Skin problems can be confusing. Furuncle and Folliculitis most frequent ones people are faced with are folliculitis and furuncles. Although they might appear similar at first sight understanding the differences between them is essential for a correct assessment and therapy.
We will look at the differences among furuncles (boils) and folliculitis from their causes to clinical symptoms to the treatment options available that will help you manage these skin conditions efficiently.
Definition of Furuncle
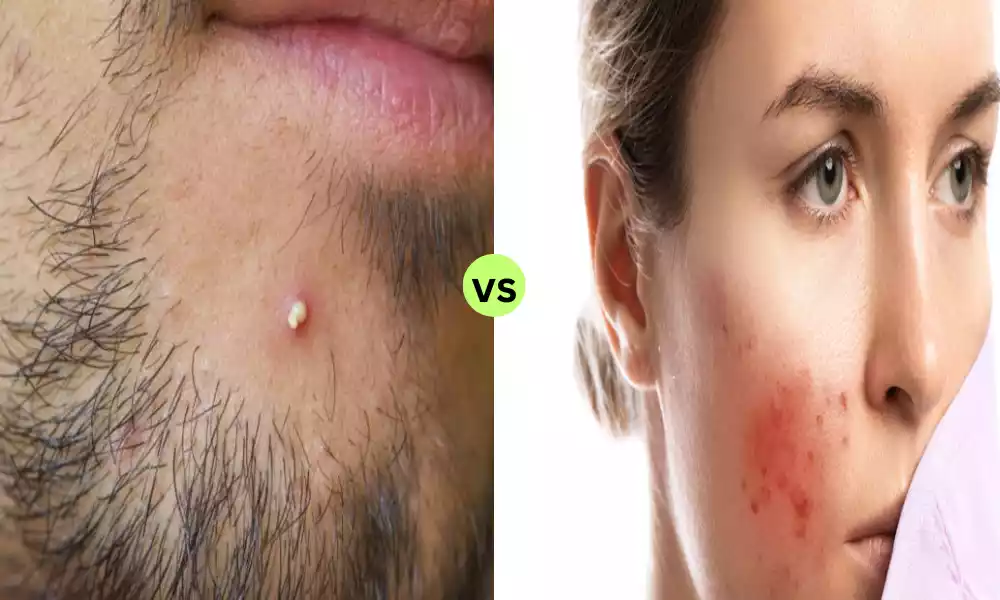
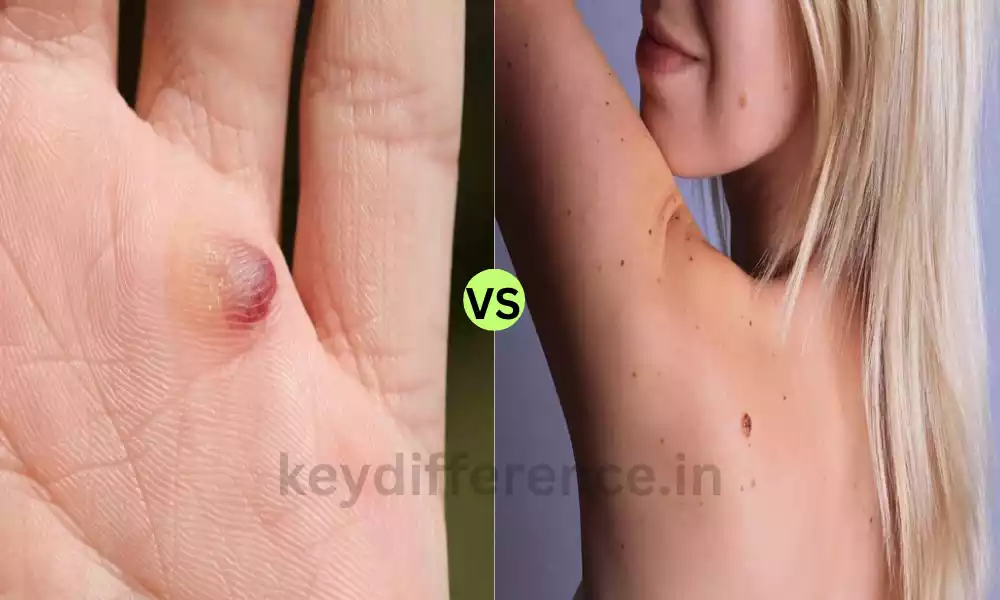
A furuncle, also known as boils is a painful and localized skin ailment that typically appears as a red swelling, tender lump. This is the result of an infection caused by bacteria, usually caused by Staphylococcus aureus, and may lead to the formation of pus-filled central (pustule) as the condition gets worse.
