In the realm of diagnostic medical procedures, techniques like the Lumbar Puncture and Bone Marrow Biopsy can be essential instruments for medical professionals.
Both procedures play a crucial role in diagnosing various health ailments but they are distinct in the way they are executed, their purpose, and consequences. In the following article, we’ll explore the distinct characteristics of lumbar puncture as well as bone marrow biopsy.
We will shed light on their procedures their indications, risks, and their applications, eventually aiding you in understanding when and the reason each one of these diagnostic procedures is employed within the field of medicine.
Definition of Lumbar Puncture
Lumbar puncture, sometimes referred to by the name of a spinal tap is a procedure in medicine that involves the insertion of a thin hollow needle into the lower portion of the vertebral column typically in the lumbar area in the lower back.
This procedure is carried out to obtain the cerebrospinal liquid (CSF) which is which is the transparent fluid that covers the spinal cord and brain. Lumbar puncture is mostly used for diagnosis purposes and allows medical professionals to examine the CSF for various health ailments, such as bleeding, infections, and neurological diseases.
It serves as a way to reduce an increase in intracranial pressure or inject medication directly into the cerebrospinal fluid. A lumbar puncture is an important tool in neurology, as well as other medical specialties that aid in diagnosing and treating a variety of central and neurological system issues.
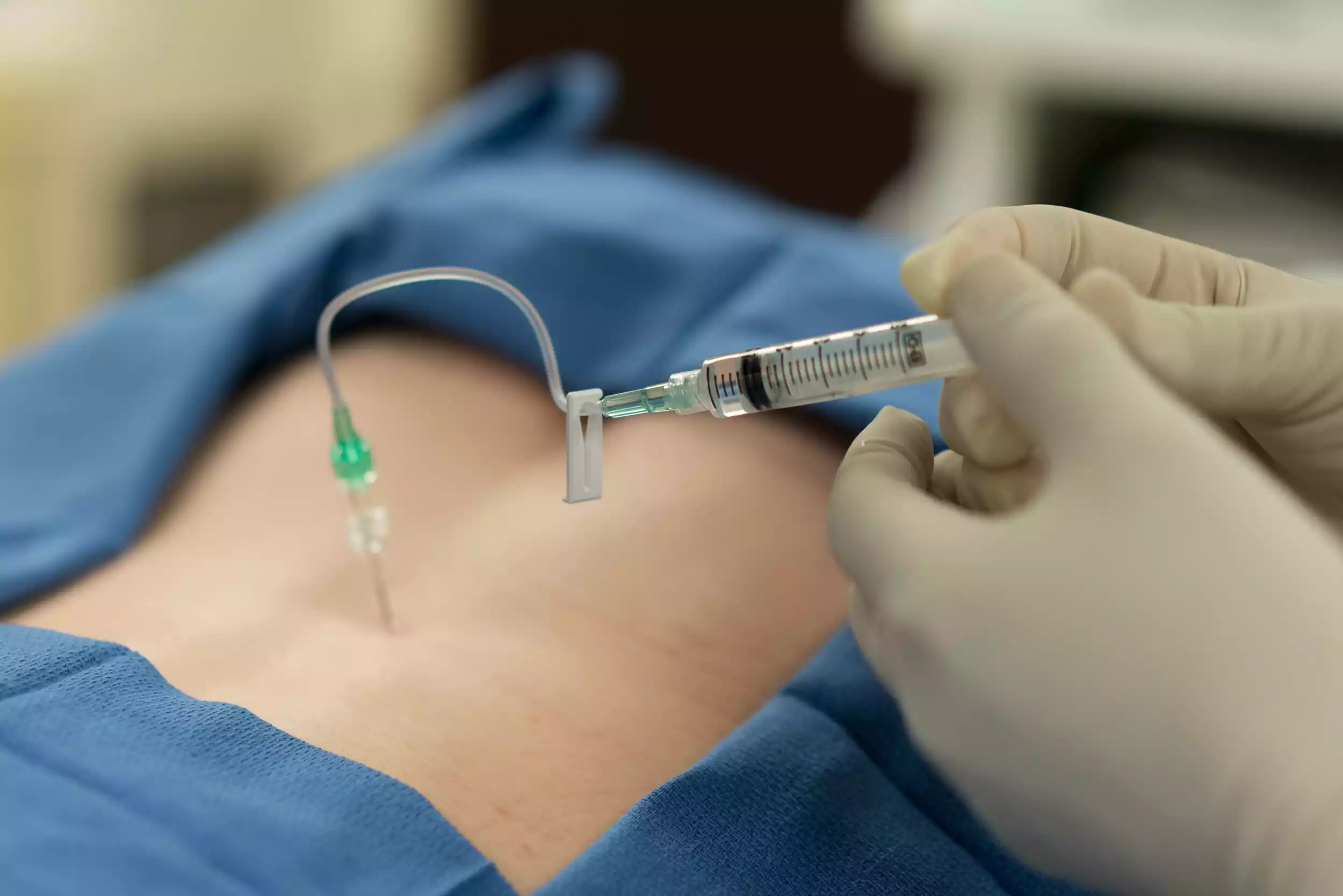
Definition of Bone Marrow Biopsy
The bone marrow biopsy is a medical procedure that is used to take a sample of bone marrow tissues to determine the diagnosis. It involves removing the bone’s small core as well as the bone marrow from a particular area, which is usually that of the hipbone (ilium) or the breastbone (sternum).
The bone marrow comprises the bone marrow, a spongy organ inside the bones that is responsible for the production of blood cells, which include white blood cells, as well as platelets.
Bone marrow biopsy has several important functions:
- Diagnose: It aids in the identification of various Hematological diseases, like lymphoma, leukemia, myeloma, and other types of anemia. By studying the cellular composition of the bone marrow medical professionals can detect the presence of blood cells that are not producing as they should.
- Monitoring and Staging: For cancer-related cases such as leukemia and myeloma bone marrow biopsy can help determine the severity affected by the disease (staging) and track the effect of treatment over the course of time.
