Pannus and Thrombus, represent two separate medical conditions, each with distinct characteristics and implications for clinical care. Knowing the distinctions between them is essential to ensure a correct diagnosis and proper treatment.
We will go over the definitions, processes of formation and locations, the consequences for clinical and diagnostic techniques as well as treatment strategies and strategies to prevent both thrombus and pannus to help illuminate the key medical concepts.
Definition of Pannus
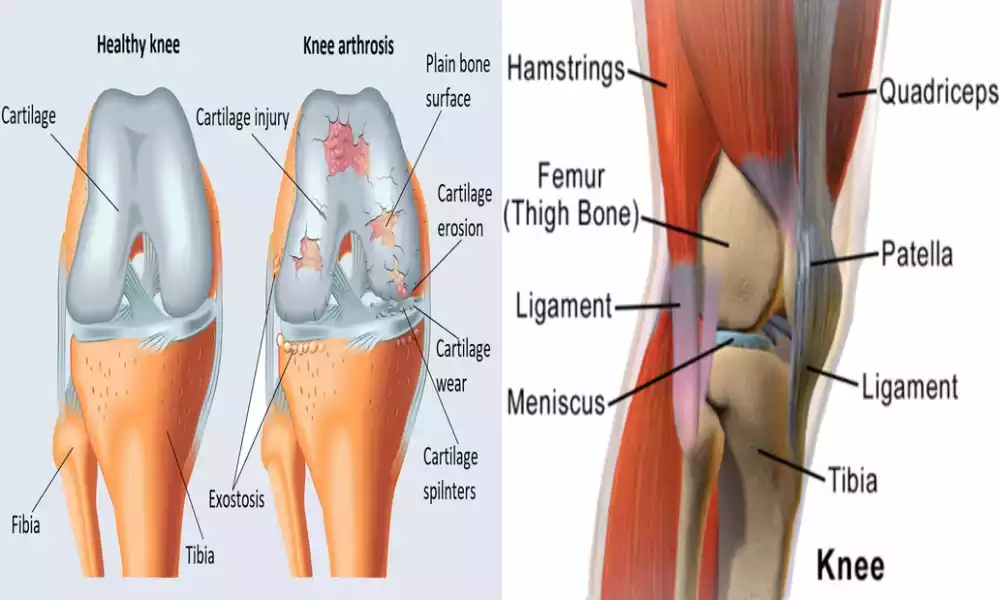
Pannus is a malformed tissue growth, characterized by the creation of an inflammation-related fibrous, vascularized, and fibrous mass that may occur in a variety of parts of our body. However, it is often associated with synovial tissue within joints.
In the field of medical treatment, pannus is typically seen in people suffering from autoimmune disorders like Rheumatoid Arthritis. It is usually the result of chronic inflammation. It can result in the destruction of tissues affected and cause stiffness, pain as well and functional limitations. Pannus is often a medical intervention to stop the progression of the condition and its related complications.

Definition of Thrombus
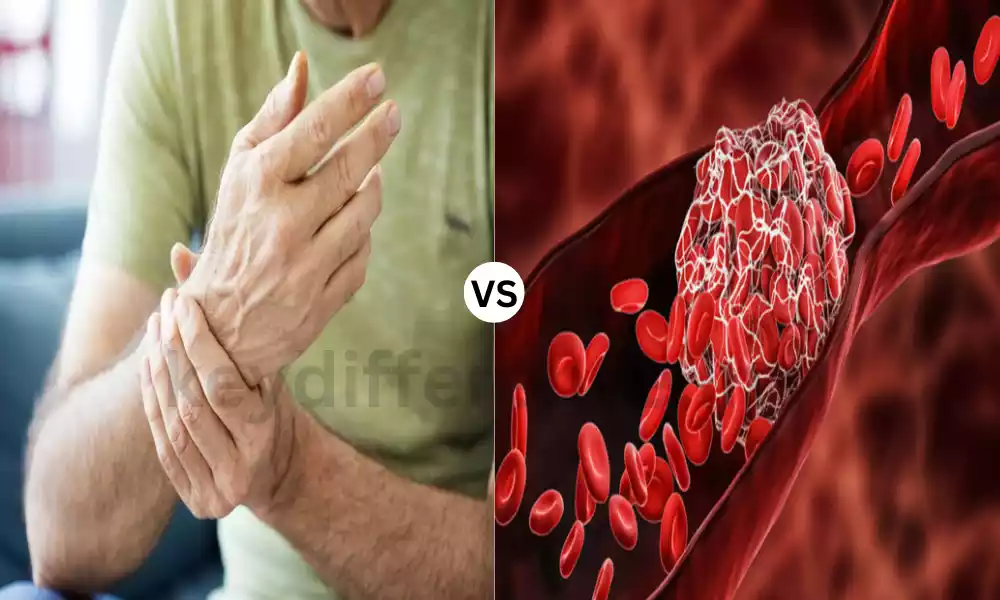
A”thrombus” is a medical term that refers to the formation of blood clots in a blood vessel blocking the circulation of blood. The thrombus can occur in veins as well as arteries and is generally comprised of fibrin, platelets, and other blood components. The clots may vary in size and development can be triggered by a variety of factors, including blood stasis, vascular injuries, or hypercoagulable conditions.
