal nerve. This is frequently to blame for the extreme facial pain that sufferers suffering from TN.
Here’s a brief outline of the microvascular decompression procedure:
- Indicates: Microvascular decompression is generally recommended when the pain that is associated with Trigeminal Neuralgia becomes chronic, and severe and does not respond well to treatment. It can also be utilized to treat hemifacial spasms and glossopharyngeal neuralgia, in certain instances.
- Procedure: During the surgery, the patient is put under general anesthesia. The neurosurgeon creates a small cut behind the ear on the side afflicted by TN. They then make a small hole in the skull (craniotomy) to reach the part of the brain that is at the base which is where the trigeminal neuron leaves the brainstem.
- Decompression: Its primary goal in this procedure is to determine and alleviate any pressure or contact with the nerve’s trigeminal blood vessel. Teflon or similar materials are commonly used to isolate the vessel that is compressing from the nerve. This helps relieve the pressure and irritation of the nerve. which can reduce or eliminate discomfort.
- Minimumly Invasive Techniques: Recently methods that are minimally invasive such as endoscopic assisted the MVD procedure, were created. These procedures require smaller incisions, and less manipulation of the brain tissue, resulting in faster recovery times and lower risk.
- Rehabilitation: After the surgery, patients are closely watched during their stay in the hospital. couple of days. After they’re stable, they are able to go to their homes. The length of recovery varies from person to person, however many sufferers experience relief from pain right away or within a few hours after the operation. Complete recovery can take weeks or even months.
- Success Rates: Microvascular decompression has a high rate of success when it comes to giving long-term relief from pain for Trigeminal Neuralgia patients. But, as with any surgical procedure, it comes with risks that include bleeding, infection, and, in some instances, nerve damage or loss of hearing.
- Alternatives: MVD is considered one of the best surgical options for TN. But, other procedures, for example, percutaneous procedures like radiofrequency ablation and radiosurgery using gamma knives, could be considered by those who aren’t suitable for MVD.
It is essential for those who are considering microvascular decompression surgery to examine the procedures, their risks advantages, risks, and alternatives with an expert in neurosurgery or a healthcare professional. The choice to undergo MVD is best made following a careful analysis of the particular conditions and with an expert in medical care.
Medical history and clinical examination
Clinical examination and medical history are crucial elements of the diagnostic process of healthcare. They are valuable to health professionals to better understand the health of a patient, spot potential problems, and make educated decisions about the diagnosis and treatment.
Here’s a quick outline of the medical history as well as the clinical exam:
Medical History:
- patient interview: A medical record starts with an in-depth interview with the patient. The healthcare professional asks questions regarding the patient’s current health issues, previous medical conditions as well as family medical history, medication, allergies as well as lifestyle aspects (such as exercise and diet) as well and the social past (such as alcohol and smoking consumption).
- Chief complaint: the primary cause to seek medical attention, also known as the primary complaint is discussed in depth. This assists healthcare professionals in understanding the particular issue or symptoms that require attention.
- Past Medical Histories: Information about the patient’s prior illnesses, surgeries hospitalizations, surgeries, and other chronic medical conditions is gathered. This can provide important details and risks.
- Family Medical History: The family history of illnesses particularly hereditary or genetic conditions could provide insight into the susceptibility of a patient to certain ailments.
- Medication Histories: The patient is inquired about the medications they currently take such as prescription medications as well as over-the-counter medications supplementation, and herbal remedies. This assists in preventing interactions with drugs and helps to identify possible adverse consequences.
- Allergic reactions: All known allergic reactions to food, medications, or environmental triggers are confirmed. Allergies may have serious implications for treatment decisions.
- Social Background: Information about the patient’s lifestyle, including diet, exercise smoking, alcohol consumption, and drug use are gathered. These variables can cause health issues and help guide prevention recommendations.
- System Review: A systematic review of different organ systems (e.g. respiratory, cardiovascular, digestive, etc.)) is carried out to find any additional signs or symptoms.
Clinical Examination:
- Physical Exam: A comprehensive physical exam is carried out, involving the evaluation of vital signs (e.g. blood pressure or heart rate) as well as general appearance and the examination of particular organ systems. The results may help in the diagnosis of diseases and determine general health.
