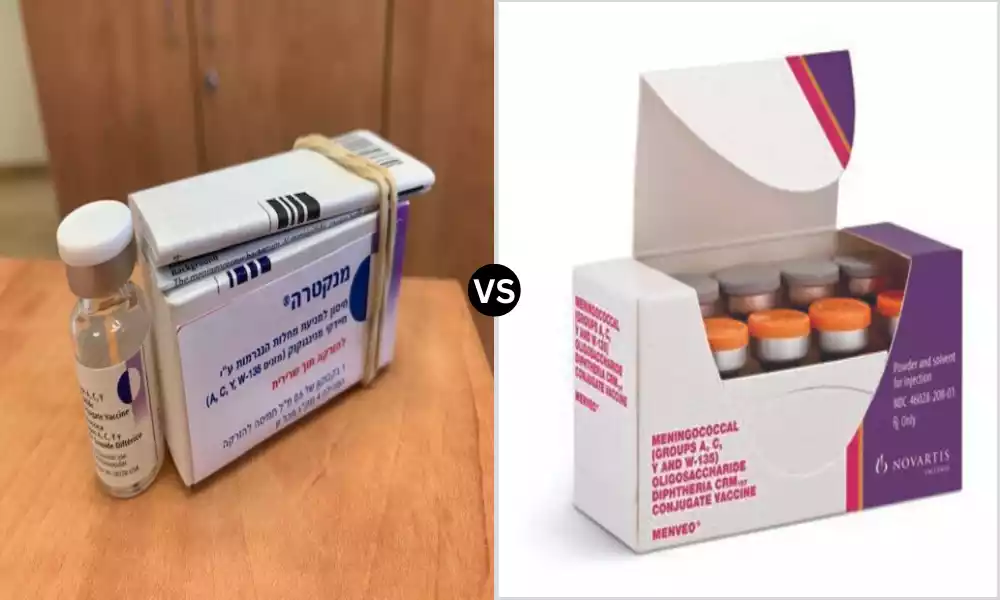
Meningococcal Disease is a deadly and possibly life-threatening condition that affects individuals of all ages. Vaccination plays an essential role in the prevention of this disease and the two most commonly utilized treatments are Menactra and Menveo.
Although both vaccines protect against meningococcal infections however they differ in regards to composition as well as recommended age ranges and other elements. In this overview, we will look at these differences to help people make informed decisions regarding their choices regarding vaccination.
What is Menactra?
Menactra is the brand name of meningococcal conjugate vaccination. It’s made to guard patients from infections caused by bacterial strains. by Neisseria meningitidis. It is targeted at specific serogroups in this bacteria.
Menactra is made up of antigens from several serogroups. It’s administered in the form of an injection to boost the immune system, thereby providing protection against meningococcal diseases. Menactra is frequently used to treat invasive meningococcal diseases, such as meningitis, for those who fall who are in certain age groups as advised by health professionals.
What is Menveo?
Menveo is the brand name of a meningococcal conjugate vaccination. This vaccine is designed to protect against bacterial infections caused by Neisseria meningitidis with a particular focus on serogroups that this bacterium has.
Menveo includes antigens of multiple meningococcal serogroups. It is administered by injection to increase the strength of immunity, providing protection against meningococcal diseases. It is generally used to treat aggressive meningococcal illness, including meningitis. It is also advised for people in specific age ranges by health authorities.
Importance of vaccination against meningococcal disease
The vaccination against meningococcal disease is vital because of a variety of reasons:
- Life-threatening Disease: Meningococcal illness, which is caused by the bacterium Neisseria meningitidis, may cause severe and life-threatening infections. The infections can progress quickly and can cause ailments like meningitis (inflammation of the membranes that protect the spinal cord and brain) as well as Septicemia (bloodstream infections).
- Very High Rate of Mortality: Meningococcal disease is fatal. Even with prompt medical care mortality rates are extremely high. The timely vaccination offers the most effective protection from the illness.
- Long-Term Health Risks: Survivors of meningococcal disease can suffer long-term health problems which include hearing loss, neurological damage as well as limb amputations, and cognitive impairments. Vaccination is a way to avoid these debilitating effects.
- Outbreak Control: Meningococcal infections can happen in close-contact environments such as military barracks, campuses of colleges as well as healthcare facilities. Vaccination is a way to prevent outbreaks by establishing herd immunity and reducing the spread of the bacteria.
- Protection for vulnerable populations: Certain age groups including youngsters, teenagers, and young adults are more at risk of contracting meningococcal diseases. Vaccination strategies target these groups to give them essential protection.
- Serogroup diversity: Neisseria meningitidis bacteria can be found in several serogroups (A B, C, W, and Y). Different age groups and regions might have different predominant serogroups. Meningococcal vaccines are developed specifically to attack specific groups of serotypes in a specific population, thereby addressing the differences in disease burden across regions.