- Evaluation of Bone Marrow health: It provides valuable information on the general health and function of bone marrow including the presence of infection or fibrosis as well as other conditions that affect the production of blood cells.
Bone bone marrow biopsy is an invasive procedure that is usually performed by a hematologist, or an oncologist. The bone marrow sample taken is sent to a lab to be analyzed in depth, which contributes to the correct diagnosis and treatment of a variety of cancerous and hematological disorders.
Significance of understanding the differences
Understanding the distinctions between the two procedures of lumbar puncture as well as bone marrow biopsy is crucial significance in the medical field and also for the health of patients for a variety of reasons:
- Accurate diagnosis: Knowing when and how to utilize each procedure is essential to make sure you get the right diagnosis. If you choose the wrong procedure, it can lead to misdiagnosis and delayed diagnosis, which could compromise the outcomes of patients.
- Patient safety: Understanding the distinctions aids healthcare professionals in choosing the most non-invasive and safest treatment for their patients thus minimizing the risk of discomfort and unnecessary risks.
- Treatment Plan: The choice between the lumbar puncture or bone marrow biopsy can affect the treatment decision in a significant way. The accuracy of the diagnostic data assists health professionals in determining the most appropriate treatment, which includes chemotherapy, medication radiation therapy, and surgical procedures.
- Efficiency and Cost-Effectiveness: Selecting the best diagnosis method right from the start will speed up the process of diagnosing and reduce the need for further tests or treatments, ultimately helping save time and resources for healthcare.
- Patient Experience: Patients gain complete knowledge of what to expect when undergoing a lumbar puncture or bone marrow biopsy. This includes the potential risks and recovery timeframes. Patients who are informed have a higher likelihood of adhering to the prescribed procedures and follow-up treatment.
- Avoiding unnecessary procedures: Knowledge of the distinctions can help prevent unnecessary lumbar punctures and bone marrow biopsies, thereby avoiding discomfort and possible complications when other tests that are less invasive may be sufficient.
- Specification: Different medical specialties like neurology, and hematology/oncology rely on these procedures for the particular purpose of diagnosis. Knowing the distinctions ensures experts are selected in each instance.