Thrombi in arteries could result in serious illnesses such as myocardial infarction (heart attack) or stroke as they may block the flow of blood to vital organs. When thrombi are found in veins could cause the condition of deep vein thrombosis (DVT) and also have the possibility of breaking loose and traveling through the bloodstream causing an embolism in the pulmonary system (PE) when they are lodged in the lungs. Early diagnosis and treatment of thrombi is crucial to avoid potentially fatal complications.
Importance of Understanding the Difference Between Pannus and Thrombus
Knowing the difference between the pannus and the thrombus is of crucial importance for several reasons:
- Accurate Diagnoses: Pannus and thrombus are associated with different medical conditions that require different ways of diagnosing and treating. Understanding the difference can help healthcare professionals identify patients and begin appropriate treatments.
- Treatment Choice: Strategies for managing thrombus and pannus are quite different. Pannus typically involves medication and, in a few instances, surgical procedures, while treatment for thrombus is primarily anticoagulation or thrombolytic treatments. It is vital to know the distinction for providing effective treatment.
- Risk assessment: Understanding the nature of the disease–whether it’s thrombus or pannus, helps health professionals assess the risk profile of a patient. As an example, thrombus-related diseases could lead to life-threatening incidents like pulmonary embolisms, strokes, or strokes while pannus is primarily a threat to joint function. A thorough risk assessment can guide the right actions and preventive actions.
- Information for Patients: Patients who are aware of their medical conditions can be part of their treatment plans, stick to prescribed medications, and implement lifestyle adjustments if necessary. Knowing the difference between thrombus and pannus helps patients to understand their condition and take an active role in their treatment.
- Prevention: Information about the risk factors and causes that are associated with thrombus and pannus allows healthcare professionals and patients to make preventive steps. The prevention of the condition or minimizing its effects through lifestyle modifications or medication compliance can dramatically improve the quality of life.
- Research and Development: A thorough understanding of the distinctions between thrombus and pannus could encourage research to develop better diagnosis tools, treatment options, and preventive strategies for these ailments. Medical advances depend on a thorough understanding of the various ailments.
- Health Efficiency: Utilizing efficient healthcare resources is crucial. Making the right distinction between thrombus and pannus avoids unnecessary treatments, tests, and hospitalizations, which can optimize the utilization of healthcare.
Knowing the distinction between thrombus and pannus is essential for a correct diagnosis, effective treatment and the assessment of risk, education for patients as well as research and efficiency in healthcare. This ultimately leads to better outcomes for patients and advances in knowledge and techniques in medicine.
Comparison Table of Pannus and Thrombus
Here’s a comparison table highlighting the key differences between pannus and thrombus:
| Characteristic | Pannus | Thrombus |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Abnormal tissue growth | Blood clot obstructing a blood vessel |
| Formation | Chronic inflammation | Blood coagulation |
| Location | Often in synovial joints (e.g., RA) | Arteries or veins |
| Causes | Autoimmune diseases (e.g., RA) | Vascular injury, stasis, hypercoagulable conditions |
| Composition | Inflammatory, fibrous, vascularized | Platelets, fibrin, blood components |
| Clinical Implications | Joint pain, stiffness, functional impairment | Myocardial infarction, stroke, deep vein thrombosis, pulmonary embolism |
| Diagnosis | Clinical assessment, imaging, blood tests | Imaging (ultrasound, CT, MRI), blood tests |
| Treatment | Medications, surgical interventions | Anticoagulants, thrombolytics, surgery (in some cases) |
| Prevention | Managing underlying autoimmune conditions | Managing risk factors (e.g., blood thinners, lifestyle changes) |
This table provides a concise overview of the differences between pannus and thrombus in terms of their nature, formation, location, causes, composition, clinical implications, diagnosis, treatment, and prevention. Understanding these distinctions is vital for healthcare professionals and patients to effectively manage these conditions.
Clinical Consequences
Here’s a fuller explanation of the consequences for patients or implications that are associated with pannus as well as thrombus:
Pannus:
- Joint pain: Pannus development, commonly seen in cases such as Rheumatoid arthritis (RA) can cause chronic arthritis, pain tenderness, and swelling. The discomfort can be severe and impact the quality of life of the patient.
