The lung abscess and pneumatocele are two distinct lung conditions that result in the development of lung abscess-like cavities. tissue. Knowing the main distinctions between these two conditions is essential for a precise diagnosis and the appropriate treatment.
The distinct characteristics of lung abscess and pneumatocele and lung abscess, focusing on their causes and pathophysiology, as well as their clinical manifestation as well as treatment and prognosis. It will provide complete information on the pulmonary diseases.
What is Pneumatocele?
A pneumatocele can be described as a medical disease that manifests as the growth of air-filled sacs or cavities in the lung tissue. These sacs are generally caused by lung trauma or infection and may vary in dimensions.
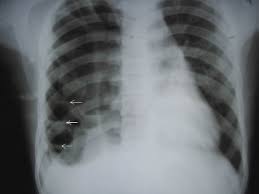
Pneumatoceles differ from lung abscesses because they are mostly composed of air and not necrotic or pus. The treatment of pneumatoceles could require addressing the root reason, observation, or, in more severe instances surgical intervention.
What is Lung Abscess?
An abscess in the lung is typically a walled-off, localized infiltration of pus within lung tissue. It usually occurs as a due of a bacterial infection within the lung, which leads to necrosis of tissue and the creation of a cavity stuffed with a purulent substance. Lung abscesses are often associated with symptoms like cough, fever, and chest discomfort.
Treatment usually involves antibiotics to treat the root of the infection, and, in a few cases drainage procedures to get rid of the pus that has accumulated. Lung abscesses can cause serious consequences if they are not treated.
Importance of understanding the differences
Understanding the distinction between a lung abscess and a pneumatocele is crucial for a number of reasons:
- Accurate diagnosis: The distinction between these two conditions is essential for medical professionals. Incorrect diagnosis can lead to ineffective treatment options, possibly causing delays in the recovery process and inflicting harm on the patient.
- Treatment Choice: The treatment strategies for lung abscess and pneumatocele differ greatly. Although pneumatoceles may require treatment of the cause, or surgical intervention, lung abscesses require antibiotic treatment and, in certain cases drainage procedures. Knowing the cause is crucial to choose the best treatment route.
- Prognosis: Both of these conditions have distinct prognostic implications. Pneumatoceles usually heal without lasting effects if the root cause is properly addressed however lung abscesses may result in grave complications if not dealt with promptly. Being aware of the type of condition present can help provide patients with accurate information regarding their outlook.
- Preventing complications: Finding the proper problem early will help avoid complications. Lung abscesses could lead to grave issues such as sepsis and lung tissue damage, so immediate intervention is vital. However, the unnecessary procedures to treat pneumatoceles can be avoided by a precise diagnosis.
- Cost-Efficiency: Understanding the difference will help you avoid unneeded medical interventions and therapies that are cost-effective for both healthcare providers and patients. systems.
- Research and Education: The ability to distinguish between a lung abscess and a pneumatocele is essential in medical research, education, and training. It is essential doctors are aware of these ailments and aid in the development of medical understanding.
- Health and Well-being of Patients: Correct diagnosis and the right treatment can improve the patient’s outcomes. Patients will experience quicker recovery, less discomfort, and pain, as well as an improvement in their level of living when the proper condition is diagnosed.
The significance of knowing the distinctions between lung abscess and pneumatocele is the ability to offer precise and efficient medical treatment that ultimately will benefit both patients and the health system in general.
Comparison Table of Pneumatocele and Lung Abscess
Here is a comparison table highlighting the key differences between pneumatocele and lung abscess:
| Characteristic | Pneumatocele | Lung Abscess |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | The air-filled cavity within the lung tissue | The pus-filled cavity within the lung tissue |
| Etiology and Causes | Often results from trauma, infection, or barotrauma | Mainly caused by bacterial infection, aspiration, or immune system compromise |
| Pathophysiology | Air-filled cavity typically lacks necrotic tissue | Accumulation of pus often involves necrotic tissue |
| Clinical Presentation | Typically asymptomatic, may cause respiratory distress in severe cases | Symptoms include fever, productive cough, chest pain, and systemic signs of infection |
| Radiological Findings | The presence of a cavity filled with air | The presence of a well-defined cavity containing pus |
| Diagnostic Methods | Radiological imaging (e.g., X-ray or CT scan), clinical history | Radiological imaging (e.g., CT scan), microbiological analysis of sputum or aspirated material |
| Treatment | Management of underlying cause, observation, or surgical intervention in severe cases | Antibiotics to treat the underlying infection, and possible drainage (percutaneous or surgical) |
| Prognosis | Generally good if the underlying cause is addressed | Good with appropriate antibiotic therapy; complications may arise if not treated promptly |
Understanding these distinctions is essential for accurate diagnosis, effective treatment, and improved patient outcomes.
Radiological findings of a well-defined cavity
The expression “Radiological findings of a well-defined cavity” refers to the typical findings in medical imaging for example, chest radiograph or CT scan in the event that there is a lung abscess. When a healthcare professional looks over these images, they could be able to identify specific features that signal the presence of an abscess.
These include:
- Well-Defined Cavity The lung abscess typically appears as a clearly circular cavity inside the lung tissues. The cavity can contain pus, and then be surrounded by necrotic or inflamed lung tissue.
