Peripheral Arterial Disease (PAD) and Venous Insufficiency are two distinct vascular disorders that affect the circulation system frequently creating discomfort and complications. Knowing the basic distinctions between these two conditions is vital for a timely diagnosis and efficient treatment.
The anatomy of the condition, its causes, symptoms diagnosis methods, and treatment options, as well as complications, prognosis, and preventive strategies that can be applied to each PAD as well as Venous Insufficiency and Venous Insufficiency, providing light on the distinct characteristics of each condition to aid patients and healthcare professionals differentiate between the two.
What is Peripheral Arterial Disease (PAD)?
Peripheral Arterial Disease (PAD) is a circulatory disorder that is defined by the narrowing or blocking of arteries that carry blood flow to extremities primarily the legs. This is caused by the accumulation of fatty deposits, also known as atherosclerosis, inside the arterial wall.
In the process, blood circulation to the limbs is restricted, causing symptoms like discomfort, numbness, or weakness, particularly when performing physical activities.
The condition does not only impact the quality of life of a person but also puts them in high danger of more severe issues, such as the development of gangrene, tissue damage, and even limb amputations If left untreated.
What is Venous Insufficiency?
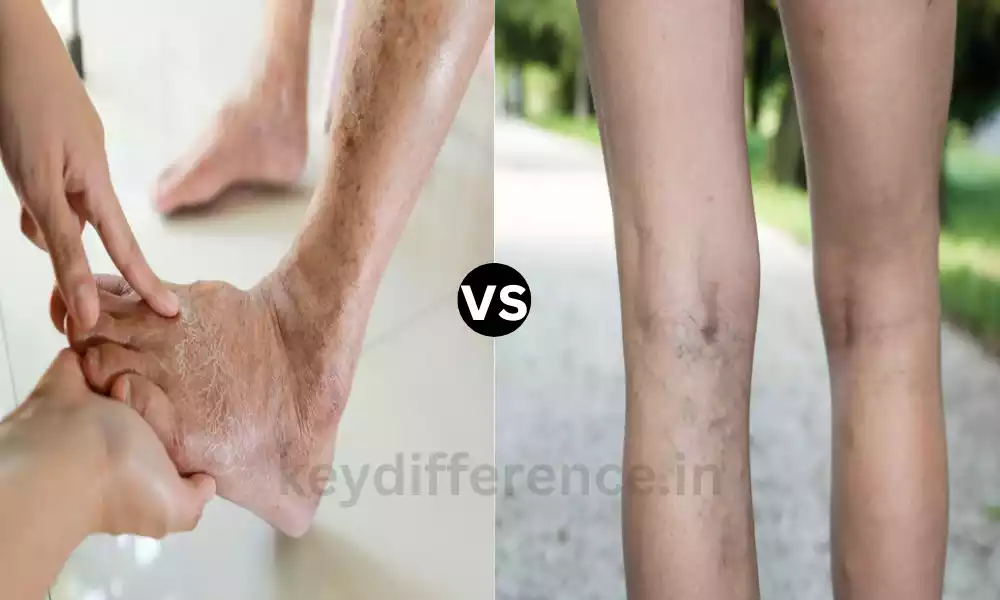
Venous Insufficiency is a medical condition in which the veins of the legs or in other parts of the body are unable to return blood efficiently back to the heart. The root cause is usually due to a malfunction in the valves with one-way connections in the veins that stop the flow of backward blood.