- Focused Examination: Based on the main complaint of the patient along with the history of medical conditions, this exam might focus on specific regions or organs of the body. For instance, in the case of Trigeminal Neuralgia, a neurological examination of the face or head might be of particular importance.
- Diagnostic tests: There are occasions additional diagnostic tests, like imaging tests, blood tests (e.g., MRI, CT scan), or tests that are specialized (e.g. electrocardiogram or biopsy) are often required to confirm the diagnosis or examine a problem.
- Interpretation: The healthcare provider interprets the results of the examination and history in relation to the overall health of the patient as well as medical background. This information is used to guide the treatment and diagnosis.
The medical history and the clinical examination are essential tools that healthcare professionals use to evaluate patients, make diagnoses, and formulate treatment plans. They are vital for delivering individualized treatment and guaranteeing the highest quality of outcomes for those who seek medical treatment.
Challenges in managing atypical TN
The management of Atypical Trigeminal Neuropathy (TN) poses a variety of difficulties due to its distinct features and the underlying causes.
Here are some most important issues to be faced when managing atypical TN:
- Diagnose: Atypical TN can be harder to diagnose in comparison to the normal type. Its burning, constant, or aching pain does not have the triggers and paroxysms typical of found in normal TN. This could lead to a delay in diagnosis and the appropriate treatment.
- Substantiating Causes: Atypical TN can be the result of different medical problems, like neurological disorders or structural anomalies. Finding and treating these root causes requires specialized diagnostic tests and a coordinated approach by multiple medical professionals.
- Treatment Response: Atypical TN might not be responsive to standard treatments that are used for common TN including certain medications or microvascular decompression surgery. Finding treatment options that are effective and offer significant pain relief could be a challenge.
- Chronic Pain: The continuous or chronic nature of chronic pain of atypical TN could affect the quality of life of a person. The treatment of chronic pain usually requires a multimodal approach, that could include pain medication or physical therapy as well as psychological assistance.
- Side Effects of Medication: Certain medications employed to treat the symptoms of atypical TN can have serious adverse consequences. The balance between pain relief and the ease of use of these medications could be a difficult task.
- psychological impact: Living with chronic physical pain can cause mental and emotional issues including anxiety, depression, and a decrease in the quality of your life. In order to address these issues, it might necessitate a multidisciplinary strategy that involves mental health experts.
- Specific Care: The treatment of atypical TTN typically requires collaboration between various medical specialists, including neurologists as well as pain management specialists, neurosurgeons, and, sometimes, other subspecialists in medicine. Coordination of this multidisciplinary treatment can be a challenge logistically.
- Studies and treatment options: Atypical TN is more difficult to understand than typical TN, which may limit the number of treatments. It is essential to conduct ongoing research to understand the cause and devise more efficient treatment options.
- patient education: Patients with atypical TTN might require extensive information regarding their health, treatment options, and possible outcomes. Involving patients as active participants in their treatment is crucial.
- QOL: The chronic nature of atypical TN could greatly impact a patient’s everyday activities, such as their capacity to work, socialize, and participate in everyday activities. Strategies to improve the quality of living should become the primary goal of the management.
The treatment of the condition of atypical Trigeminal Neuralgia is complex due to its distinct features, difficulties in diagnosing as well as the underlying causes, and the necessity for multidisciplinary treatment.
It requires careful evaluation of treatments, the potential adverse effects, and the impact they have on the patient’s emotional and physical well-being. Collaboration in care, education of patients, and research ongoing are crucial to improving the treatment of an atypical TTN.
Prognosis and impact on quality of life
The prognosis and the impact on the quality of life of people who suffer from trigeminal Neuralgia (TN) depending on regardless of whether it’s the common or uncommon form, may differ significantly based on a variety of aspects.
Here’s a brief overview of the prognosis and possible impact on the health and quality of life:
Prognosis:
- Typical TN:
- The prognosis is usually more favorable for common TN than for typical TN.
- Many patients with typical TN suffer significant relief from pain and a better quality of life when they receive proper treatment.
- Decompression surgery for microvascular vessels is a particular procedure that can provide lasting relief for certain patients.
- Atypical TN:
- The prognosis of atypical TN can be more uncertain and difficult.
- The condition can be linked to medical conditions or structural anomalies that require further treatment.
