Spondylosis and spinal stenosis are two spinal conditions that can create discomfort and affect a person’s well-being. Although they have a lot in common with their connection to spinal degeneration, they’re different in their diagnosis, causes, symptoms, techniques, and treatment strategies.
The main differences between spinal stenosis and spondylosis. It will help you be aware of these conditions and make informed choices regarding your health or the health of someone else you love.
Explanation of Spinal Stenosis
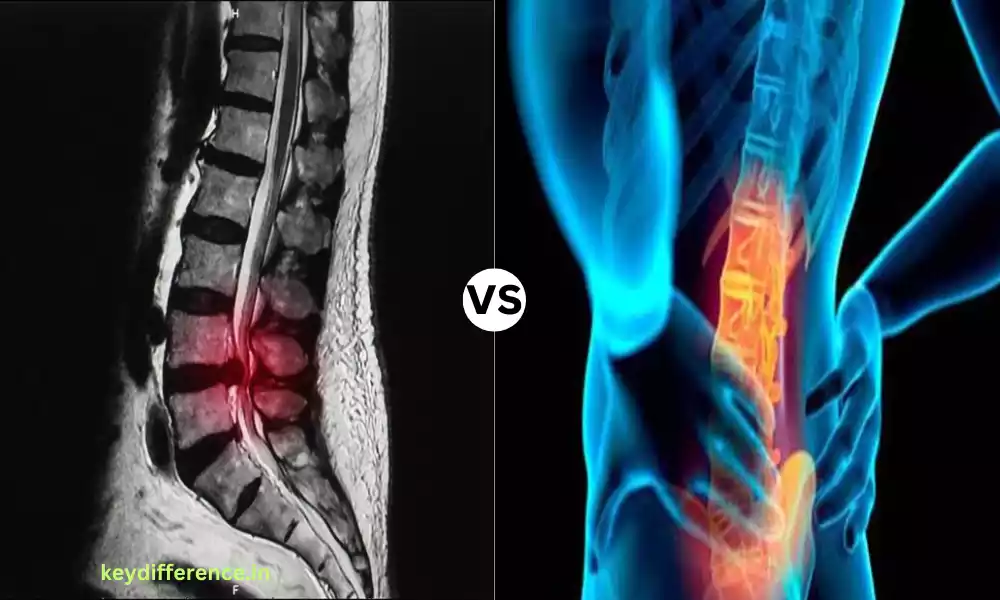
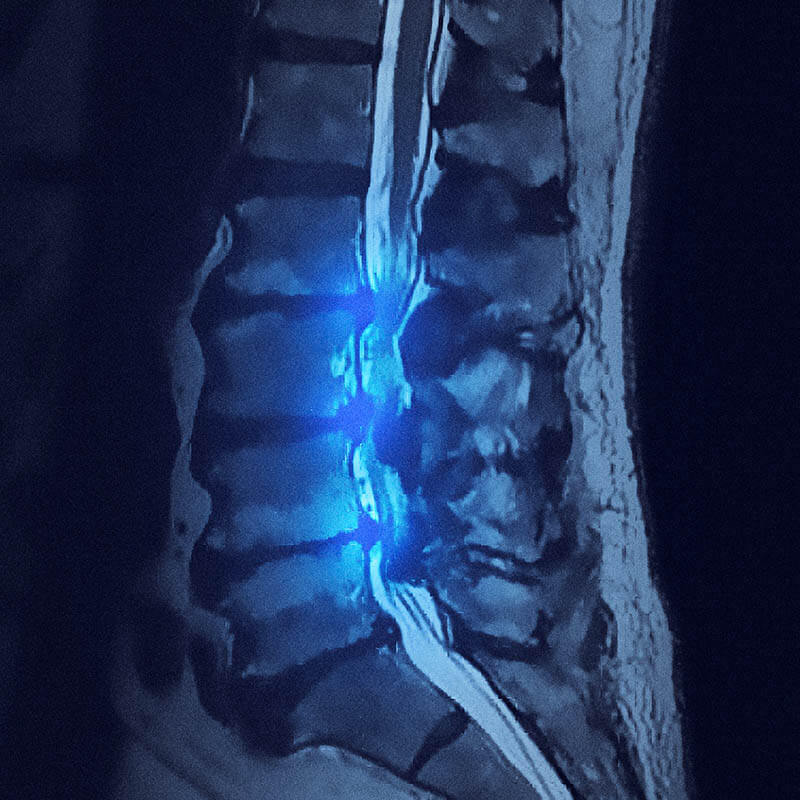
Spinal stenosis is a disease that manifests as the narrowing or simplification of the canal, or the spaces in the spine. This may result in compressing the spinal cord as well as the nerves branching out from it.