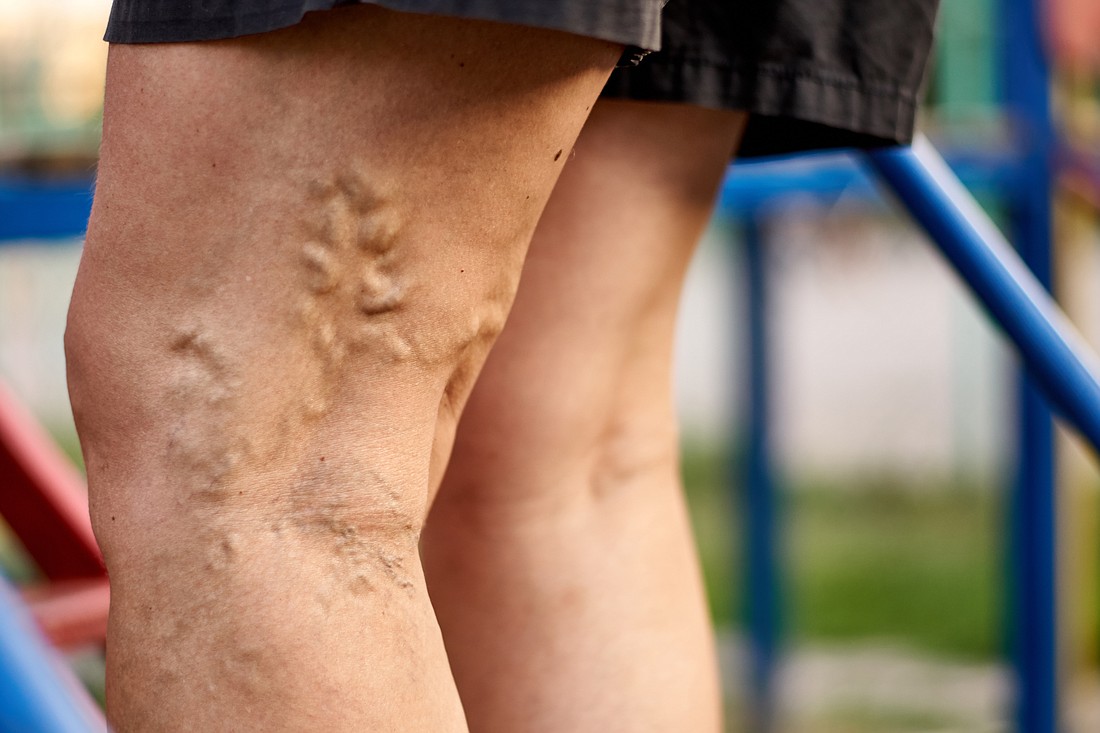
If these valves don’t work properly, blood pools within the veins, creating symptoms like varicose veins, swelling, pain, and in the most severe instances the appearance of skin ulcers and skin changes. Insufficiency in the veins can seriously affect the quality of life of a person and could cause serious complications if not managed properly.
Importance of distinguishing between PAD and Venous Insufficiency
The distinction between Peripheral Arterial Disease (PAD) and Venous Insufficiency is crucial for a variety of reasons:
- The most appropriate treatment: PAD and Venous Insufficiency require different treatment strategies. A precise diagnosis is crucial in order to make sure that the patients get appropriate treatments and interventions. Treatment of PAD in the same way as it was Venous Insufficiency, or vice versa can result in poor care.
- Prevention of Complications: Each condition is unique and has its own set of complications. If you treat one problem with procedures that are designed for the other can increase the likelihood of complications or worsen existing ones. An accurate diagnosis can reduce the risk of these issues.
- Qualities of life: PAD and Venous Insufficiency have a significant impact on the quality of life of a person. Differentiating between them allows healthcare professionals to tackle specific issues and symptoms experienced by the patient, thereby increasing their overall well-being.
- Long-term Prognosis: PAD as well as Venous Insufficiency can have different long-term outcomes. A precise diagnosis enables healthcare experts to give patients realistic expectations about their condition and prognosis, which allows patients to make informed choices regarding their medical treatment.
- Cost-Efficacy: Proper diagnosis prevents unnecessary medical costs that are a result of wrong diagnosis and improper treatment. It could save patients and healthcare institutions money by ensuring resources are utilized efficiently.
- Risk assessment: Recognizing the difference between the two conditions of PAD and Venous Insufficiency is crucial in assessing a patient’s general cardiovascular health. Incorrect diagnosis or a lack of discernment between these two conditions could lead to missing opportunities to detect other vascular disorders as well as risk factors.
- Preventive Measures: Recognizing the exact condition allows healthcare providers to give specific recommendations for lifestyle modifications or preventive measures as well as risk factors management. This will help to slow down the severity of the condition or the formation of complications.
Discerning the difference between PAD as well as Venous Insufficiency is crucial for patients to receive appropriate treatment, decrease the chance of complications, increase their lives, and make informed choices regarding their health.
It is crucial for healthcare professionals to correctly determine and distinguish between these two conditions in order to provide efficient and tailored care and support.
