Introduction
Understanding the concepts of True Meridian and Magnetic Meridian are essential in navigation, surveying, and geographical studies. Both meridians serve a crucial function in establishing directions, setting coordinates, and interpreting spatial data.While True Meridian represents Earth’s rotational axis and remains constant over time, Magnetic Meridian changes depending on Earth’s magnetic field resulting in changes both in direction and intensity.
We will explore the differences between True Meridian and Magnetic Meridian as well as their definitions, concepts and methods of calculation. Additionally, we will discuss their practical applications, their challenges as well as why knowing them accurately helps with navigation and surveying operations.
By exploring True Meridian and Magnetic Meridian, we can gain a better understanding of Earth’s orientation, improve navigation accuracy and achieve more precise spatial measurements and calculations. Let’s discover this intriguing world of meridians as they play such an integral role in geography, cartography and more.
True Meridian and Magnetic Meridian
Here’s a comparison table of True Meridian and Magnetic Meridian:
| Criteria | True Meridian | Magnetic Meridian |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | An imaginary line passing through the geographic North Pole and South Pole | An imaginary line passing through the magnetic North Pole and South Pole |
| Determination | Determined using the direction of the earth’s rotational axis relative to the stars | Determined using a compass, which indicates the direction of the earth’s magnetic field |
| Stability | A fixed reference point that does not change with time or location not | Not a fixed reference point and changes with time and location due to the earth’s magnetic field variations |
| Use in Navigation and Surveying | Used as a reference point for determining the direction of a vessel’s course and survey line | Used as a reference point for determining the direction of a vessel’s course and survey line |
| Accuracy | Accurate but does not take into account the earth’s magnetic field | Can be affected by local magnetic anomalies, leading to inaccuracies |
| Magnetic Declination | Used as a reference point for determining the magnetic declination | Represents the angle between True North and Magnetic North |
| Advantages | Reliable and stable reference point | Takes into account the earth’s magnetic field |
| Disadvantages | Does not take into account the earth’s magnetic field | Not a stable reference point and can be affected by local magnetic anomalies |
Both True Meridian and Magnetic Meridian are important reference points for navigation and surveying activities.
The True Meridian is a reliable and stable reference point, while the Magnetic Meridian takes into account the earth’s magnetic field. However, the Magnetic Meridian can be affected by local magnetic anomalies, leading to inaccuracies.
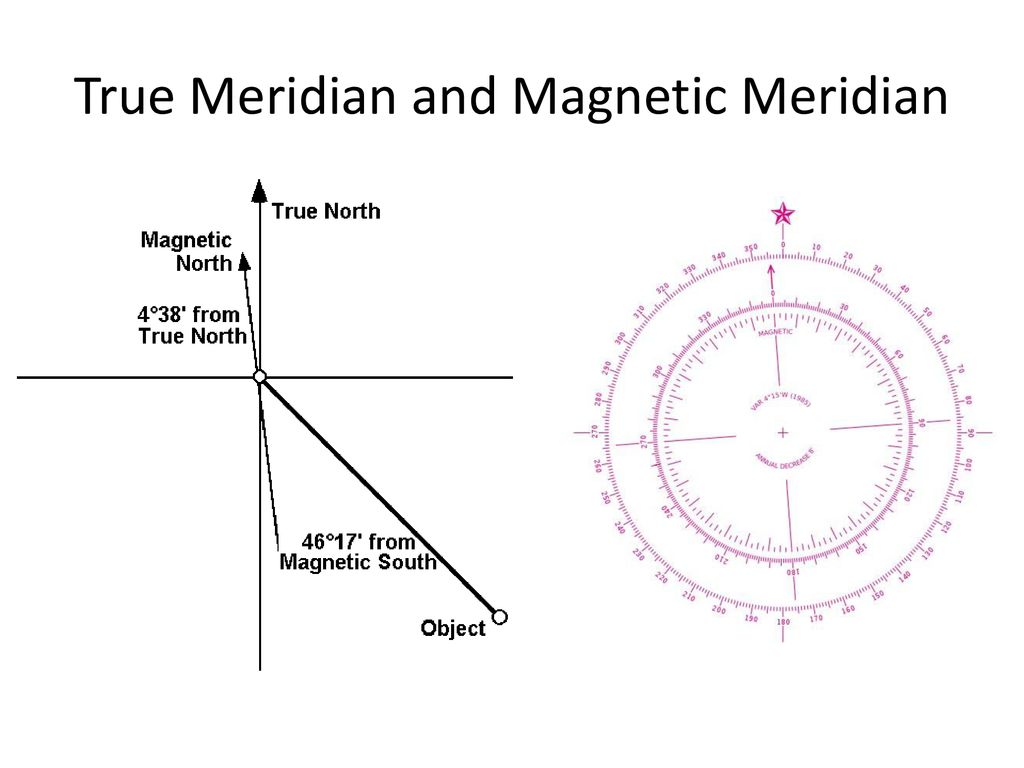
True Meridian
True Meridian is an imaginary line that is visible on Earth’s surface that runs through the geographical North Pole and South Pole. It is also referred to by the name of Geographic Meridian or the Terrestrial Meridian.It is also known as the True Meridian. True Meridian represents the direction of the true north and south, and serves as a point of reference to aid in navigation, surveying and mapping.
