Buruli ulcer and leprosy disease are both debilitating skin conditions that have afflicted populations across the globe for a long time.
Although they have some similarities in the way they affect communities and individuals, these illnesses differ greatly in terms of their origins, causes, transmission, appearance, and treatment.
The major differences between Buruli ulcer and leprosy, provide a better understanding of the causes of the disease, its diagnosis, and the social implications of these conditions.
Understanding the differences is crucial for health professionals, policymakers as well and the general public to successfully tackle and manage these diseases.
What is Buruli Ulcer?
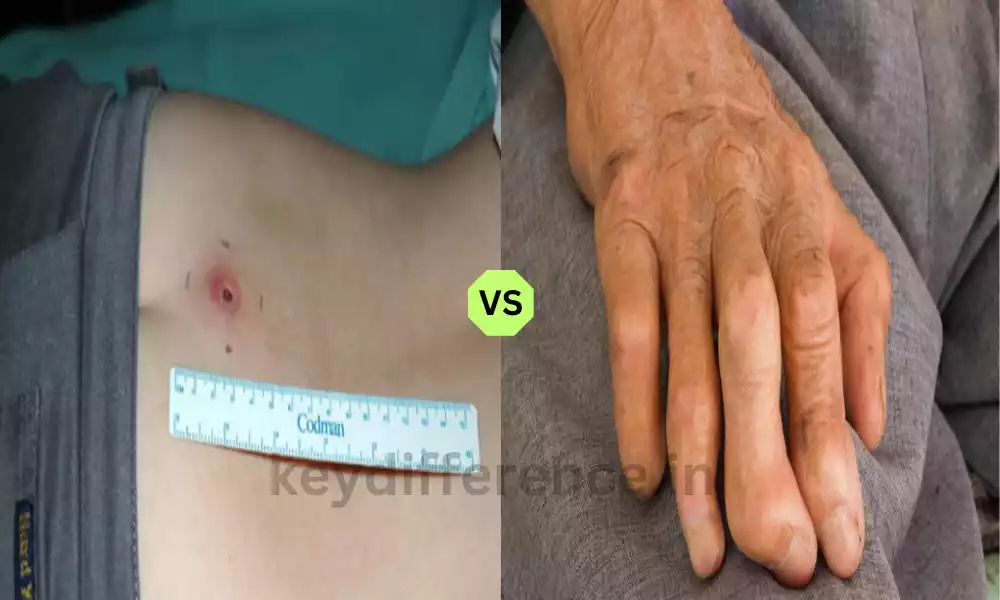
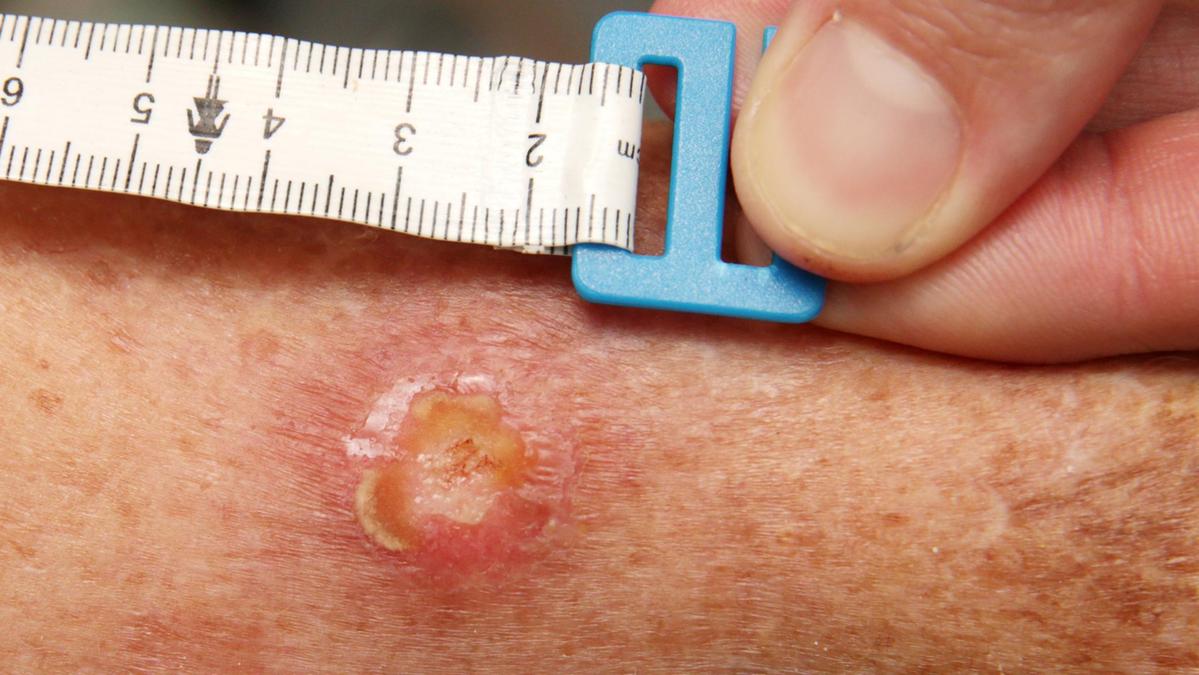
Buruli ulcer also referred to as Mycobacterium Ulcerans Disease, is a tropical disease that is not well-known. It is due to the Mycobacterium. It mostly affects the skin and in cases of severe severity subcutaneous tissues.
The condition is characterized by the development of painful necrotic (dead) skin ulcers. skin, which is often weakened edges. The resulting ulcers could cause extensive skin damage and scarring in the event that they are not treated.
Buruli ulcer is usually found in under-served and rural communities, especially in subtropical and tropical areas, and poses an enormous health risk in the affected regions.
The name is derived from Buruli County located in Uganda which was which was the first to be identified in the 1960s.
What is Leprosy?
Leprosy, sometimes referred to as Hansen’s Disease, is a persistent infection caused by the bacteria Mycobacterium Leprae. Leprosy mostly affects the peripheral nerves, and the skin as well and when it gets more severe there are other organs.
It is characterized by the formation of skin lesions, nerve damage as well and a myriad of clinical manifestations. These include the loss of feeling, weakness in muscles, and deformities that affect the affected regions.