- Research as well as Advancements: In the constantly changing area of medicine knowing the distinctions between these methods is essential for being up-to-date on the latest research findings, methods, and advances in diagnostic procedures.
The significance of knowing the distinctions between the procedure of lumbar puncture as well as bone marrow biopsy is in its ability to enhance the quality of care for patients, increase accuracy in diagnosis, improve security, and aid medical professionals in their decision-making.
This knowledge is ultimately a contributor to improved healthcare outcomes and improved patient satisfaction.
Comparison Table of Lumbar Puncture and Bone Marrow Biopsy
Here is a comparison table outlining the key differences between lumbar puncture and bone marrow biopsy:
| Aspect | Lumbar Puncture | Bone Marrow Biopsy |
|---|---|---|
| Procedure Location | Lower back (lumbar region) | Hipbone (iliac crest) or breastbone (sternum) |
| Purpose | Collect cerebrospinal fluid (CSF) for diagnostic analysis; relieve intracranial pressure | Obtain bone marrow tissue for diagnostic analysis; assess hematological disorders |
| Indications | Neurological disorders, infections, bleeding, increased intracranial pressure | Hematological disorders (leukemia, lymphoma, anemia), cancer staging, monitoring response to treatment |
| Sample Collected | Cerebrospinal fluid (CSF) | Bone marrow tissue |
| Diagnostic Applications | Neurological conditions, and infections, rule out CNS disorders | Hematological disorders, leukemia, lymphoma, multiple myeloma, anemia, bone marrow disorders |
| Procedure Invasiveness | Minimally invasive; needle inserted into the spinal canal | Moderately invasive; core of bone and marrow tissue removed |
| Risks and Complications | Headache, infection, bleeding, nerve damage (rare) | Pain, bleeding, infection, damage to adjacent structures (rare) |
| Recovery and Aftercare | Rest and hydration, monitor for complications | Pain management, rest, monitoring for complications |
| Medical Specialties | Neurology, infectious diseases, radiology | Hematology, oncology, pathology |
| Anesthesia | Local anesthesia at the insertion site | Local anesthesia or conscious sedation |
| Duration of Procedure | Usually brief (15-30 minutes) | Typically takes 20-30 minutes |
It’s important to note that the choice between lumbar puncture and bone marrow biopsy depends on the patient’s clinical presentation, suspected conditions, and the information required for an accurate diagnosis.
Healthcare professionals carefully consider these factors to determine the most appropriate diagnostic procedure for each individual case.
Medical Specialties Using Lumbar Puncture
Lumbar puncture, sometimes referred to by the name of a spinal tap is a diagnostic technique used by different medical specialties to fulfill specific needs.
Here are a few medical specialties that frequently employ lumbar puncture procedures:
- Neurology: Neurologists often use the lumbar puncture procedure to diagnose and treat a variety of neurological conditions such as:
- Meningitis and Encephalitis
- Multiple Sclerosis
- Assessment of intracranial pressure
- Neurological diseases
- Guillain-Barre syndrome
- The Infectious Disease: Specialists in infectious diseases can make use of lumbar puncture in order to identify and identify pathogens that are present in cerebrospinal fluid aiding in the identification of infections that affect your central nervous system.
- Radiology: Radiologists may perform lumbar puncture by using image guidance (fluoroscopy or ultrasonography) to collect cerebrospinal fluid samples to be used for diagnosing purposes.
- Medical Emergency: In emergency medicine, lumbar puncture can be used in situations in which there is suspicion of a central nervous system issue subarachnoid hemorrhage, or other neurological emergencies.
- Pain Management: Specialists who specialize in pain management could utilize lumbar puncture to deliver medication, like epidural anesthetics, or locally administered ones through the epidural area to treat pain issues such as chronic pain syndromes and radiculopathy.
- Cancer: Sometimes Oncologists can make use of lumbar puncture in order to assess and determine the level of the involvement of central nervous systems in tumors such as leukemia and lymphoma.