The constricting of the spine may result from a variety of causes including changes in the aging process, congenital disorders, or injuries. It frequently causes symptoms such as numbness, pain, tenderness, or tingling in the limbs depending on the region that is affected.
Explanation of Spondylosis
Spondylosis, also referred to as osteoarthritis of the spine is a degenerative disease that affects the spinal. It is defined by the wear and tear on the discs in the spine and facet joints that join the vertebrae.
As people get older, the discs that connect the vertebrae of the spine can decrease in elasticity and hydration as well and the facet joints can develop arthritis.
This can cause different symptoms, including stiffness, pain, decreased flexibility, and even in certain instances, the development of osteoporosis. Spondylosis is a typical age-related disease that is usually observed in imaging studies, such as radiographs, X-rays, and MRIs that look at the spine.
Importance of understanding the differences
Understanding the distinctions between spondylosis and spinal stenosis is essential for many important reasons:
- Accurate Diagnosis: Being aware of the distinctions between these conditions can help healthcare professionals make accurate diagnoses. Both diseases can have similar symptoms. A misdiagnosis can result in incorrect treatment or delay in treatment.
- Tailored Treatment: The most appropriate treatment for spinal stenosis is different from the treatment for spondylosis. Knowing the exact conditions is crucial to tailor treatment plans that treat the root cause and signs effectively.
- Educational Patient: Patients who understand their condition can take part in their treatment. They are able to make informed choices about treatment options, take part in preventive measures, and set expectations about the progress of their condition.
- Prognostic Expectations: Each condition carries a unique prognosis. Knowing the difference can help those with the condition and families anticipate the impact that it could have on the daily routine, mobility as well and overall well-being.
- Preventive measures: Knowledge of the reasons and risk factors that are related to these conditions allows people to take preventive measures. Lifestyle changes and early intervention can slow the progress of the condition, or even reduce the likelihood of becoming affected.
- Qualities of Living: Spinal stenosis and spondylosis are both significant factors that affect the quality of life of a person. Knowing the difference allows patients to better manage their conditions which can improve their overall wellbeing.
- Health Resource Allocation: The accuracy of diagnoses that are based on understanding the distinctions between these conditions enables healthcare organizations to distribute resources efficiently and provide appropriate procedures, treatments, and rehabilitation services.
- Research and Development: Knowing the distinctions between spondylosis and spine stenosis is crucial for researchers and healthcare professionals working on improvements in treatment and therapies. This knowledge aids in the development of targeted therapies.
Recognizing spinal stenosis and spondylosis is crucial for effective patient care, individualized treatment plans, and better overall results. It allows health experts as well as patients to make informed choices and manage their conditions better.