Leprosy has been considered a stigmatized condition throughout history because of misconceptions regarding its transmission and the physical limitations it can cause.
Treatment options are available with early detection and medical treatment that is appropriate the disease is no longer the dangerous and infectious disease it was in the past.

Significance of understanding the differences between the two diseases
Understanding the difference between Buruli ulcers and Leprosy can be a matter of great importance for a variety of reasons:
- Correct diagnosis and treatment: Distinguishing between the two types of diseases is vital for health professionals to offer precise and timely diagnosis and treatment. Treatment methods for Buruli ulcer as well as leprosy vary in treatment, and misdiagnosis may result in ineffective or dangerous treatment.
- Epidemiological Control: Knowing the geographical patterns of transmission and distribution of both diseases aids public health officials in implementing specific prevention measures. This knowledge is vital to prevent and manage outbreaks.
- Preventive strategies: Knowledge of the risks and strategies for prevention specific to each illness is crucial for those living in communities at risk. Public health programs that are effective can be designed to increase awareness and educate the general public.
- Minimizing stigma: Both Buruli ulcers, as well as leprosy, are historically linked to discrimination and stigma. Knowing the difference between these two conditions will help to reduce the perceptions as well as stigma and social stigmatization of the affected.
- The Research Program and the Funding Allocation: Knowing the distinctive features associated with Buruli Leprosy and ulcer may assist in directing research efforts and funding allocations to address the specific issues that are associated with each of the diseases.
- World Health Preferences: In the context of global health priorities change, it is crucial to know the differences between different diseases so that we can be able to allocate resources efficiently and address the most urgent problems in a targeted way.
