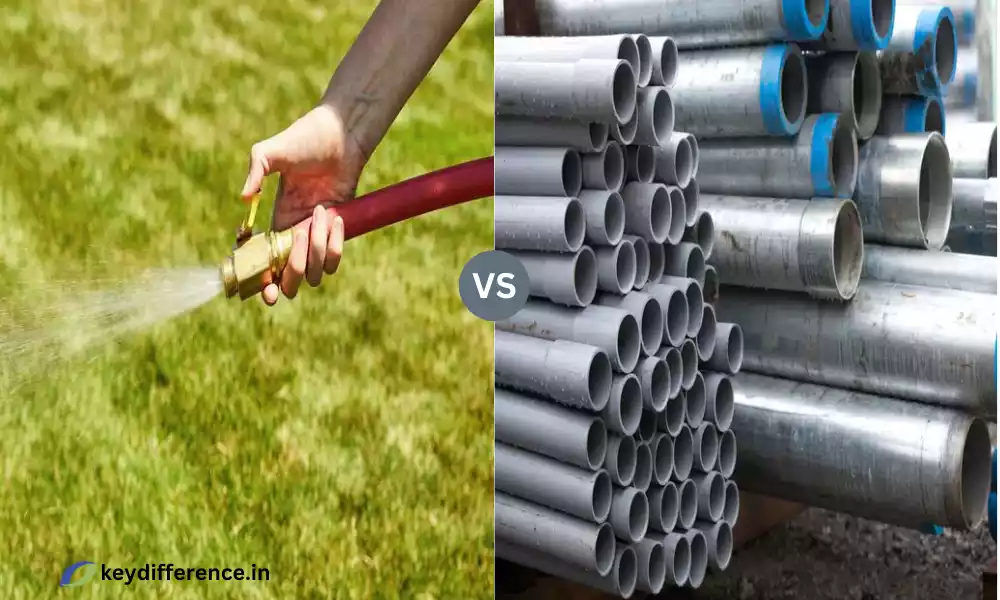
Hose and Pipe are crucial elements of various industries as well as everyday life. While both are utilized for the purpose of transporting fluids, however, they are distinct in terms of materials construction, application, and functions.
Knowing the distinctions between them is vital for making educated choices across a variety of settings, from agriculture or heavy industries. We will explore the major differences between pipes and hoses and shed light on their specific characteristics and functions.
Definition of Hose
A hose is a flexible tubular conduit that is typically composed of substances like rubber or PVC (polyvinyl chloride) polyurethane, and other synthetic substances. It is made to carry gases, fluids, and even liquids, from one area to another in a pressure.
Hoses are typically constructed with materials such as wire or textile fibers to increase their durability and resist pressure, which makes them ideal for a variety of purposes, such as gardening and automobile systems, firefighting, and a variety of industrial processes.
Hoses are admired because of their flexibility and capacity to adapt to various forms and angles, making them indispensable tools for fluid distribution and transfer.

Definition of Pipe
Pipes are rigid cylindrical conduits made of metal (e.g. copper, steel) and plastic (e.g. PVC,) or other tough materials. Pipes are made to transport gases, fluids, or solids from one location to another in a controlled and pressure-controlled way.
They are available in standard lengths and sizes, which are measured by parameters such as those of the Nominal Pipe Size (NPS) in inches. Pipes are widely used in construction, plumbing, and industrial applications, offering strength and structural support.
Like hoses, they don’t have inherent flexibility and can maintain their form and shape, which is why they are ideal for installations with high pressure and fixed construction in which a strong conduit is needed.

Importance of Understanding the Difference Between Hose and Pipe
Understanding the distinction between pipes and hoses is essential in a variety of situations in order to improve the safety, efficiency, and efficacy of the fluid transportation system.
Here are some of the main reasons to emphasize the importance of this knowledge:
- Proper Application: Selecting the correct conduits for a particular task is vital. Pipes and hoses are created for various uses, with hoses flexible and suited to mobility while pipes are rigid and perfect for fixed installation. Making the wrong choice can cause inefficiencies or system failure.
- Safety: In applications involving hazardous substances or high-pressure fluids, the use of the wrong conduit could cause bursts, leaks, or even injuries. Knowing the difference will ensure that the conduit is able to handle the pressure and materials in a safe manner.