Comparison Table of Spinal Stenosis and Spondylosis
| Criteria | Spinal Stenosis | Spondylosis |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Narrowing of the spinal canal | Degeneration of the spine, including vertebrae, discs, and ligaments |
| Affected Areas | Usually the cervical and lumbar regions | Typically cervical and lumbar spine, but can affect the entire spine |
| Primary Causes | Age-related changes- Spinal injuries – Tumors | Age-related changes – Genetic factors – Lifestyle factors (e.g., occupation, posture) |
| Common Symptoms | Pain- Numbness and tingling – Weakness in extremities- Difficulty in walking | Neck or back pain – Stiffness – Numbness and tingling – Muscle weakness |
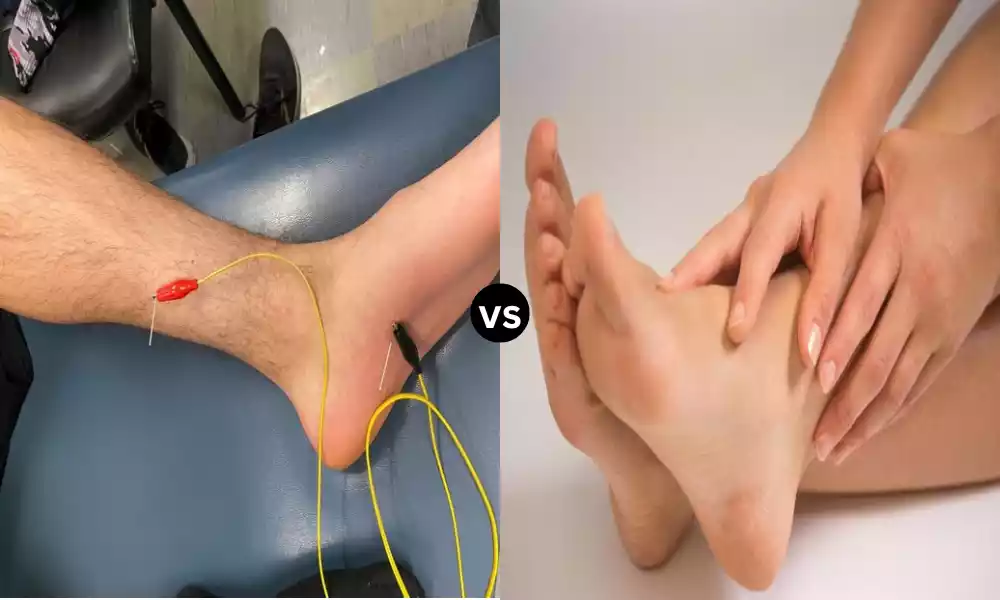
| Diagnostic Tests | Medical history – Physical examination- MRI – CT scan – Electromyography | Medical history – Physical examination – X-ray – MRI – Blood tests for inflammation |
| Treatment Options | Medication (pain relievers, anti-inflammatory drugs) – Physical therapy – Surgery (e.g., laminectomy, spinal fusions) | Medication (pain relievers, muscle relaxants) – Physical therapy – Surgery (e.g., discectomy, spinal fusions) – Alternative therapies (e.g., acupuncture) |
| Complications | Chronic pain – Reduced mobility- Neurological issues | Chronic pain – Reduced range of motion – Neurological issues |
| Prevalence | More common in people over the age of 50 | More common in middle-aged and elderly people, but can occur at a younger age |
| Prevention | Regular exercise – Maintaining a healthy weight – Proper posture | Regular exercise – Ergonomic lifestyle adjustments – Proper posture |
How are spinal stenosis and spondylosis related?
The conditions of spondylosis and spinal stenosis are connected in that they both have degenerative spinal conditions that could affect the spinal column however, they are distinct diseases that have distinct features.
The following is how they relate:
- Degenerative Nature Spinal Stenosis and spondylosis are degenerative diseases that usually develop over time, particularly as one gets older. They are usually associated with wear and tear of the spine.
- The impact on spinal Structures The two conditions may alter the spinal structures, like the discs, vertebrae, and other tissues around them which can cause a variety of signs and complications.
- The two conditions are often coexisting. Spinal stenosis as well as spondylosis are often co-existent in the same person. Spondylosis, which is a broad term that refers to degenerative changes within the spine, could be a factor in the development of spinal stenosis.
Here are the major distinctions between the two situations:
- Definitions:
- The Spinal Stenosis: Spinal stenosis is a disease that manifests as an increase in the size of neural foramina, or the spinal canal which puts tension on the spine and nerve roots.