- Tightness: When pannus infiltrates the synovial joints it may cause stiffness in joints and make the patients unable to maneuver their joints without restriction.
- Functional Impairment: Pannus could cause degeneration of cartilage as well as bone inside the joints. In time, this may cause joint deformities and impairment in function, affecting the ability of a person to complete everyday tasks.
- Reducing Mobility: Pannus’s clinical effects could result in a reduction in mobility, which affects a person’s capacity to move, hold objects, and retain their independence.
- Potential for Complications: If not treated pannus may cause serious joint deformities and damage that require surgical intervention like joint replacement surgery.
Thrombus:
- The risk of embolism: A major and important medical consequence of thrombus development is the potential for embolism. A thrombus may break away from its place of origin and move through the bloodstream. When it is able to reach organs that are vital, it could stop blood flow, leading to serious conditions such as myocardial infarction (heart attack) or stroke.
- Deep Vein Thrombosis (DVT): In veins where thrombus formation occurs, it could cause DVT. The condition is caused by bleeding blood clots inside deep veins, usually on the legs. DVT can result in swelling, pain, and redness on the limb affected.
- Pulmonary Embolism (PE): A thrombus that breaks and moves to the lungs could result in PE, a life-threatening illness. PE symptoms can include chest discomfort, shortness of breath, and a coughing up of blood.
- Cerebral thrombosis: Thrombi in the cerebral arteries could lead to cerebral thrombosis or stroke. This could cause neurological impairments such as speech problems, paralysis, and cognitive impairment.
- Other Organ-Specific Effects: Based on the location of the thrombus, additional medical consequences may occur like mesenteric artery blood clots (affecting the intestinal tract) and renal artery thrombosis (affecting the kidneys), and could cause organ damage and dysfunction.
- chronic conditions: Recurrent thrombus formation or hypercoagulable conditions that are underlying can lead to chronic thrombotic conditions, requiring regular anticoagulation treatment.
The effects of pannus are mostly related to joint issues, which can cause stiffness, pain, and functional impairment. Moreover, the formation of thrombuses could have a wide range of implications, including embolisms organ-specific concerns, and life-threatening illnesses.
Early diagnosis and proper management are essential to reduce these negative clinical consequences and enhance the outcomes of patients.
Lifestyle Changes and Risk Reduction
Lifestyle changes and risk-reduction strategies are vital for both pannus-related disorders like Rheumatoid Arthritis (RA) and thrombus-related conditions such as deep vein thrombosis (DVT) and PE. (PE).
Here are a few specific suggestions for each:
For Pannus-Related Conditions (e.g., RA):
- Medication Adherence: Continuously taking prescribed medicines for example, such as antirheumatic drugs that treat disease (DMARDs) as well as nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory medications (NSAIDs), can assist in managing inflammation and slow down the progression of the disease.
- Regular exercise: Engaging in low-impact activities like walking, swimming or yoga can assist in keeping the flexibility of joints, muscle strength, and general mobility. Talk to a PT for a specific exercise regimen.
- Balanced Diet: A diet high in foods that are anti-inflammatory, like fruits, vegetables as well as seafood (rich in omega-3 fats), and whole grains are able to lower inflammation and aid joint health. Eliminating processed foods and excessive sugar may also benefit.
- Weight Management: Being a healthy weight can reduce pressure on joints bearing weight like hips and knees, decreasing the pain and reducing joint damage caused by conditions such as osteoarthritis.
- The Management of Stress: Chronic stress can cause inflammation to increase. Methods for reducing stress like meditation deep breathing exercises or counseling could help to manage stress levels.
- Joint protection: Using assistive devices like braces, splints, or splints as well as modifying your daily routine to ease joint strain will reduce the risk of injury to joints.
- Smoking Cessation: Smoking is linked to an increase in inflammation, and it can also increase the severity of RA symptoms. Stopping smoking cigarettes could have a positive effect on general health.
For Thrombus-Related Disorders (e.g., DVT and PE):
- Medication Adherence: If you’re prescribed blood thinners (anticoagulants) it is crucial to follow the directions to stop the formation of more clots.
- Mobility and Exercise: Keep up with your regular exercise particularly if you have the risk factors for thrombus development. Easy leg workouts, ankle pumps, and calf stretching can prevent DVT when you are in prolonged periods of inactivity like when traveling.
- Hydration: Drinking enough water can aid in preventing your blood’s thickness from getting too high and vulnerable to bleeding. Try to drink enough fluids all day long.
- Compromising Stockings: When advised by an expert in healthcare wearing compression stockings could aid in improving blood flow to the legs and decrease the chance of DVT.
