“Osteoporosis and osteomalacia are two distinct yet often confused bone disorders, both affecting bone health but stemming from different causes and mechanisms.
Understanding their differences is crucial for accurate diagnosis and appropriate treatment. While both impact bone strength and integrity, their etiology, symptoms, and management strategies diverge significantly.”
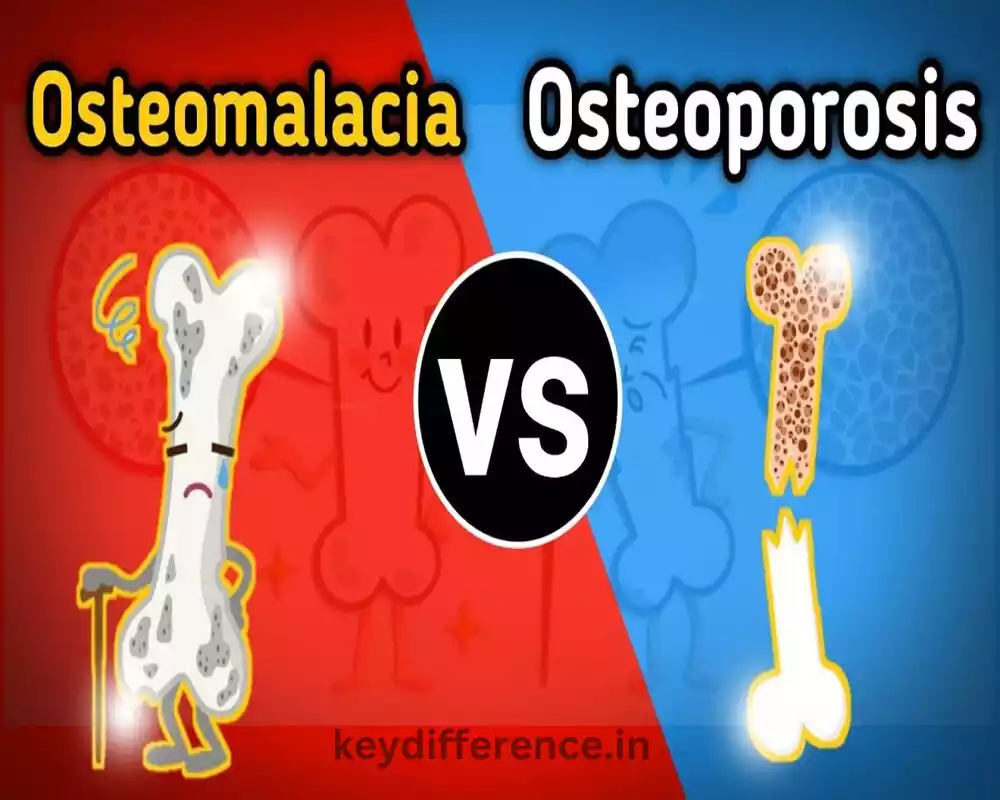
What is Osteoporosis?
Osteoporosis, a medical condition, is which is characterized by a decrease in the density of bone and its quality, which leads to weak and fractured bones. The bone’s weakening can increase the likelihood of breaking which is typically seen in the spine, hip, and wrist.
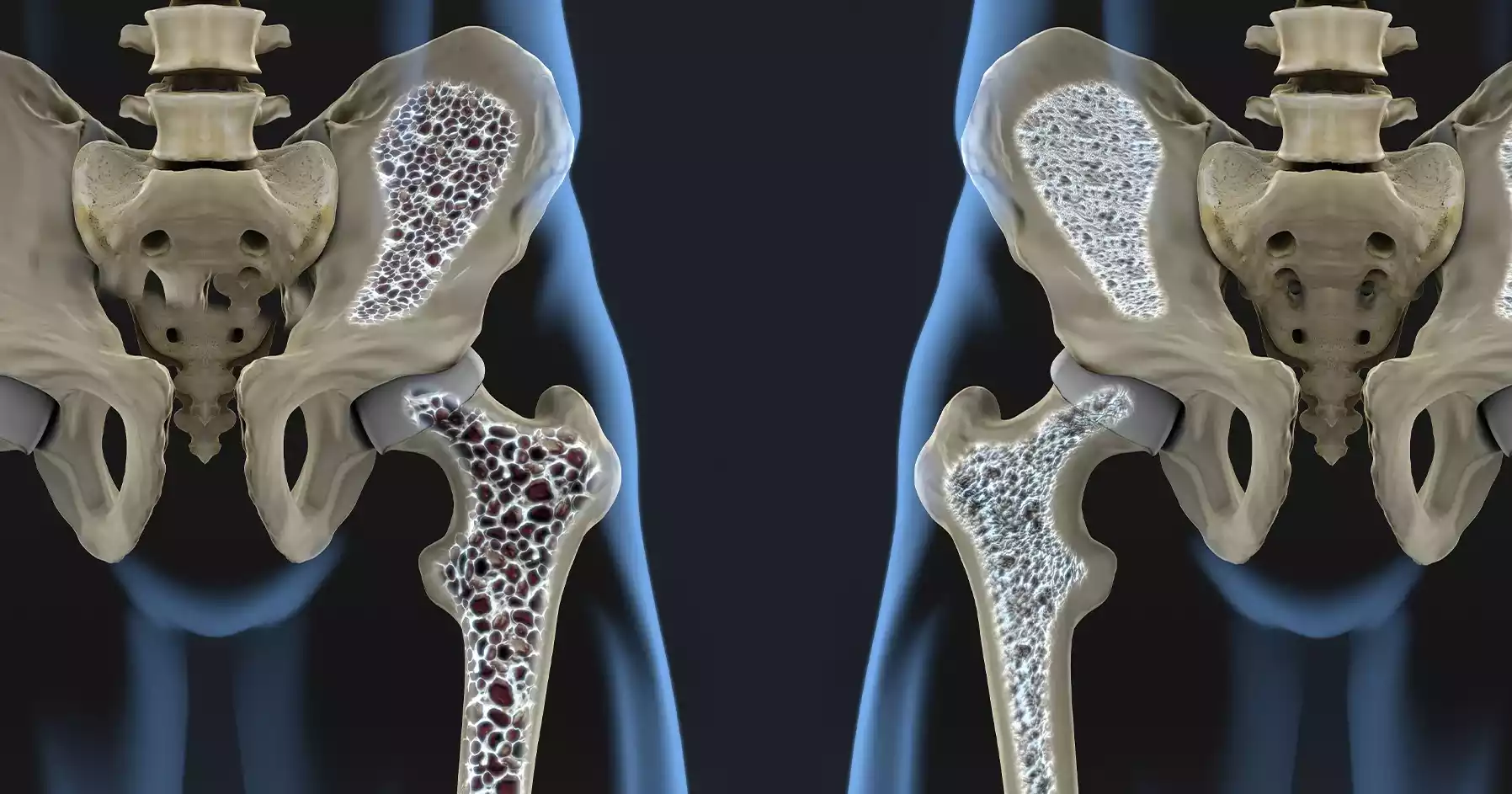
It occurs when the growth of bone tissue doesn’t match the loss of bone tissue from the past which results in a decrease in the bone’s mass as well as structural degradation. Osteoporosis can be described as a “silent disease” because it is not symptomatic until it causes a fracture, which makes early detection essential for an effective treatment.
What is Osteomalacia?
Osteomalacia is a metabolic bone disorder characterized by the bone’s softening because of inadequate mineralization, especially a deficiency of calcium as well as phosphate.
The cause of this condition is a malfunction in the process of mineralization of bone tissue that has been formed and results in weak and soft bones. It is primarily due to the lack of vitamin D, or issues with its absorption.
This interferes with the body’s ability to efficiently use calcium and phosphorus to aid in bone growth. Osteomalacia may cause muscular weakness, bone pain, and a higher chance of breaking bones due to the weakening of the structure of the bones affected.
Importance of understanding the differences
Understanding the difference between osteomalacia and osteoporosis is of great importance for many significant reasons:
- Accurate Diagnosis: Knowing the difference between these conditions is essential for medical professionals in their ability to correctly identify patients. Both diseases may have similar symptoms, like bone pain or an increase in the risk of fracture, but their root causes and treatment strategies differ. The correct diagnosis is essential to ensure proper management and treatment.
- Tailored Treatment: Effective treatment strategies for osteomalacia and osteoporosis differ dramatically. Osteoporosis is often treated with strategies to increase bone density and decrease fracture risk, which includes medication and lifestyle changes. However, treating osteomalacia is mostly about treating vitamin D deficiencies and restoring normal mineralization. Understanding the differences between these two is crucial to implementing the correct treatment program.
- Preventive measures: Knowledge about the differences can help in taking preventive measures. Knowing the risk factors and reasons that are specific for each condition allows health professionals to provide specific guidance regarding lifestyle changes, diet changes, and supplementation which could help prevent the development or progression of these bone conditions.
- Patient Education: The process of educating patients regarding their condition will improve their capacity to deal with and manage the condition. Clare’s explanations of the nature and severity of their bone concern as well as its causes and the importance of following the prescribed treatment plan allow patients to play an active part in their overall health.
- Research and development: Distinguishing between osteoporosis and osteomalacia assists researchers in conducting targeted studies to create improved diagnosis tools, treatment techniques, and preventive strategies for each disease, which in turn helps advance knowledge in medicine and providing care to patients.
Understanding the difference between osteoporosis versus osteomalacia allows for a more accurate diagnosis, individualized treatment strategies, and preventive measures, as well as patients’ empowerment and advances in medical research. All of these together contribute to improved management and outcomes for those suffering from these bone diseases.