- Public and Community Education: Informing the general public of the distinctions between these conditions can help promote understanding and compassion while reducing the fear of discrimination and prejudice against the people who are affected.
Understanding the distinctions between Buruli ulcers and Leprosy is vital to ensure a correct diagnosis, efficient treatment, prevention, and control strategies in addition to fighting discrimination and stigma related to these diseases. This information can lead to better public health outcomes and more assistance for those affected and their communities.
The importance of distinguishing between Buruli Ulcer and Leprosy
The distinction between Buruli ulcers and Leprosy is vitally important for a variety of reasons:
- Appropriate treatment: Buruli ulcer and leprosy are two distinct illnesses caused by different bacterial strains. The approaches to treating them differ greatly. An accurate diagnosis can ensure that patients receive the right treatment and avoid unproductive or harmful treatments.
- Prevention and Control: Understanding the different risk factors and transmission modes is crucial for the implementation of effective strategies for prevention and control. Specific interventions can be designed to stop any spread of illness in the endemic regions.
- Epidemiological Surveillance: Knowing the geographic distribution and frequency of Buruli ulcers and leprosy aids health professionals in identifying outbreaks and responding accordingly. This information is essential in preventing and controlling illnesses.
- Minimizing Stigma: Both Buruli ulcers, as well as leprosy, have historically been associated with discrimination and stigma. A clear diagnosis and distinction between the two illnesses will help to reduce the perceptions of stigma. Patients suffering from these diseases are able to access the help and treatment they require without any discrimination.
- Research and Prioritization of Funding: Differentiating between the two kinds of illnesses is essential in directing funds and research efforts properly. Researchers are able to focus on the distinctive features, treatments, and challenges associated with each illness, leading to more precise and efficient research results.
- Global health planning: As global health priority shifts, it is crucial to distinguish between illnesses to effectively allocate resources and tackle specific health issues. This will ensure that the resources available are effectively used to fight these illnesses.
- Information and Awareness: Awareness and education for the public are essential to dispel myths and misconceptions regarding the two diseases. Understanding the distinctions could lead to more informed and caring communities, which can reduce anxiety and discrimination towards those affected.
Knowing the difference between Buruli ulcer and leprosy condition is essential to ensure a precise diagnosis, efficient treatment, and prevention. This also aids in the reduction of stigma, improving research and funding as well as raising awareness in order to improve the lives of people suffering from these diseases.
Comparison Table of Buruli Ulcer and Leprosy
Here’s a comparison table highlighting the key differences between Buruli ulcer and leprosy:
| Characteristic | Buruli Ulcer | Leprosy |
|---|---|---|
| Causative Agent | Mycobacterium ulcerans | Mycobacterium leprae |
| Primary Affected Areas | Skin and subcutaneous tissues | Skin and peripheral nerves |
| Clinical Presentation | Painless, necrotic ulcers often with undermined edges | Skin lesions, loss of sensation, muscle weakness, and nerve damage |
| Transmission | Likely environmental, unclear human-to-human transmission | Person-to-person through respiratory droplets (airborne transmission) or prolonged close contact |
| Incubation Period | Weeks to months | Years to decades |
| Stigma | Stigmatization is less common, but still present | Historically highly stigmatized, though less so in recent times |
| Treatment | Antibiotics (e.g., rifampicin and clarithromycin) | Multi-drug therapy (MDT) for various durations depending on disease type |
| Preventative Measures | Avoidance of contaminated water and early wound care | Active case finding, contact tracing, and provision of MDT |
| Global Prevalence | Concentrated in certain regions (e.g., West Africa, Australia) | Widespread, with highest prevalence in South Asia and sub-Saharan Africa |
| Eradication Goals | Not targeted for global eradication | Targeted for global elimination as a public health problem |
This table provides a concise overview of the primary differences between Buruli ulcers and leprosy, including causative agents, affected areas, clinical presentation, transmission, incubation periods, social stigma, treatment options, prevention measures, global prevalence, and eradication goals.