Furuncles can be extremely painful and typically appear on hair follicles, particularly on areas where hair is present, like the neck, face as well as the armpits, buttocks, and face. In extreme cases, furuncles can cause chills and fever and could lead to abscesses under the skin, which require medical intervention including antibiotics or an incision and drainage.
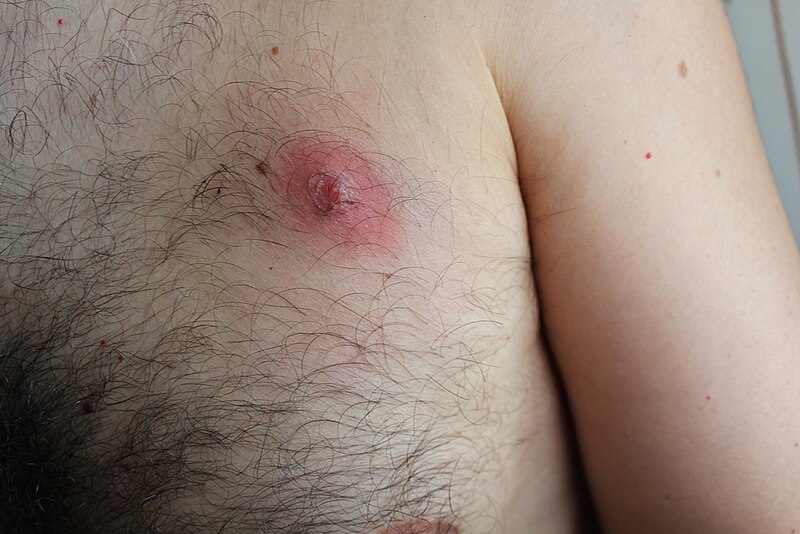
Definition of Folliculitis
Folliculitis is a typical skin condition that manifests as inflammation and infection of the hair follicles. The hair follicles are damaged or infected, which leads to the formation of small pink or red pimple-like bumps that surround the hair follicles that are affected.
Folliculitis can be caused by a variety of causes, including bacterial viral or fungal infections, and also irritation due to activities such as shaving or rubbing caused by tight clothes. Itching or burning sensations, as well as discomfort within the area affected.
Treatment options for folliculitis rely on the underlying cause. It can include oral or topical antibiotics for bacterial infections antifungal treatments to treat fungal diseases, and the avoidance of irritations to prevent repeat incidences.
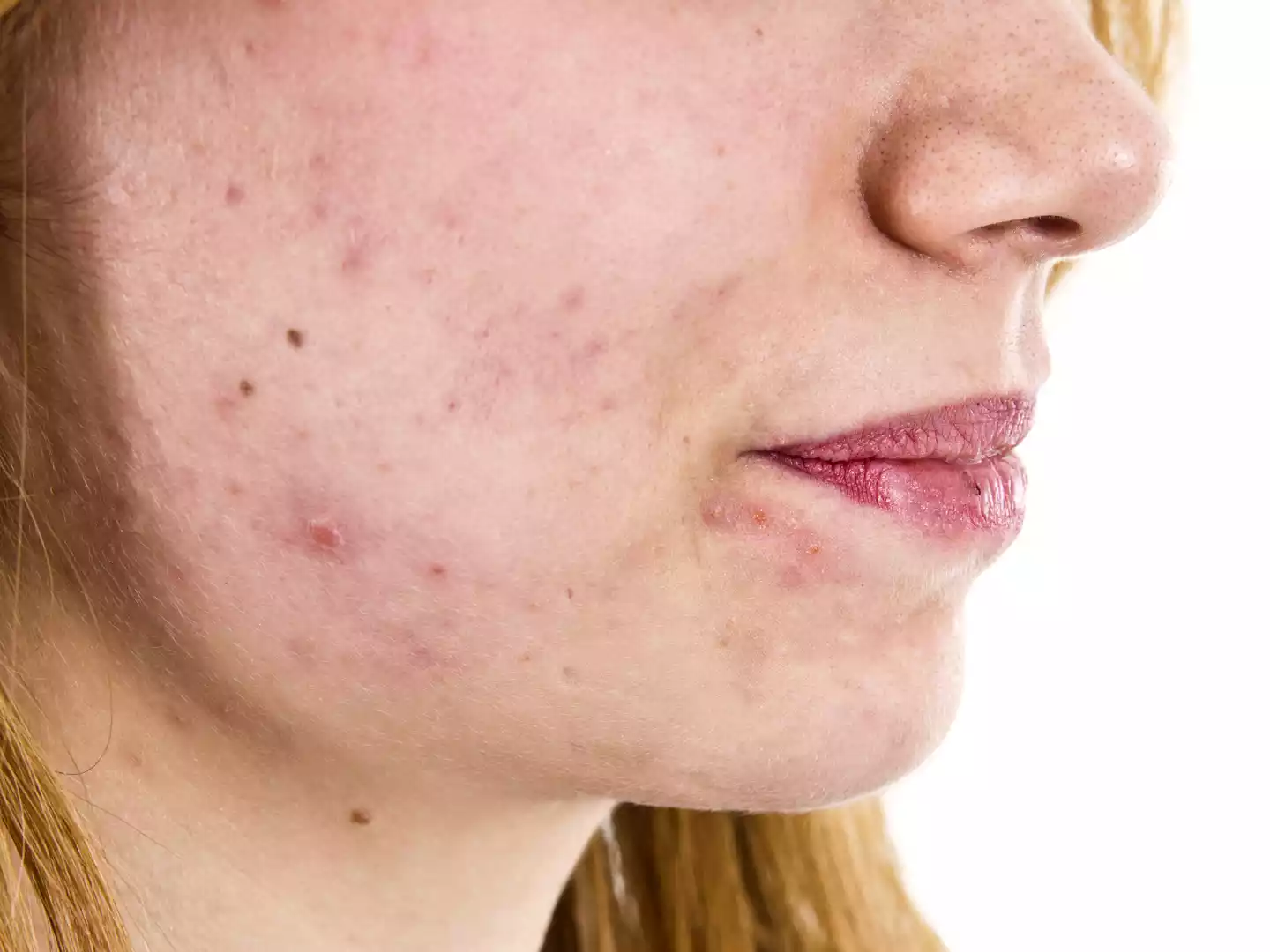
Importance of distinguishing between furuncles and folliculitis
Differentiating from furuncles (boils) and Folliculitis is crucial for a variety of reasons:
- Treatment Options: Furuncles and folliculitis have distinct causes and treatment strategies. The majority of the time, they are caused by bacterial infections and typically require antibiotics, and folliculitis could be the result of many factors, including irritation, infections, or viral or fungal causes. Finding the best treatment for you depends on the accurate identification of the problem.
- Complications and Severity: Furuncles are generally larger, more painful, and also have a greater risk for complications, such as abscess development. The mistake of identifying a folliculitis-related furuncle could cause delays in treatment and cause more serious complications.
- Prevention: Recognizing the primary causes of folliculitis regardless of whether it’s caused by fungal, bacterial, or other causes is vital to prevent repeat incidence. An accurate diagnosis can help in addressing the root of the issue and taking preventive steps.
- Public Health Concerns: In some cases, furuncles can be caused by bacteria that are resistant to antibiotics (MRSA) which could affect public health. An accurate diagnosis can help you detect these infections early and help guide the appropriate treatment to avoid the spread of resistant strains of drugs.
- Patient comfort: Furuncles are generally more painful than folliculitis. An accurate diagnosis can ensure all patients get the proper treatments and pain relief to ease discomfort.
- Avoiding unneeded treatments: Misdiagnosing folliculitis as an untreated furuncle may result in unnecessary antibiotic treatments that can cause resistance to antibiotics and could cause adverse unwanted side effects. A proper diagnosis can prevent the excessive use of antibiotics.