Comparison Table of Osteoporosis and Osteomalacia
Certainly! Here’s a comparison table highlighting the key differences between osteoporosis and osteomalacia:
| Aspect | Osteoporosis | Osteomalacia |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Bone disorder results in reduced bone density and strength, leading to increased fracture risk | Metabolic bone disorder causing softening of bones due to inadequate mineralization |
| Primary Cause | Imbalance in bone formation and resorption, often related to hormonal changes, aging, or certain medications | Vitamin D deficiency or issues with its absorption affecting the mineralization process |
| Bone Quality | Bones are fragile, porous, and prone to fractures | Bones are weakened and soft due to inadequate mineralization |
| Symptoms | Often asymptomatic until a fracture occurs; may include bone pain, height loss, and increased fracture risk | Bone pain, muscle weakness, fractures, and difficulty in weight-bearing activities |
| Diagnosis | Bone density scans (DEXA), X-rays, and blood tests measuring bone markers | Blood tests checking vitamin D levels, alkaline phosphatase levels, and bone mineral density tests |
| Treatment | Medications to improve bone density, lifestyle changes (exercise, calcium, vitamin D intake) | Vitamin D supplementation addresses underlying causes, and sometimes calcium supplements |
| Risk Factors | Age, gender (more common in postmenopausal women), low calcium intake, sedentary lifestyle, smoking, family history | Vitamin D deficiency, inadequate sunlight exposure, certain gastrointestinal disorders affecting nutrient absorption |
| Prevention Strategies | Adequate calcium and vitamin D intake, regular weight-bearing exercises, lifestyle modifications | Ensuring sufficient vitamin D levels through sunlight exposure or supplementation, dietary adjustments |
This table provides a comparative overview of osteoporosis and osteomalacia, highlighting their differences in causes, symptoms, diagnosis, treatment, risk factors, and prevention strategies.
The Main Causes of Osteoporosis?
Bone density loss is caused by various factors that contribute to its gradual decrease, these include:
As we age, our bodies naturally lose bone density and become more fragile, increasing the chances of fractures and breakages. Changes in Hormones, after menopause, the decrease of estrogen can result in bone loss; similarly, men with low testosterone levels could experience a similar loss.
Genetics, Both family history and Genetics play a significant role in Osteoporosis Risk. Smoking, excessive alcohol intake, lack of physical exercise, and eating an insufficient diet of vitamin D and calcium all increase bone loss.
Medical conditions and medications. Certain medical conditions, like Hyperthyroidism or Gastrointestinal Disorders, can increase your risk for Osteoporosis; some cancer Treatments or steroids could even contribute to bone loss.
Although these factors can play a part in osteoporosis for some individuals, their exact source can differ for each. Discuss them with your healthcare provider as individual risk factors as well as prevention and treatment methods available to you.
The Main Causes of Osteomalacia?
Osteomalacia can be caused by either insufficient Vitamin D intake or difficulty with its absorption, both essential components for maintaining bone health and strength.
1. Vitamin D: Vitamin D helps the body absorb calcium, phosphorus, and other essential minerals for strengthening and mineralizing bones – lacking enough of this nutrient can result in osteomalacia, with soft and weakened bone tissue developing over time. Vitamin D deficiency can result from numerous sources.
2. Vitamin D deficiency: An inadequate vitamin D intake through diet alone may result in deficiency symptoms for some individuals who do not consume fortified food products or fatty seafood regularly.
3. Lack of sun exposure: To produce Vitamin D, our bodies need sunshine from sunlight. People living indoors or in northern latitudes may be at increased risk for vitamin D deficiency.
4. Malabsorption disorders: Certain conditions, including celiac disease, Inflammatory bowel diseases, and gastric bypass surgeries can impede the Absorption and utilization of vitamin D and other essential nutrients, Leading to their reduced Availability for optimal use by our Bodies.
5. Chronic Kidney Disease: As kidneys play a central role in Turning vitamin D into its active form, Individuals Living with Chronic kidney disease may see reduced Metabolism of vitamin Other contributing factors, including genetic disorders such as hypophosphatasia and certain forms of cancer, can aggravate osteomalacia symptoms.
Treatment often includes calcium and vitamin D supplementation alongside therapy to address any potential deficiencies underlying conditions that could be contributing to deficiency symptoms.
Summary
Knowing the distinctions between osteomalacia and osteoporosis is essential for accurate diagnosis and customized treatment.
Both affect bone health osteoporosis causes a decrease in bone density, thereby increasing the risk of fractures, whereas osteomalacia results in weaker bones that are not well-mineralized because of vitamin D deficiencies.
Different signs, causes diagnosis methods, and treatment options emphasize the need for precise diagnosis to ensure effective treatment of preventive measures and treatment for patients.