- Spondylosis: The term “spondylosis” is more of a general term used to describe age-related degenerative changes to the spine. It covers a variety of diseases, including osteoarthritis disc degeneration, and bone spurs.
- Location:
- The Spinal Stenosis: It specifically results in the narrowing of the neural foramina, or the spinal canal that can be found in different regions within the back, like those in the cervical (neck) or the lumbar (lower back) areas.
- Spondylosis: It is described as more inclusive and could be used to refer to degeneration that happens anywhere on the spine, including the cervical and the thoracic (mid-back) or lumbar regions.
- Symptoms:
- spinal Stenosis: Symptoms are most often due to nerve compression. The symptoms can manifest as numbness, pain, or tingling in the limbs, based on the area of stenosis.
- Spondylosis: Its symptoms vary extensively and could include back stiffness, back pain, decreased range of motion as well and muscle spasms. It could also be caused by nerve compression.
- Diagnosis:
- spinal Stenosis: Diagnosis often involves imaging studies such as MRI, as well as CT, scans to evaluate the extent of neuroforamina narrowing.
- Spondylosis The diagnosis typically involves identifying degenerative changes to the spine by imaging studies and a clinical examination.
- Treatment:
- Spinal Stenosis: Treatment may consist of conservative methods (e.g. physical therapy or treatment for pain) or surgical procedures (e.g. surgical decompression) to ease the nerves of pressure.
- Spondylosis: The treatment focuses on the management of symptoms. This may include physical therapy, medications for pain relief lifestyle changes, and sometimes surgery to address specific problems such as severe disc herniation as well as spinal instability.
Both spondylosis as well as spinal stenosis are related in they both cause degeneration of the spinal column, however, they differ in their distinct characteristics, the locations within the spine, signs diagnostics, and treatment methods.
The condition spinal stenosis is a more specific condition that causes the shrinking of the canal of the spinal, or neural foramina. whereas spondylosis is a broad term that encompasses degenerative changes caused by age in the spine.
Prevention of spinal stenosis and spondylosis
The best way to prevent spondylosis and spinal stenosis requires implementing a variety of lifestyle adjustments, ensuring the health of your spine, and reducing the risk factors associated with these diseases.
While these ailments may not be totally prevented, the following methods will help lower your risk and improve your spinal health:
- Maintain a Healthy Weight:
- The excess weight of your body can cause an additional strain upon your back. A healthy weight by following a balanced diet as well as regular exercise can lower the likelihood of developing these ailments.
- Stay Active and Exercise Regularly:
- Engage in low-impact activities such as swimming, walking, and yoga to maintain your spine’s flexibility and strengthen the muscles supporting it. Avoid activities that cause high impact, which could put a lot of tension on the spine.
- Maintain Good Posture:
- Make sure you are in a good position when sitting, standing, or lifting items. A good alignment helps reduce the stress on your spine and can help to prevent wear and tear.
- Ergonomic Workspace:
- If you work at work at a desk, ensure that your workplace is designed ergonomically. Choose a chair that has the lumbar support, and ensure you have the right levels of your keyboard and monitors to ease the strain on your back and neck.
- Avoid Smoking:
- Smoking is associated with the increase in disk degeneration that occurs in spinal vertebrae. Stopping smoking cigarettes can boost the overall health of your spine.
- Lift Safely:
- When lifting large objects make sure you use your legs and keep the object as close the body. Avoid twisting when lifting as this could stress your spine.
- Stay Hydrated:
- Hydration is essential to maintain the amount of fluid in the spinal discs which can lower the chance of disc degeneration.
- Maintain a Strong Core:
- The strengthening of the muscles around your stomach and back (core muscles) will provide more back support, and decrease the chance of injuries.
- Stretch and Flexibility Exercises:
- Include stretching exercises in your routine to keep the flexibility of your spine. Pilates and yoga Pilates are excellent options.
- Regular Health Check-ups:
- Regular medical examinations are a great way to determine early indications of spinal problems and can allow for prompt intervention.