- Performance: Hoses have limitations in the area of flow and pressure handling in comparison to pipes. Selecting the appropriate conduit will improve the efficiency of fluid transport systems, which can reduce energy use and operating costs.
- Durability: Hoses are more susceptible to kinking, wear, and being damaged as time passes by as compared to pipes. Knowing which option to choose can prolong the life of the entire system while reducing the requirement for regular replacements.
- Cost Management Selecting the right conduit first in accordance with the particular needs of the application will save money in the long term. It is possible that hoses are cheaper in the beginning but the maintenance and replacement costs could be costly over the course of time.
- Environmental impact: Knowing the ecological impacts of utilizing hoses as opposed to pipes is crucial to sustainable design and implementation. Some hoses can be a source of plastic waste while pipes can be recycled and have less environmental impact.
- Regulation Compliance: Different industries and areas often have distinct rules and standards that govern the pipes and hoses used in various ways. Understanding the distinctions between these is vital to make sure that you are in that you are in compliance, and also avoid legal problems.
- Optimizing performance: For industrial applications the choice of pipes and hoses could significantly influence the efficiency of the devices and system. The right choice can result in higher productivity and better-quality products.
- Maintenance and repairs Knowing if the system uses pipes or hoses can simplify repair and maintenance procedures. This ensures that the appropriate replacement parts are utilized to reduce downtime and prevent any further harm.
Knowing the distinction between hoses and pipes is vital to making educated decisions in a variety of fields and applications. It can ensure safety, efficiency, longevity, and efficiency while also reducing environmental impacts and issues with compliance.
Comparison Table of Hose and Pipe
Here’s a comparison table highlighting the key differences between hoses and pipes:
| Aspect | Hose | Pipe |
|---|---|---|
| Composition & Material | Flexible materials (e.g., rubber, PVC, polyurethane) with reinforcements (e.g., textile, wire) | Rigid materials (e.g., metal, plastic, copper) |
| Shape & Structure | Tubular and flexible | Cylindrical and rigid |
| Function & Applications | Flexible fluid conduit for various applications (e.g., gardening, automotive, firefighting) | Rigid conduit for plumbing, construction, and industrial purposes |
| Pressure Handling | Suitable for low to moderate-pressure applications, with reinforcement for increased pressure resistance | Designed for high-pressure applications |
| Size & Diameter | Various sizes and diameters, typically measured in inches or millimeters | Standardized sizes (NPS) measured in inches |
| Connection Methods | Connected using hose clamps, barbed fittings, quick-connect couplings | Joined using threaded connections, welding, soldering, flanges |
| Durability & Lifespan | Susceptible to wear, kinking, and damage; lifespan varies based on material and usage | Long-lasting and durable; can last for decades with proper maintenance |
| Cost Considerations | Generally more affordable upfront, but may have higher long-term replacement and maintenance costs | Higher initial investment but lower long-term maintenance costs |
| Environmental Impact | May contribute to plastic waste; environmental concerns related to materials used | Potential for recycling and reuse; environmental impact varies by material |
This comparison table summarizes the primary distinctions between hoses and pipes, emphasizing their differences in composition, structure, function, and various practical considerations. Understanding these differences is essential for selecting the appropriate conduit for specific applications.
Material choice is influenced by factors like pressure and chemical compatibility
The choice of materials for both pipes and hoses is heavily affected by variables such as pressure as well as chemical compatibility. Let’s go over this vital aspect:
- Pressure Handling:
- Hoses: are usually selected based on the demands of the pressure. The various hose materials and types provide different degrees of resistance to pressure. For applications that require high pressure, hoses reinforced with strong materials such as steel wire braiding and spiral reinforcement are utilized.
- Pipes: Materials and wall thickness are determined to be able to withstand certain pressure levels. Pipes made for high-pressure systems have stronger walls and are typically made of steel or high-strength aluminum alloys.
- Chemical Compatibility:
- Hoses: The choice of the hose’s material is crucial when transporting fluids that could be reactive or corrosive. Different materials provide different degrees of resistance to chemicals. For instance, hoses constructed of fluoropolymer compounds such as PTFE (Teflon) can be renowned for their outstanding chemical resistance.