Comparison Table of PAD and Venous Insufficiency
Here’s a comparison table highlighting the key differences between Peripheral Arterial Disease (PAD) and Venous Insufficiency:
| Aspect | Peripheral Arterial Disease (PAD) | Venous Insufficiency |
|---|---|---|
| Affected Blood Vessels | Arteries | Veins |
| Cause | Atherosclerosis (plaque buildup) | Valve dysfunction |
| Typical Symptoms | Leg pain, claudication (cramping during exercise) | Swelling, varicose veins, leg pain, ulcers |
| Pain Characteristics | Intermittent, often relieved by rest | Persistent, often worsened with prolonged standing |
| Skin Changes | Cool, pale, thin, shiny skin | Warm, brownish skin with pigmentation changes |
| Ulcers | Typically dry, with well-defined edges | Typically moist, irregular-shaped ulcers |
| Risk Factors | Smoking, diabetes, hypertension, high cholesterol | Age, obesity, family history, sedentary lifestyle |
| Diagnostic Tests | Ankle-Brachial Index (ABI), angiography | Doppler ultrasound, venography |
| Treatment | Lifestyle changes, medications (antiplatelet drugs, statins), invasive procedures (angioplasty, bypass surgery) | Compression stockings, lifestyle changes, endovenous procedures (sclerotherapy, laser therapy) |
| Complications | Critical limb ischemia, amputation | Venous ulcers, deep vein thrombosis (DVT) |
| Prognosis | Risk of limb amputation if untreated | Risk of chronic ulcers and deep vein thrombosis if untreated |
| Prevention Strategies | Smoking cessation, exercise, healthy diet, blood pressure control | Regular leg movement, weight management, compression therapy |
| Affected Population | Common in older adults and smokers | Common in older adults, especially women |
| Typical Onset Age | Over 50, but can occur earlier, often linked to risk factors | Over 50, more common in women |
| Management Focus | Restoring blood flow, preventing complications | Improving venous return, symptom relief |
This table provides a concise overview of the primary differences between PAD and Venous Insufficiency, including their causes, symptoms, diagnostic methods, treatment options, complications, and preventive measures.
Please note that individual cases may vary, and a healthcare professional should provide a precise diagnosis and treatment plan based on an individual’s specific condition.
How PAD and Venous Insufficiency affect Circulation
Peripheral Arterial Disease (PAD) and Venous Insufficiency impact circulation differently because of their distinct mechanisms and causes:
- Peripheral Arterial Disease (PAD):
PAD primarily affects the arterial circulation, which transports oxygenated blood out of the heart and to other areas in the body. It does this through narrowing or blocking arteries, usually within areas of the lower extremities. This narrowing is the result of atherosclerosis. cholesterol, fatty deposits, and other compounds build up on the arterial wall.
-
- Lower Blood Flow: Atherosclerosis within the arteries can reduce the lumen’s size, thus limiting the circulation of oxygenated blood to muscles and tissues of the legs. This may cause an oxygen shortage (ischemia) in the course of physical exercise.
- Intermittent Claudication: Patients suffering from PAD typically suffer from intermittent claudication, a condition that causes the sensation of cramping, pain, and discomfort in the leg while doing walking or exercising. The reason for this is that the muscles aren’t receiving enough nutrition and oxygen.
- The risk of complications: If untreated, PAD can progress to critical limb ischemia where there is a serious deficiency of blood circulation into the extremities. This can lead to swelling, gangrene, or even an amputation of limbs.
- Venous Insufficiency:
Venous Insufficiency impacts the circulation of venous blood that is responsible for bringing blood that is deoxygenated from the extremities towards the heart. The problem occurs when the valves that allow one-way flow in the veins, that hinder the flow of backward blood, get damaged or malfunctioning.
-
- Inefficient Blood Return: If these valves fail to work properly, blood may collect in the veins, especially within the extremities below. This can lead to an increase in pressure on the venous vessels and congested blood vessels, making it hard for the veins in order to effectively deliver blood to the heart.
- Varicose Veins and Swelling: The increased pressure within the veins could cause leg swelling and the development of varicose veins. Varicose veins are twisted, swollen veins visible under the skin.
- Skin Ulcers and Skin Changes: Over time, chronic venous insufficiency may result in skin conditions, such as swelling and discoloration. It can also lead to ulcers of the venous that tend to be sores with open sides that are hard to heal.
PAD impacts the circulation of blood by decreasing the flow of blood to your extremities, which leads to cramps and pain during exercise.
Venous Insufficiency, on the contrary, impacts the venous circulation by causing poor blood return, resulting in inflammation, varicose vessels, and, in more severe instances, skin changes as well as ulcers.
The two conditions differ in their impact on circulation due to their distinct anatomical positions and their underlying causes.
Complications of untreated Venous Insufficiency
Untreated Venous Insufficiency could cause a variety of complications that can have a significant impact on the health and general health.
Some of the possible problems that can arise from untreated Venous Insufficiency are:
- Venous Ulcers: A very frequent and severe complication associated with Venous Insufficiency involves the emergence of Venous ulcers. These are open sores that usually develop in the lower limbs, especially near the ankles. Venous ulcers can be painful and take a long time to heal and may be chronic if not treated.