- Smoking Cessation of Smoking: Smoking cigarettes is a risk cause for the formation of clots. Stopping smoking is crucial in reducing the chance of developing thrombus-related diseases.
- Healthy Diet: Consuming a balanced and balanced diet that is rich in fiber food items, lean proteins as well and plenty of vegetables and fruits can improve overall cardiovascular health.
- Regular check-ups: If you are a parent of clotting disorders or any other factors that could increase your risk, think about regular check-ups with your health professional to assess your risk of clotting as well as talk about ways to prevent it.
- Travel Safety Tips: During long flights or road trips, you should take breaks to stretch and move your legs. If you’re at a high risk for the formation of thrombuses or thrombus formation, your doctor may suggest blood-thinning medications or compression stockings to travel.
It’s crucial to collaborate closely with healthcare professionals to adapt lifestyle changes and risk-reduction strategies to suit your particular health condition and needs. Regular follow-up appointments as well as open dialogue with your healthcare provider are essential to effectively managing these ailments and minimizing the risk.
Similarities Between Pannus and Thrombus
Although thrombus and pannus are medical entities that are distinct in nature they do have some similarities, mostly in relation to their formation as well as possible consequences for clinical practice.
Here are some of the key similarities between thrombus and pannus:
- Inflammatory Component: Both thrombus and pannus are inflammatory processes.
- Pannus is characterized by chronic inflammation, particularly when it comes to autoimmune diseases such as rheumatoid arthritis (RA).
- The formation of a thrombus can be caused by inflammatory conditions or blood vessel injuries.
- The Tissue Injury: In both cases, there is a chance for tissue damage
- Pannus can cause destruction of joint tissues that can result in discomfort and impairment in function.
- Thrombus can impede blood flow, which could lead to organ dysfunction.
- Risk of complications: Both pannus and thrombus may cause serious complications if untreated or not properly managed.
- Pannus can lead to joint deformities as well as disability.
- Thrombus may cause embolisms, including embolisms of the lungs (PE) and stroke which could be life-threatening.
- Diagnostic Imaging: Medical professionals typically employ diagnostic imaging techniques to determine the severity of both ailments:
- In the case of pannus, imaging such as X-rays and MRI scans can be utilized to assess joint damage.
- The diagnosis of thrombosis is based on techniques such as ultrasonography, CT scans, or MRI to locate blood clots that are present in blood vessels.
- Medical Intervention: In some cases, it is recommended to seek medical attention to treat both thrombus and pannus:
- Pannus management can involve medication to manage inflammation or surgical procedures to fix or replace damaged joints.
- The treatment for thrombosis often includes anticoagulants to stop bleeding from clots, as well as surgical treatments in the case of severe bleeding.
- Chronic Nature: Pannus-related conditions (e.g., RA) and thrombus-related diseases (e.g. chronic deep vein thrombosis) can develop into chronic conditions and require continual care.
It’s crucial to understand that, despite the similarities, pannus and the thrombus are two distinct medical conditions that have their own characteristics as well as causes and treatments. Knowing the distinctions between them is essential for an accurate diagnosis as well as individualized management strategies.
Reference Books
Certainly! Here are some reference books covering various topics and fields. Please note that my knowledge is current as of September 2021, and there may have been new publications since then. Always check for the latest editions and reviews when considering reference books.
General Reference:
- “The Oxford English Dictionary” – A comprehensive dictionary of the English language.
- “Encyclopedia Britannica” – A well-regarded encyclopedia that covers a wide range of topics.
Science and Technology:
- “CRC Handbook of Chemistry and Physics” – A trusted source for chemical and physical data.
- “The Feynman Lectures on Physics” by Richard P. Feynman – A classic physics reference covering a broad range of topics.
- “Campbell Biology” by Jane B. Reece, Lisa A. Urry, et al. – A widely used biology textbook.
- “Introduction to the Theory of Computation” by Michael Sipser – A fundamental text in computer science.
Medicine and Healthcare:
- “Harrison’s Principles of Internal Medicine” edited by Dan Longo, et al. – A comprehensive resource for internal medicine.
- “Robbins and Cotran Pathologic Basis of Disease” by Vinay Kumar, Abul K. Abbas, et al. – A leading pathology reference.
- “Merck Manual of Diagnosis and Therapy” – A trusted medical reference for healthcare professionals.
Conclusion
knowing the difference between thrombus and pannus can be vital to a precise diagnosis, efficient treatments, as well as risk evaluation within the context of medical diseases. Although they have some commonalities they are different in their genesis as well as their causes and effects.
The timely intervention and lifestyle changes are crucial in treating both pannus-related diseases and thrombus-related diseases and ultimately improve the quality of life for patients as well as overall well-being. To gain a comprehensive understanding of medicine and healthcare an array of reference books is offered to help you learn and practice.