- Pipes: Materials for pipes should also be selected with care in order to make sure they are compatible with the fluids that are being carried. Certain chemicals may corrode or react with certain pipe materials. For example, copper pipes are vulnerable to corrosion when exposed to acidic or alkaline chemicals.
- Temperature Resistance:
- Hoses: Hoses should be chosen according to their capacity to withstand the extreme temperatures that are encountered in the process. Certain hoses are specifically designed for extreme temperatures, whereas others can become brittle or weaken at low temperatures.
- Pipes: Materials for pipes should be picked taking into account the temperature specifications. For instance, plastic pipes such as PVC have limits on temperature, and for applications that require high temperatures metals like stainless steel are a good choice.
- Flexibility and Handling:
- Hoses: The flexibility of hoses is advantageous in situations that require movement or bending. However, the flexibility of hoses can be compromised if high pressure is present.
- Pipes: They are rigid and are not appropriate for use in situations where flexibility is required. In these cases, flexible hoses and expansion joints could be included in the pipeline system.
- Environmental Conditions:
- Hoses: Environmental factors such as exposure to UV and resistance to weather could affect the hose’s material selection. For instance, garden hoses have to be durable enough for the elements of outdoor.
- Pipes: Pipes that are employed outdoors or in harsh environments might need protective coatings, or other materials which resist corrosion and UV damage.
Both pipes and hoses should be chosen with care according to their characteristics to ensure that they are able to stand up to the pressure, temperature, and chemical compatibility demands of the particular application. If these elements are not taken into consideration, it could cause leaks, system malfunctions, and safety risks.
Designed to transport fluids under pressure
both hoses and pipes are made to carry liquids at a certain pressure. The pressure may vary depending on the application and the selection of pipe or hose material, along with its structural integrity plays a vital role in the safety and efficiency of fluid transportation.
Here are some important aspects concerning the transportation of sub-pressured fluids:
- Hoses under Pressure:
- Hoses are typically used in areas where mobility and flexibility are crucial, for instance in pneumatic systems and firefighting equipment.
- To deal with different pressure levels, hoses are made with different levels of reinforcement. High-pressure hoses usually have several layers of reinforcement, such as steel wire braiding, or spiral reinforcement.
- A well-chosen hose is vital to avoid bursts or leaks when under pressure. This involves taking into consideration factors such as the nature of the fluid, temperature, as well as the pressure that the hose will be exposed to.
- Pipes under Pressure:
- Pipes are commonly utilized in areas in which a rigid conduit is required or when more pressure levels have to be maintained, for instance in industrial processes, plumbing, and distribution of gas.
- The selection of the pipe’s construction, material, and diameter is crucial to ensure that the pipe is able to be able to withstand the pressure it is intended for without breaking or leaks.
- Pipes that are designed for high-pressure use can include features such as threaded connections, seams welded, or flanges to ensure their integrity.
- Pressure Regulation:
- In numerous fluid transportation systems Pressure regulation is a must to regulate how fluid flows and ensure secure operating conditions.
- Regulators, pressure relief valves along with other mechanisms for control are usually installed in both pipes and hose systems to avoid over-pressurization that could result in injury or even accidents.
- Safety Considerations:
- When using hoses or pipes the safety factor is crucial when working with fluids that are pressurized. Correct installation, maintenance, and inspection are essential to avoid leaks, accidents, or system failures.
- Regularly checking pipes and hoses for wear, damage, or signs of deterioration is essential to spot potential problems prior to them causing massive failures.
Pipes and hoses are both essential components used to transport fluids under pressure in a variety of applications. The design, selection of materials, and upkeep of the conduits are vital to ensure the safe and efficient operation of the fluid transport systems.
Common applications include gardening, firefighting, and automotive
Hoses have common uses in a variety of areas which include firefighting, gardening, and even the automotive industries.
Here’s a brief description of how hoses can be used for each one of the fields:
- Gardening:
- Garden Hoses: They are made to be used outdoors in commercial or residential gardens. They are usually made from materials such as rubber PVC and reinforced polyurethane. Garden hoses are flexible, and are available in different lengths and sizes.
- Applications: Garden hoses can be used to water lawns, plants, and gardens, and also for cleaning vehicles and outdoor surfaces. They typically have adjustable spray heads or nozzles for various water patterns.