Understanding these distinctions is essential for accurate diagnosis, treatment, and public health efforts related to both diseases.
Prevalence and incidence rates of both diseases
The incidence and prevalence rates of Buruli ulcer and leprosy may differ greatly by location and time. The following statistics provide an overview of the situation at the time of my last information update on September 20, 2021 however, it is important to remember that these rates could have changed since that time.
Buruli Ulcer:
- Incidence: Buruli ulcer is mostly found in certain regions of Africa which includes West as well as Central Africa, as well as certain areas of Australia. The frequency can be quite high, with certain countries with high instances. The prevalence can vary locally within these regions.
- The rate of incidence: The rate of Buruli ulcer is variable and endemic areas experience variations in the seasons. The incidence rates are usually listed per 100,000 inhabitants. In some areas that are endemic, the rate of incidence is up to 100 instances per 100,000.
Leprosy:
- Prevalence: Leprosy is more prevalent than Buruli ulcer and was once common in many parts of the globe. However, coordinated efforts to eradicate and manage the disease have decreased its incidence in a variety of regions. Leprosy is expected to be eliminated by 2021. is the most prevalent within South Asia, Southeast Asia, and sub-Saharan African countries.
- Incidence: Leprosy incidence is different significantly by region and country. The worldwide incidence rate in 2019 was 2.7 instances per 100,000 as per the World Health Organization (WHO). However, certain countries and regions have greater rates of incidence, especially in regions in which the disease is in a state of endemic.
It is important to be aware that these incidence and prevalence rates may fluctuate due to many aspects, such as public health initiatives accessibility to healthcare, social and economic conditions, as well as the climate.
Monitoring and reporting on the diseases are continually evolving and there could be more current data from research or public health institutions for an up-to-date analysis of the condition.
Risk factors associated with transmission
Risk factors that are associated with transmitting Buruli ulcer or leprosy vary because of the different nature of each disease.
Below are risk elements that can be associated with the spread of both diseases:
Buruli Ulcer:
- exposure to Aquatic environments Mycobacterium ulcerans that causes Buruli ulcer is thought to be associated with specific aquatic environments. People who are regularly in contact with stagnant or slow-moving bodies of water, like swamps and wetlands, may be at greater risk.
- Inadequate wound care: Poor techniques for wound care, such as the inability to wash the wound and wrap it up, may cause the risk of infection. The bacteria can enter the body through wounds, scratches, or even open wounds, particularly in endemic regions.
- Prolonged exposure: A prolonged stay in areas that have a significant incidence of Buruli ulcer, in areas where the bacterium could be found in the environment which increases the risk of transmitting.
- Individual susceptibility: The factors that impact the immune system of an individual may influence their vulnerability to infections. Individuals with weaker immune systems might be more susceptible to illness.
Leprosy:
- Close and prolonged contact: Leprosy is spread through respiratory droplets when an untreated sufferer of leprosy coughs coughs or sneezes. In close and extended contact with an infected person is a major risk element. Family members of those who are infected are more at risk.
- Poor socioeconomic conditions: Unsanitary and overcrowded living conditions, frequently associated with poverty, could increase the risk of transmission because they allow close contact with people who are infected.
- Malnutrition: Nutritional deficiencies can affect immunity, which makes people more prone to contracting leprosy when exposed to the bacteria.
- Genetic susceptibility: Certain individuals could be genetically prone to making people more susceptible to developing leprosy, especially if they are in contact with Mycobacterium leprae. Genetic factors can play a part in the variance of disease susceptibility in individuals.
- Delay in diagnosis and Treatment: Delay in diagnosis and treatment for cases of leprosy increases the chance of transmission. The early diagnosis as well as treatment using Multidrug Therapy (MDT) significantly reduces the risk of transmission.
It is important to remember it is the case that Buruli ulcers and Leprosy both are both complex illnesses affected by many aspects, such as social, environmental, and individual health issues.