- Cellulitis: Blood pooling in the lower leg because of a lack of vein return may raise the chance of developing cellulitis which is an infection of the skin caused by bacteria. Cellulitis may cause inflammation, redness, warmness as well as pain as well as fever. It is a medical emergency that requires prompt treatment.
- Deep Vein Tissue Thrombosis (DVT): Venous stasis (the slowing of blood flow within the veins) is a sign of Venous Insufficiency that may increase the chance of blood clots forming in the veins that run through the legs. A DVT could be dangerous since it could cause pulmonary embolisms when the clot ruptures and moves to the lung.
- Chronic Skin Changes: Over time, untreated Venous Insufficiency can lead to chronic skin changes, such as pigmentation changes, thickening of the skin (lipodermatosclerosis), and dermatitis. The changes could result in discomfort and cosmetic issues.
- Superficial Thrombophlebitis: This type of condition is caused by inflammation and the formation of blood clots inside the veins that lie close to the face’s skin surface. While it’s generally less serious than DVT however, it may cause localized redness, pain, and swelling.
- Low quality of life: The persistent symptoms of Venous Insufficiency which include the swelling of your legs, leg pain, and discomfort, can greatly impact a person’s quality of living, making it difficult to take part in physical activities, and creating mental stress.
- The worsening effects of Venous Insufficiency: Left untreated and untreated, Venous Insufficiency tends to worsen over time, resulting in more serious problems and signs. This makes the condition difficult to manage and treat.
It’s essential to seek medical assistance if you believe you might have Venous Insufficiency or have any symptoms related to the disease. An early diagnosis and effective management can prevent the occurrence of these problems and improve your overall well-being.
Treatment typically involves changes to your lifestyle as well as compression therapy in certain cases medical procedures to treat the underlying cause of venous dysfunction.
The long-term outlook for Venous Insufficiency patients
The long-term outlook of patients suffering from Venous Insufficiency is contingent on many factors, including the extent of the condition and the risk of complications, as well as the efficacy of treatment.
Here are a few important considerations to consider for the long-term future of Venous Insufficiency patients:
- Early Intervention: The patients who receive medical treatment early and receive a prompt diagnosis and treatment that is appropriate have a better chance of a long-term outcome. A timely intervention can help control symptoms, avoid complications, and enhance the general health of the patient.
- Lifestyle and Management changes: A long-term perspective tends to be more favorable for those who are actively managing their condition. Lifestyle modifications, like regular exercise, keeping an appropriate weight, and elevating legs, can ease symptoms and help slow the progression in the course of Venous Insufficiency.
- Compression Therapy Stockings for compression or garments are commonly used as a procedure for treating Venous Insufficiency. When they are used regularly they will aid in venous return, lessen swelling, and avoid complications. Compliance with compression therapy is crucial for the long-term benefit.
- Prevention of Complications: Venous Insufficiency patients must be aware of the potential for complications like cellulitis, venous ulcers as well and deep vein thrombosis. Early detection and treatment for these conditions are crucial for an optimistic long-term outlook.
- Follow-Up Care: Regular appointments with a health professional are essential for monitoring the course of the illness and adjusting treatments as required. This ensures that the treatment continues to be efficient over the long run.
- Educational for Patients: Educating patients about their medical condition and the importance of staying on track with treatment and self-care strategies allows patients to take an active part in managing their Venous Insufficiency and sustaining an optimistic outlook for the long term.
- The severity of Venous Impairment: The long-term outlook for patients will vary depending on the degree of the disease. Certain individuals might suffer from moderate cases, which can be easy to manage, whereas others might have more severe disease that requires more aggressive treatments.
- Qualitative of Life: In the end, the long-term perspective should focus on increasing the health and quality of life. While the condition may have no cure, with the right management and treatment, a lot of people can live a full and happy life with little disruption to their illness.
It is crucial for patients with Venous Insufficiency to collaborate closely with their healthcare providers to design a personalized treatment plan and adhere to the recommended methods to manage the disease.
Early interventions and active self-care may improve the long-term prospects of patients with Venous Insufficiency patients.
Strategies to prevent Venous Insufficiency
The prevention of Venous Insufficiency or decreasing its risk requires adopting various lifestyle changes and practices that help to improve circulation.
Here are some suggestions to prevent Venous Insufficiency:
- Regular exercise: Engage in regular physical exercise to increase the circulation of blood in your legs. Activities like swimming, walking, and cycling are all beneficial. Concentrate on exercises that strengthen the calf muscles as they assist in pumping blood back to the heart.