- Firefighting:
- The Fire Hoses: They are crucial components of equipment for fighting fires. They are made to withstand pressures of high and provide large amounts of water in order to battle fires.
- Applications: fire hoses are utilized by firefighters to supply foam or water to put out fires. They come in a variety of sizes and are able to be attached to fire trucks, fire hydrants, or portable pumps.
- Automotive:
- Automotive Hoses: in the automobile sector, the hoses perform a crucial role in a variety of components of vehicles.
- Applications :
- Coolant Hoses: They circulate coolant to regulate the temperature of the engine.
- The Fuel Hoses: The fuel hoses carry diesel or gasoline through the tanks to get it into the engines.
- Brake Hoses: Brake lines and hoses transport brake fluids to the brake system.
- Vacuum Hoses: Vacuum hoses to power various accessories such as cruise control, power brakes, and many more.
- Air Intake Hoses: These hoses bring an air stream into the engine to aid in combustion.
These typical applications show the flexibility of hoses when it comes to aiding in the transfer of fluids, be it for chores at home, emergency response in the fight against fire, or vital roles in vehicles. Hoses for these purposes differ in terms of materials size, shape, and design to meet their particular needs and needs.
Lifespan varies based on material and usage
The life span of hoses differs greatly based on the material they are constructed from and the method of use.
This article will provide a more detailed review of how the material used and use impacts the longevity of hoses:
- Material:
- Rubber Hoses Hoses made of rubber are strong and employed in a variety of applications. Their lifespan varies based on the type of rubber as well as whether they’re reinforced. The best rubber hoses will last for a long time particularly if they’re not subjected the extreme heat or harmful chemicals.
- PVC Hoses: PVC hoses are relatively lightweight and cost-effective, however, they could be less durable when compared with rubber hoses or reinforced ones. They can be more vulnerable to cracking and becoming brittle as time passes, particularly during colder weather.
- Polyester Hoses: The hoses made of polyurethane are noted for their ability to bend and resist scratches. They typically have a longer life span than PVC hoses and are commonly employed in applications that require a lot of force.
- Reinforced hoses: The hoses that are reinforced with reinforcement layers, for example, wire, textile, or steel braids tend to last longer because they are able to withstand greater tensions, and also resist damage more effectively.
- Usage:
- Frequency of Utilization: Hoses that are regularly used and for long periods of time are more prone to use and tear. Regular usage can result in wear and tear, kinking, and eventually, a shorter life span.
- Temperature and Pressure: Hoses used under extreme temperatures or high-pressure conditions can experience wear that is more rapid. It is essential to select hoses that are designed to meet the temperature and pressure requirements of the specific application.
- Chemical Exposition: Hoses that carry reactive or corrosive fluids can become degraded more quickly in the event that they are not constructed with materials specifically designed to withstand this chemical. A proper selection of materials is vital in these instances.
- Maintenance Regular cleaning, inspections, and the proper storage of hoses will prolong their life. The hoses that are neglected tend to degrade quickly.
- Environmental Factors:
- Exposure to Sunlight: Hoses that are left open to sunlight direct (UV radiations) for prolonged periods of time can become degraded quickly. UV-resistant hoses can be found to help with this problem.
- Freezing temperatures: Hoses that are left outside in frigid temperatures are more susceptible to cracking. It is essential to flush hoses and store them in a safe manner in cold temperatures.
- Physical Injury: Hoses may be damaged by physical impacts or sharp objects, as well as vehicles that roll on them. The prevention of such events can increase their life span.
The life span of hoses is determined by a variety of factors that include the materials they are constructed from as well as the environment in the environment they are utilized, and the amount of maintenance they are subjected to.
Selecting the appropriate hose material for your use and using it in conformity with the guidelines it has been given can extend the life of your hose.
Replacement and maintenance costs may add up
Maintenance and replacement expenses can be significant for hoses that require replacement and hoses, particularly in commercial or industrial settings.
The way these costs can be accumulated:
- Frequent Replacement:
- Hoses that are exposed to heavy usage or harsh conditions can be worn out fairly quickly. This requires frequent replacement to ensure the system’s functionality.
- Repetition of purchasing new hoses may cause significant replacement costs over the course of time.
- Material Quality:
- Hoses of lower quality may have a shorter life span and will require frequent replacement.