- Pediatrics: Neurologists in pediatrics and specialists for infectious diseases could make use of lumbar puncture for children to determine the severity of conditions like meningitis in the pediatric population and other neurological disorders.
- Researchers and Clinical Trials: A lumbar puncture is an important tool for clinical trials and research, especially in studies in connection with neurological and central nervous system disorders.
It is important to remember that the lumbar puncture procedure is a highly specialized procedure that must be carried out by trained healthcare professionals and its usage varies based on the particular medical situation and the clinical manifestation of the patient.
The decision to perform the procedure is usually determined by the patient’s medical symptoms as well as medical history and the need for information to diagnose to inform the treatment decision.
Medical Specialties Using Bone Marrow Biopsy
Bone Marrow biopsy is an effective diagnostic procedure that is used by a variety of medical specialties to determine and diagnose a variety of conditions.
Here are the specialties in medicine that typically utilize bone Marrow biopsy:
- Hematology: Hematologists specialize in the field of blood disorders. They often make use of bone marrow biopsies to detect and monitor illnesses like:
- Leukemia
- Lymphoma
- Myelodysplastic syndromes
- Aplastic anemia
- Hematological malignancies
- Oncology: Cancerologists, especially those who specialize in the care of tumors arising from blood depend on biopsies of the bone marrow to assess the extent of involvement by cancer as well as staged tumors and determine the response to treatment.
- Internal Medicine: Internists may make use of bone marrow biopsies to look into undiagnosed anemia or thrombocytopenia. It can also be used to investigate leukopenia within their patients.
- Pediatric Hematology-Oncology: The specialists in this field utilize bone marrow biopsies to identify and treat cancers and blood disorders in children, including pediatric leukemia.
- Rheumatology: The Rheumatologist may conduct bone marrow biopsies in order to diagnose and track conditions such as systemic lupus and erythematosus (SLE) as well as vasculitis which may affect the bone marrow.
- Infectious Disease: In some instances, specialists in infectious disease might use bone marrow biopsies in order to identify certain infections that impact the bone marrow, for example, tuberculosis and histoplasmosis.
- Transplantation Medical: Doctors who are involved with stem cell transplantation like hematopoietic stem cell transplantation for the treatment of blood-related diseases can make use of biopsies from the bone marrow to evaluate the compatibility of donor and recipient.
- Pathology: They are accountable for studying bone marrow samples in order for definitive diagnoses and provide crucial data to aid in making treatment decisions.
- Clinical Research: Biopsies of the bone marrow are commonly conducted in research labs for clinical studies to test new treatments, assess the efficacy of treatment, and improve our understanding of a variety of cancerous and hematological diseases.
- Orthopedic Oncology: Orthopedic Oncologists can do bone marrow biopsies as part of the assessment and staging procedure for bone tumors like osteosarcoma.
- Radiotherapy Oncology: In some instances, radiation oncologists can make use of bone marrow biopsy findings to aid in planning treatment for cancers that are affecting bone marrow.
Bone bone marrow biopsy is a special procedure that requires expertise in its implementation and its interpretation. The decision to conduct the bone marrow biopsy is generally determined by the patient’s symptoms, presentation, and the requirement for specific diagnostic data to aid in the treatment and management of a patient.
Risks associated with each procedure
Both lumbar puncture, as well as bone marrow biopsy, are both medical procedures that are associated with dangers and possible complications. It is essential for healthcare professionals and their patients to understand the risks prior to performing these procedures.
Here are the potential risks that come with every procedure:
Risques Associated With Lumbar Puncture (Spinal Tap):
- Headache: A very frequent consequence of lumbar puncture is post-dural headache (PDPH). It happens when there is a tiny bleeding of the cerebrospinal fluid that has escaped the puncture site, which leads to headaches that are generally a result of position (worse when standing or sitting) and can be present for a number of days.
- The Infection: It is possible to run the chance of spreading infection to the cerebrospinal fluid. However, the risk is low in the event that proper sterile procedures are employed.
- The bleeding can be quite severe: Sometimes, a puncture in the lumbar region can lead to bleeding in the spinal cord, or into the cerebrospinal liquid, which can cause neurological signs.