- Manage Chronic Conditions:
- If you suffer from ailments such as osteoarthritis or rheumatoid arthritis consult your doctor to effectively manage them. These conditions can cause degeneration of the spine.
- Use Proper Body Mechanics:
- Make sure you are using the correct body mechanics while you are doing daily tasks like bent knees, sitting and standing. Beware of sudden and intense movements.
- Avoid Prolonged Inactivity:
- Being sedentary for a long time could cause stiffness and weakening of muscles. Pause to stretch and move around in particular if you hold a work at a desk.
- Consider Physical Therapy:
- If you’ve experienced a long-term background of back issues or are at risk because of your job or lifestyle, you should consult an occupational therapist to get advice on posture and exercises.
- Manage Stress:
- Chronic stress can result in tension in muscles, which can result in back pain. Try stress-reduction methods like mindfulness and breathing deeply.
Although these preventive measures may lower the risk of developing spondylosis and spinal stenosis, it is essential to speak with your doctor to get individualized advice and prompt intervention when you notice symptoms or show risk factors for these ailments.
Being active and being proactive about your spinal health can be a huge help in protecting the health that your spinal column.
Lifestyle changes for managing spinal stenosis and spondylosis
Lifestyle changes play a vital part in preventing spinal stenosis and spondylosis because they can ease symptoms slow the progression of diseases and increase the quality of your life overall.
Here are a few lifestyle changes to think about if you suffer from spinal stenosis or spondylosis:
- Maintain a healthy weight: Excess weight puts extra strain on your spinal column, causing more symptoms and slowing the process of degeneration. If you’re overweight, speak to your doctor for advice on a weight-management plan.
- Regular exercise: Physical activity is vital to manage these ailments. Make sure to do exercises that help strengthen the core, increase flexibility, and aid in maintaining the proper posture. Activities that are low-impact like walking, swimming, or cycling are usually well-accepted.
- Physical Therapy: Physical therapists can create a custom-designed workout program that addresses your individual needs and conditions. They can also instruct you on the correct techniques and body mechanics for the treatment of pain.
- Posture Enhancement: Pay attention to your posture throughout your day. Be sure to maintain a proper alignment while standing, sitting, and walking. ergonomic chairs and workplace setups will also aid.
- Flexibility and Stretching: Incorporate regular stretching exercises into your daily routine to improve your flexibility and reduce tension in the muscles. Yoga and Pilates can be extremely beneficial.
- Treatment for Pain: Apply and learn methods for managing pain like treatment with cold and heat as well as over-the-counter pain medications (under Medical supervision) or relaxation techniques such as deep breathing.
- Dietary Options: A balanced diet that is good for bone health can be beneficial. Be sure to get enough calcium as well as vitamin D to build strong bones. Speak to your doctor or dietitian for individualized dietary recommendations.
- Keep H2O: Proper hydration is vital to keep the amount of fluid inside the discs of your spine. Drink plenty of fluids during the entire day.
- Smoking Cessation: If you are a smoker take a look at abstaining. Smoking is linked to an increase in disc degeneration, and it can increase the severity of symptoms.
- Stress Management: Chronic stress can lead to muscle tension and increase discomfort. Implement techniques to reduce stress, like deep breathing exercises, meditation, or mindfulness exercises.
- adaptive equipment: You may want to consider using assistance devices and equipment that can be adapted to make everyday tasks easier to manage. For instance, a lumbar cushion to sit or a reacher to pick up objects could reduce stress on your spine.
- Avoid high-impact activities: Steer clear of activities with high impact or that could aggravate your symptoms. Talk to your doctor for advice on activities that are suitable.
- You’re Pacing: Be aware of your body’s signals and stay away from overexerting. Relieve yourself when you need to and try not to push yourself too hard.
- Orthopedic Supports: Orthopedic supports like braces or lumbar belts can give additional support and relief. Speak with your healthcare professional or physical therapy professional to determine if they fit your needs.