- Selecting hoses of high quality upfront can cut down on the requirement for regular replacements, and also reduce long-term costs.
- Maintenance:
- Regular maintenance is crucial to prolong the life of hoses and to prevent premature failure.
- Maintenance tasks can consist of cleaning, inspections replacement of worn-out connectors or fittings.
- The hiring of employees or committing resources for maintenance of hoses can increase operating expenses.
- Downtime:
- If hoses fail suddenly this can cause interruptions in commercial or industrial operations. In the event of downtime, it can lead to loss of production and income.
- The cost of replacing hoses expeditiously during unexpected downtimes could be more expensive.
- Safety Concerns:
- The failure of a hose could cause dangers to safety and could cause injuries, accidents, or damage to equipment and personal property.
- Securing the safety of employees and property is often a matter of the proper maintenance of hoses as well as inspections and replacements when required.
- Environmental Impact:
- Wasted hoses cause pollution and waste. Recycling or proper disposal of hoses that are old may result in cost-plus charges.
- The use of environmentally responsible disposal methods could be legally required in certain areas, which can increase the overall cost.
- Training and Education:
- ensuring that workers are properly competent to handle hoses properly and safely could require expenses for training.
- Education and training can reduce the risk of accidents involving hoses and increase their life span.
- Spare Parts Inventory:
- The maintenance of a spare parts inventory that includes replacement hoses and fittings, takes the investment of capital as well as storage space.
- Management of inventory and related costs can rise over time.
To reduce the cost of replacement and maintenance Organizations often devise proactive maintenance programs make investments in hoses of high quality and give priority to the proper training of employees.
Regular inspections and preventive maintenance will assist in identifying issues prior to them causing costly failures. Furthermore, choosing the appropriate hose for the job and observing recommended operating conditions will extend the life of the hoses, thereby reducing the cost of replacement and maintenance.
Environmental concerns related to materials used
Concerns about the environment related to materials that are used in hoses and pipes are important considerations, particularly when it comes to sustainability and environmental impact. Here are some of the major environmental concerns that are associated with these substances:
- The impact of plastics: The majority of pipes and hoses, specifically made of PVC (polyvinyl chloride) and other plastic materials are a source of pollution caused by plastic when they are not properly removed. The hoses and pipes that are dumped could end up in landfills or even the environment of water in which they can be left for decades, without disintegrating.
- Chemical leaching: Certain materials that are used in pipes and hoses may release dangerous chemicals into the surroundings. For instance, certain plastic hoses can release phthalates and other harmful chemicals when exposed to sunlight or heat and could contaminate soil and water resources.
- Energy-Intensive Production: Processes used to manufacture specific materials, including metals such as copper or steel may be high in energy and leave carbon footprints. A high consumption of energy contributes the greenhouse emissions as well as climate change.
- Resources Depletion: Metals (e.g. aluminum, copper) employed in pipes are limited resources. In excess, the use of such resources may reduce the value of minerals and cause disruption to the habitat in mining zones.
- Habitat Use and the Impact on Habitat: The manufacturing and extraction of the materials used in pipes and hoses may result in changes to land use that affect natural habitats. This may include deforestation in order to facilitate rubber production as well as habitat destruction close to mining sites.
- Recycling: The removal of pipes and hoses when they reach the conclusion of their lifespan could be a problem. Materials that aren’t easily recycled could end in landfills or incinerators and contribute to pollution and challenges in managing waste.
To address the environmental issues There are a variety of strategies that can be employed:
- Choice of Material: Select materials for pipes and hoses that are less harmful to the environment. impact. You should consider using biodegradable or recycled materials when they are suitable.
- Recycling and reuse: encourage the reuse and recycling of pipes and hoses after they reach the conclusion of their life. Recycling programs and sustainable disposal options must be considered.
- Green Manufacturing: Choose products and manufacturing methods that leave a lesser footprint on the environment, like using recycled materials or more efficient production methods that use less energy.
- Regulatory Compliance: Follow environmental regulations and standards that regulate the use, production, and disposal of pipes and hoses. This could include implementing appropriate waste management practices as well as emission control.
- Information and awareness: to raise awareness among businesses, consumers, and industry about the environmental impacts of pipes and hoses. Promote responsible use, disposal, and recycling.