- Travel Tips: Travelers to regions where there is a greater risk of meningococcal diseases, commonly called”the “meningitis belt” in sub-Saharan Africa, ought to consider getting vaccinated to lower the risk of getting exposed.
- Prevention of Outbreaks in Close-Contact Settings: Institutions like schools or colleges as well as military bases could benefit from meningococcal vaccination programs to avoid outbreaks in the populations they serve.
- Peace of mind: The vaccinated person can rest at ease being confident that they are safe against a disease that could be devastating.
The fact is that meningococcal vaccination is vital for the health of both individuals and the public. It assists in preventing life-threatening illness reduces the chance of outbreaks, and safeguards those at risk, creating the safest and healthiest environment for everyone.
Comparison Table of Menactra and Menveo
Here’s a comparison table outlining key differences and similarities between Menactra and Menveo, two commonly used meningococcal vaccines:
| Aspect | Menactra | Menveo |
|---|---|---|
| Manufacturer | Sanofi Pasteur | GlaxoSmithKline (GSK) |
| Approved Date | 2005 | 2010 |
| Composition | Quadrivalent: A, C, Y, W-135 serogroups | Quadrivalent: A, C, Y, W-135 serogroups |
| Recommended Age Groups | Adolescents (11-18 years) and adults | Infants (as young as 2 months), Adolescents, and adults |
| Primary Vaccination Schedule | Single dose | Single-dose (2 months and older) or two-dose series (2-55 years old) |
| Booster Doses | Generally not required | Recommended for some individuals |
| Duration of Immunity | Several years | Several years |
| Common Side Effects | Pain or swelling at the injection site, mild fever, headache | Pain or swelling at the injection site, mild fever, headache |
| Rare but Severe Reactions | Anaphylaxis (extremely rare) | Anaphylaxis (extremely rare) |
| Availability and Cost | Availability may vary by location and healthcare provider; cost varies | Availability may vary by location and healthcare provider; cost varies |
Please note that specific recommendations for Menactra and Menveo may change over time, and it is essential to consult with a healthcare provider or the latest guidelines for the most up-to-date information on these vaccines, including indications, dosing, and availability.
Protection against meningococcal serogroups
The two vaccines Menactra and Menveo offer protection against certain groups of Neisseria meningitidis, which is the bacteria that causes meningococcal illness. Here’s a breakdown of serogroups protected in each vaccination:
Menactra:
- Menactra is a four-rival meningococcal conjugate vaccine. It offers protection against four serogroups of meningococcal that include A, C, W-135, and Y.
Menveo:
- Menveo can also be a meningococcal conjugate quadrivalent vaccine that provides protection against four of the serogroups that are Menactra: A C, Y, and W-135.
Both vaccines work in preventing the spread of meningococcal infection caused by these serogroups and are believed to cause a substantial proportion of cases of meningococcal diseases all over the world. However, it is crucial to keep in mind that there are different serogroups in Neisseria meningitidis (e.g. serogroup B) that are not covered by these vaccines. Specific vaccines, like those that target serogroup B, are recommended in certain regions or locations where this particular serogroup is more common.
Side Effects and Adverse Reactions
Each of Menactra along with Menveo are generally well-tolerated vaccinations However, like any other medical treatment, they could be associated with side effects and, in rare instances adverse reactions.
Here are the most common adverse reactions and extremely rare adverse reactions linked to these vaccines:
Common Side Effects (Usually Mild and Temporary):
- Redness, pain, or swelling at the site of injection.
- The discomfort or mild fever may be mild.
- Headache.
- Tiredness or fatigue.
- Joint pain or muscle pain.
Rare but Severe Adverse Reactions (Extremely Rare):
- Anaphylaxis: The severe reaction can occur within a few minutes to hours following vaccination. It can cause breathing problems and swelling of the throat and face as well as a rapid heart rate and a decrease in blood pressure. Anaphylaxis is a rare condition, but medical professionals are ready to treat it in the event of it.
It’s crucial to know that the likelihood of sustaining an extreme adverse reaction to the vaccines is extremely minimal. The advantages of vaccination in the prevention of meningococcal disease generally exceed the risk of adverse reactions that could occur.
People who have a confirmed severe allergic reaction to a vaccine component (e.g. a part of the vaccine that is not an active antibody) should speak with their healthcare doctor for advice.
Most people experience minor and short-term side effects, for example, soreness around the injection site or flu-like symptoms. The symptoms typically resolve by themselves within some days. Should you, or your kid experience extreme or unusual reactions following vaccinations and/or vaccination, it is important to seek medical attention right away.
Like any other vaccination, one should be sure to discuss your medical background, allergies, and any concerns you have with your physician prior to taking Menactra and Menveo. Your doctor can provide specific information and suggestions according to your individual medical needs.