- Regular Check-ups: Make sure you follow up with your doctor regularly to check on the progress of your condition, and then adjust your treatment plan if necessary.
It is essential to collaborate with your doctor and possibly a physiotherapist to design an individual plan that is tailored to your particular condition and requirements.
Lifestyle changes, in conjunction with medical treatments when needed, can greatly improve your ability to manage and manage spinal stenosis as well as spondylosis. smoking causes many other diseases.
New and emerging treatments for spinal stenosis and spondylosis
In my last information report in the month of September 2021, there were numerous promising and new treatment options for spinal stenosis as well as spondylosis which proved promising in clinical and research studies.
It is important to keep in mind that advances in medical technology could have taken place since when I last updated. Always consult a healthcare practitioner for the most current advice and information.
Here are some of the latest and upcoming treatments in the process of being researched:
- Minimally Invasive Procedures:
- Modern techniques for minimally invasive surgery allow for more precise treatments for spinal stenosis as well as spondylosis. Techniques such as minimally invasive decompression surgery as well as endoscopic spinal surgery offer relief through smaller incisions, less tissue damage, and speedier recovery times when compared to traditional open surgeries.
- Regenerative Medicine:
- Stem cell therapy as well as platelet-rich plasma (PRP) injections are currently being studied as potential treatment options for spinal issues. These therapies are designed to aid in the healing and regeneration of the tissues in the spine and could provide relief from symptoms while slowing down the degeneration process.
- Biologics:
- Biologic medicines, such as anti-inflammatory medications and drugs that modify disease are being investigated for their ability to decrease inflammation and stop the progress of degenerative spinal disease in conditions such as spondylosis.
- Motion-Preserving Devices:
- Artificial discs are a new alternative to conventional surgical fusion. The devices are designed to preserve movement in the affected segment, which could reduce the chance of degeneration in the adjacent segment.
- Neuromodulation and Nerve Stimulation:
- The procedure of spinal cord stimulation (SCS) and dorsal root Ganglion (DRG) stimulations are two methods that involve the implanting of electrodes that deliver electric stimulation for the nerve roots or spinal cord. These treatments may help relieve the pain and discomfort that comes with spondylosis and spinal stenosis.
- Pharmacological Therapies:
- The research into new medications like specific anti-inflammatory drugs or other disease-modifying drugs, continues to look at possibilities for treating symptoms and slowing the progression of disease.
- Genetic and Personalized Medicine:
- The advancements in genomics have helped researchers better identify the genetic factors that contribute to spinal problems. This information could result in individualized treatment strategies that are based on a person’s genetic constitution.
- Biomechanical Interventions:
- Implants for orthopedics and wearable devices that incorporate sensors are being designed to monitor the movement of the spine and posture. These devices aim to provide immediate feedback and assist individuals to keep their spine in alignment.
- Telemedicine and Remote Monitoring:
- Telemedicine and remote monitoring technology are increasingly important in managing spinal disorders which allows patients to connect with their healthcare specialists via virtual consultations, and track their health status via the internet.
- Exercise and Rehabilitation Programs:
- Specific exercise programs, typically led by physical therapists are being developed to tackle specific spinal problems. The programs aim to strengthen muscles that support the spine while also improving posture and improving spinal stability.
It is essential to speak with a doctor who is skilled in treating spinal issues to discuss the most suitable treatments for your specific condition. Be aware that your treatment choices must be based on an in-depth assessment of your health condition, which includes the severity of it and its location within the spine, in addition to your general health and personal requirements.
Similarities Between Spinal Stenosis and Spondylosis
Spondylosis and spinal stenosis are both degenerative conditions that may affect the spine. they have a number of similarities:
- Age-related Degeneration: The condition of spinal stenosis and spondylosis are often associated with the process of aging. As we age the structures of the spine naturally change and develop degeneration, which may be a factor in the development of these diseases.
- Progressive Condition: Both conditions tend to progress, which means they become worse as time passes. As the spine degrades the symptoms can get more severe and impact your daily activities.