The balance between the practical requirements of pipes and hoses while minimizing the environmental impacts they have is an essential element of sustainable design and sustainable resource management. An effort to minimize the environmental impact of the conduits will aid in an environmentally sustainable and green approach to various sectors.
Similarities Between Hose and Pipe
Pipes and hoses, despite their distinct features, have some similarities, specifically in their function as conduits to facilitate the flow of fluids.
Here are some commonalities among pipes and hoses:
- Fluid Conduction: Both hoses as well as pipes are made to move fluids, be they gas, liquids, or solids from one place to another. They function as conduits for various substances across various applications.
- Pressure handling: Hoses and pipes are both designed to withstand pressure and allow for control of the flow of liquids when under pressure. The amount of pressure they are able to handle is contingent on their design, materials, and construction.
- Flexibility in Application: Although hoses and pipes are both best suited for specific uses, however, both are able to be used for a variety of applications. Hoses, due to their flexibility are ideal for situations in which flexibility or mobility is needed, while pipes are typically used in fixed or stationary installations.
- Dimension and Diameter Variability: Both hoses as well as pipes are available in a variety of sizes and diameters to suit various flow rates and needs. This flexibility in size allows for customizing to the specific requirements.
- Connection methods: Both conduits require fittings and connectors to connect sections, adjust to various components, and make leak-proof connections. Common methods of connection include threaded connections, clamps couplings, and Flanges.
- Materials Options: Pipes and hoses are made of various materials to meet your specific requirements. Materials vary from rubber metal, and plastic to special materials such as polyurethane (or PTFE) (Teflon).
- Maintenance requirements: Hoses as well as pipes need regular maintenance in order to ensure their performance and prolong their life. Maintenance could consist of cleaning, inspections, and repairing damaged sections or connectors.
- Environmental considerations: Both conduits be a source of environmental harm as well and sustainable alternatives are readily available for both. For instance, environmentally friendly materials and recycling methods can be used on pipes and hoses in order to decrease their impact on the environment.
- Legal Compliance: Both pipes and hoses could be subject to specific industry norms and regulations, like those that deal with security, safety ratings for pressure as well and material compatibility. Conformity with these standards is vital to ensure safe and efficient transport of fluids.
- Cost factors: Cost factors apply to the pipes and hoses. While initial costs could differ based on the material and specifications, the longer-term cost associated with maintenance or replacement and operational efficiency must be considered in the process of selecting.
Even though the hoses and pipes vary in regards to their flexibility, materials, and use They share a number of similar characteristics that are related to their use as conduits for the transportation of fluids.
Understanding the commonalities and the distinct differences between them is crucial to making informed decisions in a variety of sectors and in various applications.
Reference Books
Certainly, here are some reference books on various topics that you might find valuable. These books cover a wide range of subjects, so feel free to explore the ones that align with your interests and needs:
- Science and Technology:
- “The Innovators” by Walter Isaacson
- “A Brief History of Time” by Stephen Hawking
- “Sapiens: A Brief History of Humankind” by Yuval Noah Harari
- “The Code Book: The Science of Secrecy from Ancient Egypt to Quantum Cryptography” by Simon Singh
- Literature and Fiction:
- “To Kill a Mockingbird” by Harper Lee
- “1984” by George Orwell
- “The Great Gatsby” by F. Scott Fitzgerald
- “The Catcher in the Rye” by J.D. Salinger
- History and Politics:
- “Guns, Germs, and Steel: The Fates of Human Societies” by Jared Diamond
- “A People’s History of the United States” by Howard Zinn
- “The Art of War” by Sun Tzu
- “The Federalist Papers” by Alexander Hamilton, James Madison, and John Jay
- Business and Economics:
- “Thinking, Fast and Slow” by Daniel Kahneman
- “The Lean Startup” by Eric Ries
- “Freakonomics: A Rogue Economist Explores the Hidden Side of Everything” by Steven D. Levitt and Stephen J. Dubner
- “Good to Great” by Jim Collins
Conclusion
Reference books are a valuable resource that provides in-depth information and information on a wide spectrum of subjects. You may be looking for information on literature, science, history, or personal development There are reference books that will fill your needs and aid your education.
A well-chosen choice of reference books could provide you with a continuous source of inspiration, information and personal growth.