Effective control and prevention strategies for both diseases are based on the identification and treatment of these risk factors in order to limit transmission and the negative impact of the diseases on communities that are affected.
Progression and complications of both diseases
The course of treatment and possible problems associated with Buruli ulcers as well as leprosy can differ due to the unique features of each.
Here’s a summary of the course of progression and possible complications that may arise with either:
Buruli Ulcer:
- Progression:
- Buruli ulcers typically begin with a painful nodule or swelling on the location of the inflammation.
- As time passes the nodule could grow to develop into an ulcer usually with edges that are weakened. The ulcers may take a long time to form, but they may grow massive and deep, affecting both the subcutaneous and skin tissues.
- If not treated promptly The ulcer may continue to grow, causing significant tissue destruction and scarring.
- Complications:
- The scarring Buruli wounds can cause significant scarring, particularly when treatment and diagnosis are not completed.
- Limb Deformities: In a few instances, the disease could cause joint pain, resulting in the development of limb contractures as well as limb deformities.
- Long-Term Disability: Extreme cases, left untreated and untreated, may cause long-term disabilities especially when the condition is affecting joints or bones.
Leprosy:
- Progression:
- Leprosy can manifest in a variety of clinical forms and has an array of severity.
- The most common affliction is those with skin conditions, the peripheral nerves as well and mucous membranes. It tends to progress slowly, with symptoms arising over a long time.
- Two main types are lepromatous therapy (more serious) or tuberculoid (less serious). Leprosy’s course is dependent on the person’s immune system.
- Complications:
- Injuries to the Nerve: Leprosy may cause damage to nerves, which can result in the loss of feeling, weakness in muscles, and even paralysis. Nerve damage could cause infections and injuries since those affected might not feel discomfort or pain.
- The skin lesions can get larger and can cause disfigurement.
- Eye Involvement: The disease can cause eye problems, and possibly cause blindness if it is not treated.
- Disabilities for Long-Term: in extreme instances, leprosy may result in long-term physical disability.
It is important to remember that early diagnosis and treatment could dramatically slow the progression and complications associated with the two conditions: Buruli ulcers and Leprosy.
Medical interventions that are effective like antibiotics to treat Buruli ulcer, and multidrug treatment (MDT) in leprosy can help prevent further harm and impairment.
Thus the early detection of leprosy and access to the appropriate treatment are crucial in preventing these illnesses and limiting their effects on the affected.
Management and care for affected individuals
Treatment and care for people affected by Buruli ulcers and leprosy demands an integrated approach that considers psychological, medical, as well as other aspects that are associated with these conditions.
These are the main aspects of care and management for those affected:
Buruli Ulcer:
- Medical Treatment:
- The early diagnosis is vital. If Buruli ulcers are suspected medical professionals should conduct specific diagnostic tests, including the PCR or the culture to confirm the diagnosis.
- The most common treatment for Buruli ulcer is to use antibiotics, which are usually a mix of clarithromycin and rifampicin. The type of antibiotic and duration of treatment may differ based on the extent of the condition and the individual circumstances.
- The care of wounds and surgical procedures are sometimes required, especially in cases of extreme severity. Wounds must be cleaned and properly dressed to avoid secondary infections.
- Pain Management:
- Management of pain is vital especially after and during surgery and as part of the general treatment. Medicines for pain relief may be prescribed.
- Psychosocial Support:
- People with the disease might experience mental anxiety due to the obvious nature of the condition and the possibility of visible disfigurement. Counseling, psychosocial support, and education can assist sufferers in coping with these issues.
- Physical Rehabilitation:
- Patients with severe instances of Buruli ulcers might require physical therapy in order to recover the ability to move and function following the injury to tissues and scarring.
Leprosy:
- Multidrug Therapy (MDT):
- Leprosy can be treated with MDT which typically includes an array of antibiotics like dapsone, rifampicin, and Clofazimine. The treatment method and time frame depend on the severity and type of leprosy.