- Discomfort and Pain: Spinal stenosis and spondylosis can cause discomfort and pain within the affected part of the spinal column. The pain may range from mild to intense and could be localized or spread into other areas of the body.
- Impaired mobility: Individuals with either condition may notice a decrease in range as well as mobility. Stiffness, trouble bending or twisting, as well as muscles that are weak, can be typical symptoms.
- Neurological symptoms: Both conditions can cause neurologic symptoms caused by nerve irritation or compression. The symptoms could include numbness or tingling and weakness in the limbs depending on the extent and location of the problem.
- Imaging Results: Imaging for diagnosis, including MRI as well as CT scans, is often utilized to detect both spondylosis and spinal stenosis. Imaging studies can show the narrowing of the spine canal and neural foramina and other changes that are degenerative.
- Conventional TreatmentIn the beginning, these ailments are usually treated with conventional treatments. This could include physical therapy, painkillers, or lifestyle modifications as well as exercises designed to improve the health of the spine.
- Surgery Solutions: In cases where traditional treatments don’t offer enough relief, or if the condition is advancing surgery is a possibility to treat both spinal stenosis as well as spondylosis. Surgery is a procedure that aims to relieve nerves and stabilize the spine or resolve structural issues.
- The importance of lifestyle modifications: Lifestyle changes are essential in managing both of the conditions. A healthy weight, focusing on proper posture, remaining physically active, and avoiding smoking are all common suggestions to improve the health of your spine for those suffering from spinal stenosis or spondylosis.
- Individual Variation: The presentation as well as severity of symptoms may differ greatly among patients suffering from the condition of spondylosis and spinal stenosis. Every person’s experience with these conditions could be different as are treatment strategies typically specifically tailored to the individual’s needs.
Although spondylosis and spinal stenosis are similar it’s important to recognize that they’re distinct diseases that have different causes, specific anatomical changes, and treatment strategies.
Therefore, an accurate diagnosis and a customized treatment plan that is based on the patient’s particular condition are vital for effective treatment.
Reference Books
Certainly! Here are some reference books across various categories and subjects that have been highly regarded for their content and educational value.
Please note that my knowledge is based on information available up to September 2021, so there may be newer publications in these fields:
Science and Nature:
- “Cosmos” by Carl Sagan – A classic exploration of the universe and our place in it.
- “A Short History of Nearly Everything” by Bill Bryson – A popular science book that covers a wide range of topics.
- “The Selfish Gene” by Richard Dawkins – A foundational work in evolutionary biology.
History:
- “A People’s History of the United States” by Howard Zinn – A critical look at American history from a different perspective.
- “The Guns of August” by Barbara W. Tuchman – A detailed account of the outbreak of World War I.
- “Sapiens: A Brief History of Humankind” by Yuval Noah Harari – Explores the history of Homo sapiens from the emergence of our species to the present.
Philosophy:
- “Meditations” by Marcus Aurelius – A collection of personal writings by the Roman Emperor.
- “Critique of Pure Reason” by Immanuel Kant – A foundational work in modern philosophy.
- “The Republic” by Plato – A classic treatise on justice, politics, and the ideal society.
Literature:
- “To Kill a Mockingbird” by Harper Lee – A classic novel addressing racial injustice in the American South.
- “One Hundred Years of Solitude” by Gabriel García Márquez – A magical realist novel often considered one of the greatest of the 20th century.
- “The Great Gatsby” by F. Scott Fitzgerald – A portrayal of the American Dream during the Roaring Twenties.
Conclusion
Reference books can be valuable sources of information and details on various subject areas. When it comes to exploring the depths of history, science or literature, philosophy, or another field they provide an excellent foundation for understanding and learning.
The list below includes the most well-known and classic titles but the field of reference books is constantly evolving, with newer editions and books that provide the most current information. By embracing these sources, you open the door to the riches of human wisdom and knowledge and enrich our knowledge of the world and the concepts that define it. what is the smell coming out of your mouth?