- Skin Health: Furuncles and folliculitis may impact the appearance and condition of the skin. An accurate diagnosis permits the choice of treatments that aid in skin healing and decrease the chance of scarring.
Knowing the difference between furuncles and folliculitis is vital for ensuring appropriate and effective treatment, reducing complications as well and improving the patient’s care and comfort. Additionally, it plays a part in public health, dealing with potential issues of antibiotic resistance related to furuncles that result from resistant bacteria.
Comparison Table of Furuncle and Folliculitis
Here’s a comparison table highlighting the key differences between furuncles (boils) and folliculitis:
| Characteristic | Furuncle (Boil) | Folliculitis |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Painful, localized skin infection with a pus-filled center | Inflammation or infection of hair follicles |
| Causes | Primarily bacterial infection, often Staphylococcus aureus | Can result from bacterial, fungal, or viral infections, or irritation |
| Clinical Presentation | Red, tender, swollen lump; may develop a pus-filled center (pustule) | Small red or pink pimple-like bumps around hair follicles; may have pus-filled tops |
| Pain | Typically more painful | Often less painful, may involve itching or burning |
| Location | Deeper within the skin | Around hair follicles on the skin’s surface |
| Symptoms | Fever and chills (in severe cases) | Symptoms usually localized to the affected area |
| Severity and Complications | This may lead to abscess formation; which can be more severe | Typically milder, with fewer complications |
| Common Locations | Face, neck, armpits, buttocks | Common in areas with hair (face, scalp, legs, groin) |
| Treatment | Antibiotics, incision, and drainage (in severe cases), warm compresses | Treatment depends on the cause, including antibiotics (if bacterial), antifungals (if fungal), and avoidance of irritants |
| Recurrence Risk | Lower recurrence risk if treated adequately | Recurrence is possible if the underlying cause is not addressed |
| Complications | Potential for scarring, especially if not treated properly | Mainly localized skin issues; fewer systemic complications |
Please note that accurate diagnosis and treatment should be determined by a healthcare professional, as other skin conditions may mimic these symptoms.
Can be caused by various factors, including infections and irritation
I’m able to provide an explanation that is more thorough. Folliculitis is caused by many reasons, such as infections or irritation.
This is a more detailed explanation:
- Bacterial Infections: The most frequent causes of folliculitis can be a bacteria-related infection, usually caused due to Staphylococcus aureus. Bacteria can invade and cause hair follicle infections, which can lead to inflammation and the development of pimple-like bumps in the affected hair follicles. The condition is known as bacterial folliculitis.
- Fungal Infections: Fungal infections, such as yeast or dermatophytes, may also affect hair follicles, which can cause a form of folliculitis called fungal hair folliculitis. This may occur in regions of the body that are prone to fungi like the groin area or on the scalp.
- Viral Infections: Herpes simplex virus may cause an illness known as viral folliculitis. The condition is characterized by itchy, small bumps and sores that surround hair follicles.
- Itching: Folliculitis can result from mechanical irritation or injury to the hair follicles. It could be due to actions like shaving, waxing or tightening clothing, or excessive friction. This can lead to an illness known as mechanical folliculitis. Chemical irritants in oil-based products or skincare products can cause irritation and folliculitis.
- Ingrown hairs: When hairs grow back to the skin instead of outward, they may get trapped, causing inflammation and an infection in the hair follicle. This is referred to as pseudofolliculitis, also known as ingrown hair folliculitis.
- HOT Tubs or Pools: Folliculitis may also be caused by exposure to water that is contaminated in hot tubs and pools often called “hot tub folliculitis” or “pseudomonas folliculitis.”
- Imperfection Compromises: Patients with weaker immune systems could be more prone to folliculitis because their bodies might have trouble fighting off infections, which includes those that cause hair follicles to be affected.
Folliculitis could be caused by a variety of factors, such as fungal, bacterial, and viral infections, along with physical irritations, chemicals ingrown hairs, as well as immune system-related factors. The identification of the root of the folliculitis problem is vital to determine the best treatment and preventive actions.
How to care for a furuncle or folliculitis at home
Treatment at home for folliculitis or furuncle (boil) or folliculitis could assist in relieving symptoms, aid in healing, and help prevent complications. It’s crucial to remember that severe or persistent cases could require medical care.