- Air-Fluid Level: Images from radiology may show an air-fluid concentration inside the cavity. This happens because the pus in the abscess settles to the bottom, while the top portion is a reservoir of air.
- The Infiltrate or Opacity Apart from the cavity there may be areas with increased density or opacity on the image, indicating the presence of inflammation, infection, and lung tissue’s reaction to the abscess.
These radiological findings are essential in the diagnosis and evaluation of lung abscesses as they can help differentiate the disease from other lung diseases, like pneumatoceles. The correct understanding of these images assists health professionals in providing the right medical treatment and care to the patient.
Microbiological analysis of sputum or aspirated material
A microbiological examination of sputum or aspirated tissue is a vital method of determining the underlying cause of lung abscess.
What is this procedure:
- Sputum collection: Sputum refers to mucus, along with other substances, that are expelled in the respiratory tract. For the purpose of collecting a sputum sample, A patient is generally required to cough vigorously to create the phlegm sample. The sample is taken and stored in a sterilized container.
- Aspirated material: In some instances in which the abscess isn’t flowing through the airways healthcare professionals might need to use a more aggressive procedure to expel (withdraw) substance straight from the abscess. This is typically accomplished with a syringe and needle with guidance from an imaging scan.
- Analyzing Microbiological Data: The sputum that is collected or aspirated matter is sent to a lab to conduct a microbiological analysis. The analysis comprises:
- Gram stain: A Gram stain is used to identify the Gram-related characteristics that the bacteria possess (Gram-positive and Gram-negative). The initial test gives an overview of the type of bacteria that are present.
- Tests for Culture and Sensitivity: The sample is then cultured using appropriate Agar Plates in order to promote the growth of bacteria. After the bacteria have been growing and are identified, and sensitivity testing is performed to identify which antibiotics are effective against the particular bacteria.
- Additional Tests: Based on the situation in the clinic Additional tests can be conducted, for instance, acid-fast staining for mycobacteria, or fungal cultures in the event of suspicion of an infection that is not bacterial.
- Results and treatment: After the microbiological examination is complete the healthcare provider will receive an analysis of the kind of bacteria (or other microorganisms) responsible for the infection, as well as the antibiotics that are most effective. This information helps in the choice of an appropriate treatment for the patient.
The microbiological analysis of sputum and aspirated materials is vital in determining the best treatment for the exact causative agent making sure that the patient is treated effectively for lung abscess and stopping any further complications.
Observation and conservative treatment in mild cases
The use of observation and conservative treatment are the most common options in cases of mild pneumatoceles that are not severe.
This is what these options entail:
- Observation: If the patient is diagnosed with a tiny or unasymptomatic pneumatocele health professionals might decide to observe the condition, but without prompt intervention.
This type of observation includes:- Regular follow-up appointments are a good way to assess the size of the pneumatocele as well as the patient’s health status.
- Studies of periodic imaging (such as chest X-rays or CT scans) to evaluate whether there are any modifications in the pneumatocele.
- Be on the lookout for signs or symptoms of deterioration, like respiratory distress or signs of infection.
- Conservative treatment: In the case of minor cases, conservative treatment seeks to treat the root causes (e.g. treating inflammation or reducing trauma) and aid in healing. It can include:
- The treatment of any contributing factors like administering antibiotics to related diseases.
- Reducing the risk of further trauma or barotrauma to lung tissue.
- Controlling pain or discomfort in the event of.
- Promotion of lung health by means like quitting smoking and respiratory therapy.
The decision to seek an observational or conservative approach is typically determined on a case-by-case basis, taking into account aspects like the size and durability of the pneumatocele, the general health of the patient in addition to the absence of major symptoms.
It is crucial that patients maintain an open dialogue with their medical professionals to ensure that any changes to their health are addressed promptly.
Similarities Between Pneumatocele and Lung Abscess
The lung abscess and pneumatoceles are two lung conditions However, they differ in.
There are however some similarities between the two conditions:
- Pulmonary Involvement: Both pneumatoceles as well as lung abscesses impact the respiratory system particularly those of the lungs.
- Imaging features: The two conditions can be easily detected by using imaging methods that use radiology, such as chest X-rays or CT scans. The results of radiological imaging are crucial to determine the cause in both cases.
- Potential Complications: The risks they bring between pneumatoceles and lung abscesses could result in more severe problems. If they are not handled appropriately, could become more complicated which may require surgery. Lung abscesses could cause serious complications to the system and require urgent treatment if they are not dealt with promptly.
- Infection Relationship: While the nature of the illness is different (pneumatoceles are not directly linked with infection, but can result from it) infections can be a common cause in both cases. For lung abscesses, infection can be the primary reason.
- Care by Health Professionals: Both pneumatoceles and lung abscesses need evaluation for treatment and management by health professionals such as radiologists, pulmonologists, or infectious diseases experts.
These similarities do not obscure the major differences between pneumatoceles as well as lung abscesses as they are distinct in their etiologies, pathophysiology clinical manifestations, and management strategies. Understanding these differences is crucial for a proper diagnosis and treatment.
Conclusion
The distinction between pneumatocele as well as lung abscess is essential for accurate diagnosis and efficient treatment. Although there are some similarities between the two, both pulmonary diseases have distinct causes, pathophysiology, clinical signs, and treatment options. Knowing the difference is vital for providing patients with the best care possible and improving their outcomes.