- Nerve damage: Rarely, instances, damage to the spinal nerves can result in the sensation of numbness, pain, and weakness of the lower legs.
- Herniation: Lumbar puncture could potentially cause herniation of the brain, in particular in the case of extremely intense intracranial pressure. However, this possibility is very rare and generally only occurs in certain circumstances.
The risks associated with Bone Marrow Biopsy:
- The pain: The most common immediate complication of the bone marrow biopsy is discomfort or pain on the biopsy site. The discomfort will usually disappear within several days.
- Bleeding: The risk of bleeding is high. chance of bleeding occurring on the biopsy site that could cause bleeding, hematoma growth, or, in some rare instances serious bleeding that requires medical intervention.
- The infection is: Although rare, there is a chance of infection either at the site of biopsy or within the bone marrow.
- Organ or Nerve injury: In very rare instances the needle used for biopsy may accidentally damage blood vessels, nerves, or organs.
- Fracture or breakage in the Needle: The biopsy needle may break at times during the procedure. However, it is very rare.
- The patient may experience pain or discomfort during the procedure: While local anesthesia is employed to numb the site of the biopsy, some patients might experience discomfort or discomfort throughout the procedure.
It is important to remember the fact that these procedures can be considered to be safe when carried out by skilled healthcare professionals who use appropriate techniques and precautions.
The benefits and risks of these procedures must be addressed with the patient prior to they’re performed. Additionally, the healthcare professional will consider the medical history of the patient and medical condition to determine if the procedures are suitable for them.
Medical conditions where each procedure is typically used
Bone marrow and lumbar puncture are two distinct diagnostic procedures, each having its own medical conditions that they are usually employed.
Here’s a list of circumstances in which these procedures are typically used:
Lumbar Puncture:
- Meningitis as well as Encephalitis: The puncture of the lumbar region is an essential test for diagnosing any infectious agent (bacteria or viruses, or fungi) in the cerebrospinal liquid and aiding in diagnosing these severe central nervous system disorders.
- Subarachnoid Hemorrhage: It is used to identify whether there is blood present in cerebrospinal fluid. This could indicate subarachnoid hemorrhage which is a life-threatening condition that is often the result of ruptured brain aneurysms.
- Sclerosis (MS): Lumbar puncture can be used to determine whether there are oligoclonal bands in cerebrospinal fluid which is a reliable test for diagnosing MS.
- Neurological disorders: The HTML0 code is utilized to diagnose or rule out diverse neurological disorders that include Guillain Barre syndrome, myelitis, and demyelinating disorders.
- Intracranial Pressure Assessment: Lumbar puncture is a method to determine intracranial pressure in instances of elevated pressure inside the skull. This is evident in cases of hydrocephalus or brain tumors.
- Neurological Infections: It’s used to detect infections in the case of mysterious neurological symptoms.
Bone Marrow Biopsy:
- Hematological disorders: Bone marrow biopsies are often used in the evaluation and diagnosis of a variety of blood-related diseases, such as:
- Leukemia
- Lymphoma
- Myelodysplastic Syndromes (MDS)
- Aplastic anemia
- Thrombocytopenia
- Hematological malignancies
- Cancer staging: In cases of suspected or known cancers, like leukemia, lymphoma, or multiple myeloma, a bone marrow biopsy can help determine the degree of disease involvement, assisting in the staging of cancer and prognosis.
- Unexplained Anemia: If patients experience anemia that is not explained or pancytopenia (reduction in the blood cell types of all types) A bone marrow biopsy may help determine the root cause.
- Bone Marrow Disorders: It is used to determine bone marrow-related diseases, including myelofibrosis and myeloproliferative neoplasm.
- Evaluation of Response to Treatment: In the case of blood-borne diseases, repeated bone marrow biopsies can be conducted to evaluate the effect of treatment and help guide future therapy.
- Evaluation of bone tumors: Orthopedic Oncologists might make use of bone marrow biopsies as part of the assessment and treatment process for bone tumors like osteosarcoma.