Below are some guidelines to care for these ailments at home:
For Furuncles (Boils):
- Maintain it Clean: Cleanse the affected area using moderate soap and hot water. Avoid aggressive cleaning or scrubbing because it may cause irritation.
- Warm Compress: Place a fresh moist, warm cloth or compress on the furuncle for around 20 minutes, a few times throughout the day. It can ease pain and help encourage the boil to develop into the point of the head (develop a pus-filled central area).
- Pain Management: Pain relievers that are available over-the-counter, such as Acetaminophen and ibuprofen are able to help alleviate pain and discomfort. Be sure to follow the dosage guidelines printed on the bottle.
- Avoid squeezes: Do not attempt to squeeze or pop the furuncle since this could cause more infection and scarring.
- Protect it: You may cover the furuncle with sterilized gauze, non-stick bandage, or gauze to stop it from draining onto your clothes and also to keep it from getting any more.
- Hand Hygiene: Use good hand hygiene to avoid spreading germs. Make sure you wash your hands well prior to and after cleaning the furuncle.
- Antibacterial Ointment: Applying an ointment that is available over the counter (like Neosporin) after cleansing may aid in preventing secondary infections.
For Folliculitis:
- Keep it clean: Clean the affected area with gentle soap, warm water, and mild detergent. Dry it using a clean, dry towel, taking care not to rub.
- Avoid irritations: Identify and avoid any irritants which could trigger folliculitis like harsh products for skin care and tight clothing. Also, avoid things like waxing or shaving.
- Warm Compress: Like furuncles, You can apply a moist, warm compress for 15 to 20 minutes at a time throughout the day to ease the discomfort and inflammation.
- Topical antibiotics: When the condition is considered to be bacterial in origin, an over-the-counter topical anti-bacterial cream or ointment can prove beneficial. Apply it according to the directions.
- Avoid shaving: If shaving is an important factor, think about having a rest from shaving until your folliculitis is healed.
- loose clothing: Wear loose-fitting clothing to minimize friction and irritation to the area affected.
- Avoid scratching: Refrain from scratching the area affected to avoid any further irritation or infection.
- Hand Hygiene: Similar to furuncles ensure that you wash your hands regularly to avoid the spread of germs.
If your folliculitis gets worse, does not improve in several days, or you experience a fever, seek medical attention. Your doctor might prescribe antibiotics or suggest alternative therapies, such as the incision and drainage of an enlarged furuncle or specific antifungal medicines for fungal Folliculitis.
Be aware that home-based self-care is intended for minor conditions, and an evaluation by a professional medical professional is necessary for more serious or chronic ailments.
When to seek medical attention for a furuncle or folliculitis
The need to seek medical attention for folliculitis (boil) (also known as folliculitis) can be crucial in the following situations:
For Furuncles (Boils):
- Size and Severity: When the furuncle is very large (larger than half an inch in size) Particularly when it’s located on your spine or face or is extremely painful or is becoming worse.
- high fever: In the event that you have an increase in fever and the appearance of a furuncle, it could be a sign of an infection that is more serious.
- Multiple Furuncles: If you’ve got multiple furuncles that appear simultaneously this could indicate an undiagnosed health issue that needs medical attention.
- Persistent Symptoms: If the condition does not get better within one week of taking care at home or persists for more than 2 weeks.
- Recurrent Furuncles: If you’ve got a history of frequent boils or furuncles it could be a reason to investigate the root cause or conditions that cause you to be more prone.
- The Pus as well as the Drainage: When the furuncle does not naturally rise and drain, trying the squeeze yourself could result in complications. In these instances, it is recommended to seek out professional help.
For Folliculitis:
- More severe or worsening symptoms: If the folliculitis is rapidly spreading and causing extreme pain or is associated with fever.
- Massive Areas Affected: A large portion that is affected with folliculitis particularly if it appears in pimple-like bumps.
- No improvement: If the folliculitis does not improve after just a few days of at-home treatment, or worsens in spite of treatment.
- Viral or Fungal Folliculitis: The possibility of viral or fungal folliculitis should be examined by a medical professional to determine the appropriate assessment and diagnosis.