- A few people may be more difficult to obtain complete relief from pain and their condition could turn into chronic.
Impact on Quality of Life:
- Typical TN:
- While the pain that is common in TN can be extreme It is typically seen in short, sporadic episodes.
- In between episodes, many people have a fairly good level of quality.
- Treatment can greatly improve the quality of life for people suffering from typical TN and allow patients to take part in everyday actions and interact with others.
- Atypical TN:
- Atypical TN may cause more severe effects on quality of life, due to the ongoing or chronic nature of the discomfort.
- Chronic pain can hinder the ability of a person to sleep, work eat, or do the things that are routine for them.
- It can cause anxiety, depression anxiety, depression, and decreased feelings of well-being.
- Managing the symptoms of atypical TN typically requires a multimodal strategy that can include pain medication or physical therapy as well as psychological counseling.
- Common Impact on Both Types:
- Both kinds of TN can interfere with an individual’s life routine and cause insomnia, sleep disturbances and social loneliness.
- The anxiety and fear of painful events can create anxiety and anxiety.
- Medicines used to treat TN can cause side consequences that affect overall health.
It’s crucial to recognize that the impact of prognosis on quality of life differs widely between individuals. Factors like the ability to respond to treatments as well as the presence of medical conditions, as well as the existence of support groups play important factors. In addition, advances in medical research as well as treatments could improve the outcomes of people suffering from TN in the future.
Individualized treatment, close collaboration with healthcare providers, as well as an emphasis on both the physical and psychological aspects of the disease, are vital to improving the prognosis as well as the quality of life for people with Trigeminal Neuralgia.
Similarities Between Typical and Atypical Trigeminal Neuralgia
In spite of their distinct characteristics, Typical as well as Atypical Trigeminal Neuralgia (TN) have a few similarities:
- The Trigeminal Nerve is involved: Both the typical and atypical Trigeminal Nerve Involvement: Both types of TN affect the triage and can be responsible for facial sensitivity. Although the cause of discomfort is different, both stem from abnormalities or irritation of the nerve.
- Facial Pain: Both of these conditions are manifested as facial discomfort. If it’s severe and sudden paroxysms typical to TN or continuous burning pain in an atypical TN it is located in the trigeminal nerve’s distribution in the face.
- Effect on quality of life: Atypical and typical conditions can have a major impact on well-being. The pain may be extremely disruptive and can affect your daily activities, sleep, and even emotional well-being.
- Diagnosis Challenges: Finding both types of TN can be a challenge. Medical history, clinical evaluation, and, sometimes, imaging studies are essential for a valid diagnosis. This process of diagnosis is similar for both kinds.
- Treatment Strategies: Although the specific methods of treatment might differ, the aim of treatment for both normal and typical TN is to provide alleviation from the pain as well as enhance the quality of life of the patient. Treatments, nerve blocks as well and surgical alternatives are all considered for both types, based on the individual situation.
- Possibility of Multidisciplinary Care: In extreme cases, or when underlying medical issues are present both kinds of TN can benefit from an approach that is multidisciplinary. This could include collaboration with neurologists surgeons, neurosurgeons, and specialists in pain management, as well as other healthcare professionals.
- patient education and support: Patients who suffer from both typical and atypical forms of TN usually require information about their conditions, treatment options, and strategies for coping with the pain. Support networks and advocacy organizations are available for patients who suffer from both types of TN.
- Effect on mental health: Living in constant or extreme pain can be a drain on your mental health. Both forms of TN can cause mental distress, such as depression and anxiety. Controlling these psychological factors is an essential aspect of treatment.
Although both types of TN have distinct features and symptoms Recognizing their commonalities will help in understanding the wider range that is Trigeminal Neuralgia and aid healthcare professionals in the development of the most appropriate treatment and diagnostic strategies.
Conclusion
Trigeminal Neuralgia (TN) encompasses both atypical and typical forms with each having its own unique set of issues and distinctive characteristics. Normal TN is defined by intense, sudden painful episodes and Atypical TN manifests as continuous burning pain.
They both impact a person’s quality of life and will require multidisciplinary approaches for diagnosis and treatment. Understanding the commonalities and differences between atypical and normal TN is vital for both healthcare professionals and patients alike since it allows for customized treatment plans and better outcomes for patients suffering from this neurodegenerative disease.