Manufacturers and approval dates
Here are the dates of approval and manufacturers to be used for Menactra as well as Menveo vaccines:
Menactra:
- Manufacturer: Sanofi Pasteur
- Date of Approval: Menactra was initially approved by the U.S. Food and Drug Administration (FDA) in 2005 to be used within the United States.
Menveo:
- Manufacturer: GlaxoSmithKline (GSK)
- Date of Approval: Menveo was approved by the FDA in 2010 to be used for use in the United States.
Note that approval dates and the manufacturers’ names may differ by country and the dates listed apply only to the United States. The approval of vaccines and their availability may alter over time, which is why it is essential to check the most up-to-date information from regulatory agencies and healthcare providers for the latest information on these vaccines.
Considerations for Vaccine Selection
In deciding to choose between Menactra and Menveo or any other vaccine in general there are a variety of factors that take into consideration. The decision to choose a vaccine should be based on personal factors such as healthcare provider recommendations and local guidelines.
Here are some important considerations to consider when choosing a vaccine:
- Age and Indication:
- Take note of the recommended age group for every vaccine. Menactra is generally recommended for adults and teens and adults, whereas Menveo might have more extensive recommendations for infants, teenagers as well and adults. Select a vaccine that is appropriate to the age group of the subject.
- Medical History and Allergies:
- Talk about any medical conditions or allergies to your doctor. Certain individuals might have specific contraindications or cautions for one vaccine but not for the other.
- Regional Epidemiology:
- The prevalence of certain meningococcal serogroups may vary depending on the location. Health professionals may suggest vaccination based on serogroups that are most prevalent in your region.
- Vaccination Schedule:
- Take note of the recommended schedule to ensure you are covered for every vaccine. Certain individuals might discover one schedule to be more suitable or more in line to their medical program.
- Vaccine Availability:
- The availability of vaccines varies by the area and healthcare provider. Consult your doctor to make sure the vaccine you’re looking for is available.
- Cost and Insurance Coverage:
- Find out the cost of the vaccination and if your insurance will cover the cost. Cost considerations may influence your decision.
- Travel Plans:
- If you plan to travel to areas with a higher chance of meningococcal diseases, talk about any travel arrangements with your physician. They may recommend vaccinations to guard against risks specific to your region.
- Herd Immunity:
- Think about the wider impact on public health. When you get vaccinated, it can contribute to herd immunity by safeguarding those who aren’t vaccine-free due to medical reasons. Certain vaccines could be more effective on herd immunity within your local area.
- Healthcare Provider Recommendations:
- In the end, your doctor’s recommendations should be a key element when making a decision. They are aware of your medical history as well as the most recent guidelines, and they can offer individual suggestions.
- Personal Preferences:
- Certain individuals might have their own preferences regarding particular vaccines based on their personal experiences or levels of comfort. Talk about the preferences you have with your doctor.
It’s crucial to have an open and knowledgeable discussion with your physician to determine the most appropriate option for your situation. Your physician can provide specific advice based on your needs and assist you in making an informed choice about the best meningococcal vaccination suitable for you and your loved family members.
Similar primary and booster vaccination schedules
Each Menactra and Menveo as meningococcal vaccines that are quadrivalent both have the same primary schedules of vaccination and don’t typically require booster doses in the majority of cases.
Here’s a brief overview of their booster and primary vaccination schedules:
Primary Vaccination Schedule:
- Menactra:
- For adults and adolescents, One dose is typically advised.
- Menveo:
- For children and infants aged 2 months and over The first schedule of vaccination consists of two doses. the second dose is given within a few months of the first, in accordance with your age child.
- For adults and adolescents (ages 11 to 55) One dose is usually suggested.
Booster Doses:
- Menactra: Doses that boost the effectiveness of Menactra aren’t typically suggested for the majority of people. However, in some situations like when there are epidemics or for those suffering from certain medical conditions medical professionals may suggest the use of a booster.
- Menveo: Booster doses of Menveo are not suggested for all people. As with Menactra, exceptions can be granted in specific situations like outbreaks or medical conditions that are specific to the patient.
It is important to remember that guidelines regarding vaccinations can differ according to location, age group, and health condition of the individual. Therefore, it’s essential to speak with your health physician or refer to the most current recommendations from regional health officials to figure out the best vaccine schedule that is suitable for you and your family members. Your physician will be aware of your particular circumstances and possible risk factors before giving recommendations regarding booster doses in the event that they are required.
Conclusion
Menactra along with Menveo are both essential vaccines to protect against meningococcal disease which is an illness that could be life-threatening. While they share a lot in common with respect to their primary vaccine schedules and efficacy in preventing specific serogroups, there are some subtle differences, including the age guidelines and the manufacturers.
The decision between these vaccinations should be based on your personal aspects, guidance from a healthcare professional as well as regional considerations. Whatever the choice of vaccine the vaccination against meningococcal disease is essential to protecting public health and individual health.
Engaging in open discussions with health professionals in order to make informed choices is essential to ensure optimal protection from this dangerous disease.