It is important to stress that the decision between lumbar puncture or bone marrow biopsy will depend on the patient’s presentation in terms of clinical symptoms, and probable ailments. Healthcare professionals take into consideration these elements to determine which method is the best for specific instances.
Similarities Between Lumbar Puncture and Bone Marrow Biopsy
The bone marrow biopsy and the lumbar puncture are two distinct medical procedures that serve different purposes and uses. But,
There are some similarities between them:
- Diagnose Procedures: Bone marrow and lumbar puncture are two diagnostic methods to collect vital diagnostic data about the health of a patient.
- Tie or Fluid Sampling: Both processes require the collection of samples for analysis in the laboratory:
- Lumbar Puncture is used to collect cerebrospinal fluid (CSF) to be analyzed.
- A Bone Marrow Biopsy Takes a marrow sample from bone tissue to be examined.
- Invasive Techniques: Both techniques are not invasive in the sense that they are not invasive. They require the introduction of needles into your body to perform the procedure, it is fairly safe when carried out by trained medical experts.
- Local Anesthesia: Local anesthesia is usually applied at the time of the procedure, to lessen discomfort and discomfort for the patient throughout both lumbar puncture as well as bone Marrow biopsy.
- For diagnosing diseases: Both procedures are employed to determine the presence of different medical conditions, but in different medical specialties.
- Lumbar Puncture: It is often employed in neurology and infectious diseases to determine conditions affecting the nervous system central.
- Bone Marrow Biopsy is primarily utilized in oncology and hematology to identify malignancies and blood disorders.
- The risk of infection: Although it is not common however, there is a chance of contracting an infection during the two procedures if appropriate procedures for sterilization are not adhered to.
- Performed by specialists: Both lumbar puncture and bone marrow biopsy are usually performed by experts in their respective fields:
- Lumbar Puncture is performed by neurologists as well as infectious disease specialists as well and other healthcare professionals.
- Bone Marrow Biopsy is performed by hematologists oncologists pathologists, and nurses with specialization.
Although these methods share similarities, it is important to understand that they’re employed for different objectives and are generally used in different medical settings dependent on the patient’s clinical appearance and any suspected medical illnesses.
Reference Books
Certainly! Here are some reference books across various subjects and fields of interest:
1. Medicine and Healthcare:
- “Harrison’s Principles of Internal Medicine” by Dan L. Longo, et al.
- “Gray’s Anatomy for Students” by Richard Drake, et al.
- “Robbins and Cotran Pathologic Basis of Disease” by Vinay Kumar, et al.
2. Science and Biology:
- “The Selfish Gene” by Richard Dawkins
- “Sapiens: A Brief History of Humankind” by Yuval Noah Harari
- “The Immortal Life of Henrietta Lacks” by Rebecca Skloot
3. History:
- “A People’s History of the United States” by Howard Zinn
- “The Guns of August” by Barbara W. Tuchman
- “SPQR: A History of Ancient Rome” by Mary Beard
4. Psychology and Self-Help:
- “Thinking, Fast and Slow” by Daniel Kahneman
- “The Power of Habit” by Charles Duhigg
- “Man’s Search for Meaning” by Viktor E. Frankl
5. Literature and Fiction:
- “To Kill a Mockingbird” by Harper Lee
- “1984” by George Orwell
- “Pride and Prejudice” by Jane Austen
Conclusion
They serve as our guides as well as our teachers as well as our portals into our past, current, and future. When we want to learn about all the mysteries surrounding the universe, the intricate complexities of our human brain and the lessons of history, or the imaginative deepness of fiction, books provide an endless source of knowledge and motivation.
Every book is a doorway to new horizons, a source of illumination as well as a companion during the solitude. They test our minds expand our horizons and inspire our imaginations. With books, we are able to connect with the wisdom of past generations and are able to create our own destiny.
Therefore, whether you set out on a trip in the pages of a textbook on medicine lose yourself in the story of an epic novel, or explore the boundaries of philosophy and science Be aware what you decide to study will always alter your perception of the universe and of your place within it. It will be through the books we can learn, explore, and develop in our lives, enhancing all around us.