- The completeness of treatment is essential in order to stop the development of resistance to antibiotics.
- Wound and Skin Care:
- Skin care and wound healing are essential to avoid secondary infections and resulting skin injury. It is recommended that people keep areas affected free of self-trauma and keep them clean.
- Nerve Damage Management:
- The treatment of nerve damage entails the prevention of numb or damaged regions to prevent injuries and physiotherapy to increase muscle strength and mobility.
- Eye Care:
- If you have an eye problem periodic eye exams and the appropriate treatment are crucial to stop blindness.
- Psychosocial Support:
- Because of the stigma that is associated with leprosy, sufferers may be confronted with mental and social difficulties. Counseling and psychosocial support can assist in addressing these issues.
- Community and Family Support:
- Engaging the affected within their community and offering help from family and friends could be a key factor in reducing social stigma and isolation.
- Follow-Up and Monitoring:
- Regular follow-up visits with healthcare providers are crucial to track the progression of your treatment, determine its effectiveness, and address any potential issues.
Both diseases benefit from early detection prompt treatment and thorough care that focuses not just on physical symptoms but also well the psychological and social well-being of the affected.
Healthcare professionals, rehabilitation specialists social workers, and community assistance are crucial in providing complete care for people suffering from Buruli ulcers and leprosy.
Impact on affected individuals and communities
Buruli ulcers and leprosy are both serious illnesses that affect people as well as the communities in the communities in which they live. The effects include social, medical and economic implications, frequently creating stigma and discrimination.
Here’s an outline of the effects of these illnesses on people as well as communities:
Impact on Affected Individuals:
Buruli Ulcer:
- physical suffering: Patients who suffer from Buruli ulcers may feel discomfort and pain due to the lesions on the skin and ulcers. In extreme instances, this may cause severe damaged tissue, impairment, and disfigurement.
- Psychological Depression: The apparent nature of the illness can cause emotional distress, such as depression and anxiety. Individuals with this condition may have anxiety about their self-esteem as well as social isolation.
- Economy Burden: The treatment and care required for Buruli ulcers can be expensive. The affected person and their family might be burdened by the cost of medical bills and loss of productivity as a result of the illness.
Leprosy:
- Nerve damage: Leprosy may cause nerve damage that can lead to the loss of motor and sensation function in the affected area. The result could be injury and complications.
- Disfigurement: Skin physical and bodily deformities brought on by leprosy can cause disfigurement, which can impact the self-esteem of an individual and the image of their body.
- Blindness: Leprosy is a disease that can affect the eyes, and result in blindness if not treated.
- Social stigmas and prejudice: The two conditions Buruli ulcer and leprosy have historically been associated with discrimination and stigma. People affected may be subject to discrimination, and rejection as well as fewer opportunities to pursue educational and job opportunities.
Impact on Communities:
Buruli Ulcer:
- Public Health Concern: Buruli ulcer poses a public health problem in regions with endemic. To combat the disease, you must take an integrated approach that could burden the local health system.
- Economic Effect: Affected individuals and their families could have financial issues, which can affect the general economic well-being of the entire community.
- Educational and Employment: Stigma and fear of transmission can result in discrimination in the workplace and in education. This may limit the options for those suffering from Buruli ulcer.
Leprosy:
- Stigmatization: The stigma that is associated with leprosy may extend to families of the affected and can cause social stigma and isolation.
- Economic as well as Social Exclusion: Individuals affected by leprosy might be denied the ability to access education jobs and social integration which may affect the development of the community’s economy.
- Community awareness: The goal is to raise awareness and dispelling the myths surrounding leprosy is essential to fight stigma and encourage social inclusion. Communities may require awareness and advocacy.
The efforts to reduce the effects of these illnesses on people and communities require more than medical treatment, but also economic and social assistance in the form of awareness campaigns, awareness programs, and involvement of the community.
The reduction of stigma and discrimination is an essential element in improving the lives of those affected as well as the overall health of communities that are affected by Buruli ulcers and leprosy.