- Immunocompromised: If you’ve got an impaired immune system due to an illness or other medication, it’s best that you seek out medical assistance as soon as you notice symptoms since you could be more prone to complications.
- Chronic or Recurrent Folliculitis: If you’re experiencing regular or frequent instances of folliculitis, it’s important to talk with an expert in your healthcare for an extensive examination to determine the underlying cause or the contributing factors.
Keep in mind that even though home-based treatment can be beneficial in mild cases of folliculitis and furuncles Any signs of worsening and unusual symptoms ought to be a reason to seek medical treatment.
A medical professional can diagnose the condition with precision and recommend the appropriate treatment options, which could include antifungal medicines, antibiotics, and other therapies to treat the condition effectively and avoid complications.
Similarities Between Furuncle and Folliculitis
Furuncles (boils) and Folliculitis are both skin disorders that affect hair follicles.
They have many similarities, including:
- The cause of inflammation: Furuncles as well and Folliculitis causes the inflammation of the hair follicles. In both instances, the affected region may be red swollen, and painful.
- Pimple-like Bumps: Both of them cause pimple-like bumps or pustules that surround the hair follicles affected. They can be filled with pus and can be tender or itchy.
- Possibility of Infection: Both conditions are caused or worsened by bacteria-related infections. Staphylococcus aureus is a frequent source of infection in both furuncles and certain types of Folliculitis.
- Common places: Furuncles and folliculitis are both common in the same areas in the body such as the neck, face armpits, scalp, and buttocks. These are areas where hair follicles can be found.
- Warm Compress: Warm and moist compression can be a common treatment option that can be utilized to ease discomfort and aid in the drainage of both folliculitis and furuncles.
- Pain or Discomfort: Both of these conditions can result in discomfort, pain, and itching of the affected region.
- Alternative Treatments: Treatment approaches for furuncles as well as some types of folliculitis can consist of the treatment with oral or topical antibiotics to treat bacterial infections.
Despite these resemblances, it’s important to keep in mind that the root causes as well as the severity and treatment for folliculitis and furuncles are different. Furuncles typically are more painful and deeper, and require an incision and drainage in the most severe cases, whereas folliculitis could result from a variety of conditions, such as irritation, inflammation, or viral or fungal causes. So, the correct diagnosis by a doctor is vital in determining the proper method of treatment for each condition.
Reference Books
Certainly, here are some reference books on various topics:
- Science and Nature:
- “Cosmos” by Carl Sagan
- “A Short History of Nearly Everything” by Bill Bryson
- “The Selfish Gene” by Richard Dawkins
- “The Double Helix: A Personal Account of the Discovery of the Structure of DNA” by James D. Watson
- History:
- “A People’s History of the United States” by Howard Zinn
- “Guns, Germs, and Steel: The Fates of Human Societies” by Jared Diamond
- “The Wright Brothers” by David McCullough
- “Sapiens: A Brief History of Humankind” by Yuval Noah Harari
- Literature:
- “To Kill a Mockingbird” by Harper Lee
- “1984” by George Orwell
- “Pride and Prejudice” by Jane Austen
- “The Catcher in the Rye” by J.D. Salinger
- Philosophy:
- “Meditations” by Marcus Aurelius
- “The Republic” by Plato
- “The Will to Power” by Friedrich Nietzsche
- “The Art of War” by Sun Tzu
- Self-Help and Personal Development:
- “The Power of Habit” by Charles Duhigg
- “Atomic Habits” by James Clear
- “Mindset: The New Psychology of Success” by Carol S. Dweck
- “The Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck” by Mark Manson
- Business and Leadership:
- “Good to Great” by Jim Collins
- “Thinking, Fast and Slow” by Daniel Kahneman
- “Leaders Eat Last” by Simon Sinek
- “Lean In: Women, Work, and the Will to Lead” by Sheryl Sandberg
Conclusion
The world of literature has many books with the most extensive knowledge and perspectives. If you are interested in science and the natural world or the self-help genre, philosophy, history, and business, technology or wellness, and health There’s a book to broaden your horizons and spark your imagination. This collection of reference titles is the beginning of your discovery and education by inviting you to explore the endless ocean of human wisdom and imagination.