The True Meridian is determined by using the direction of earth’s rotational axis with respect towards the stars. It is a reference point fixed that is the same regardless of the place and date of the observation. It is the True Meridian is used as an indication of the magnetic declination. This can be defined as the angle of True North and Magnetic North.
For navigation purposes, True Meridian is used as a reference point in making decisions about what direction the vessel is on in its route. Similar to surveying, True Meridian is used as a reference point in determining the direction of the survey line. The precision of measurements made in surveying depend on the precision in True Meridian. True Meridian used as a reference point.
One of the benefits for True Meridian is that it is a reference point that is fixed that doesn’t change with time or place. This is a safe reference point for surveying and navigation tasks. However, it is important to note that the True Meridian does not take into account the magnetic field. This could be a major influence on the accuracy of surveying and navigation actions.
Magnetic Meridian
Magnetic Meridian can be described as an imaginary line on Earth’s surface that passes across its Magnetic North Pole and South Pole. It is what direction is the earth’s magnetic field at a specific time and location.The Magnetic Meridian can be used to serve as a point of reference for surveys and navigation, especially in areas in which the magnetic field of the earth is very strong.
It is believed that the Magnetic Meridian is determined using the compass, an instrument that shows the direction of Earth’s magnetic field. It is comprised of a needle with a magnet which aligns itself with the magnetic field of earth and orients toward the Magnetic North Pole. This angle of and the Magnetic Meridian with respect to that of the True Meridian is known as the Magnetic Declination.
For navigation purposes, Magnetic Meridian is used as a reference point in to determine what direction the vessel is on in its path. In surveying, too, Magnetic Meridian is used as a reference point when to determine the direction of survey lines. The accuracy of surveying and navigation measurements is dependent on the precision in the Magnetic Meridian that is used as an indicator point.
One of the benefits that comes with Magnetic Meridian lies in the fact that it is able to take into consideration the magnetic field of the earth which could affect the precision of navigation and surveying tasks.But Magnetic Meridian is not a fixed reference point. Magnetic Meridian isn’t a permanent reference point. It shifts with time and place because of the magnetic field of the earth.
The Magnetic Meridian is altered by magnetic anomalies local to the area that are changes in the magnetic field on earth caused by geological characteristics like minerals or rocks. These anomalies could cause the compass needle be off its Magnetic Meridian, which can lead to inaccurate surveying and navigation activities.
Conclusion
True Meridian and Magnetic Meridian are two crucial landmarks used in surveys and navigation. They are used for surveying and navigation. True Meridian represents the direction of the true north and south. It’s an unchanging reference point which does not change in the passing of time or place. The Magnetic Meridian is the direction of magnetic field of the earth at a specific place and time. It is determined by using an Compass.
In contrast to True Meridian is a True Meridian is a reliable and steady reference point however, the Magnetic Meridian considers the earth’s magnetic field, however it is susceptible to the local effects of magnetic anomalies.The accuracy of surveying and navigation measurements depend on the accuracy that the point of reference chosen as well as the two True Meridian and Magnetic Meridian offer advantages and disadvantages in this respect.