- Maintain an appropriate weight: Excess weight places more pressure on your veins in your legs. Being healthy can decrease the risk of developing Venous Insufficiency.
- Increase Your Legs: Lifting your legs above your heart during resting can aid in improving the flow of venous blood and decrease swelling.
- Avoid prolonged standing or sitting: If your job or lifestyle requires long periods of sitting or standing make sure you take frequent breaks to stretch and move your legs. Altering your posture and walking around will aid in preventing blood from pooling within the veins.
- Comprise Stockings: If you’ve got an ancestral history in the area of Venous Insufficiency or are at risk, think about using compression socks. They can improve circulation and decrease the chance of developing the condition.
- Dietary Tips: Maintain a diet that is high in fiber, to avoid constipation, which may increase tension in abdominal veins. Also, be cautious about excessive intake of salt, since it can cause swelling and retention of water.
- Avoid tight clothing: Tight clothing, particularly in the area of waists and hips can impede blood circulation. Select loose-fitting clothes to avoid excessive pressure over your veins.
- Keep hydrated: Proper hydration can assist in maintaining a healthy blood viscosity, which makes the blood easier to flow throughout your blood vessels.
- Low Heels Limit: The high heel of shoes may interfere with the ability of the calf muscles to pump blood efficiently. Opt for supportive, comfortable shoes as often as you can.
- Regular Leg Movements: If you have an occupation that is sedentary or routine, you should move your legs frequently flex your ankles, and do ankle circles. This simple exercise can boost blood flow.
- Quitting Smoking: The damage to blood vessels from smoking raises the chance of developing Venous Insufficiency. Smoking cessation could have a positive effect on your cardiovascular health.
- Manage chronic conditions: If you have diabetes or high blood pressure, take care to manage these conditions with care, since they could cause vascular issues.
- Leg Elevation during Sleep: Consider elevating the feet of your bed a bit as well as using pillows to raise your legs when you sleep. This will help in the return of venous blood during the night.
- Regular check-ups: If you have a history in your family for venous Insufficiency and other risks, think about regular visits with your healthcare professional to assess your cardiovascular health.
It’s important to keep in mind that although these methods can reduce the likelihood of Venous Insufficiency they will not ensure prevention, particularly in situations where there’s a genetic predisposition.
If you suspect Venous Insufficiency or have symptoms, consult a physician to determine the correct diagnosis and treatment program.
Similarities Between PAD and Venous Insufficiency
Peripheral Arterial Disease (PAD) and Venous Insufficiency are both vascular diseases that affect circulation and can be linked to blood vessels within the extremities. However, they differ in a number of ways.
There are, however, some similarities between these two conditions:
- Leg symptoms: Both PAD and Venous Insufficiency may manifest as symptoms that affect the legs. Patients suffering from either condition might feel pain, discomfort, or a feeling of weight within their legs.
- The cause of swelling: Leg swelling is a typical sign of both of the conditions. Although the reasons for the swelling may differ (arterial and. veinous) however, it’s a common sign.
- Skin changes: These conditions can cause changes to the skin of the affected region. Changes can result in the appearance of discoloration, skin thickening, and the appearance of ulcers. However, the specific features of these changes in the skin differ between these two conditions.
- Risk Factors: Certain risks are common for both of the conditions. These include things like obesity, age, and a family history of vascular issues. In addition, smoking is an important risk cause that can lead to the development of both PAD as well as Venous Insufficiency.
- Impact on Quality of Life: Both PAD and Venous Insufficiency can adversely affect the quality of life for a person. The symptoms can hinder movement and physical activity which can result in a decline in general health and well-being.
- The progression in Disease: If they are not treated or not properly managed, the symptoms may get worse and complications could occur as time passes. For instance, ulcers can form in both conditions and may be difficult to heal if not treated properly.
Even though these resemblances exist however, it is important to recognize how PAD as well as Venous Insufficiency have distinct root causes, impact different blood vessels (arteries and veins. veins), and require different diagnosis and treatment strategies.
A precise diagnosis is essential for ensuring that sufferers receive the most appropriate treatment and care to treat their particular medical condition.
Conclusion
While Peripheral Arterial Disease (PAD) and Venous Insufficiency have some common signs and risk factors, they are two distinct blood vessels with distinct reasons and mechanisms.
An accurate diagnosis and customized treatment are essential to manage these conditions efficiently. Recognizing their distinct characteristics and obtaining urgent medical attention could make an enormous difference in the quality of life and the long-term prognosis for people affected by these vascular problems.