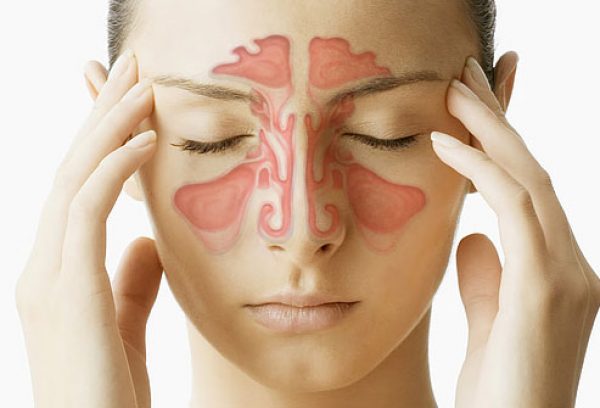
Conditions of the respiratory system can present similar symptoms, which can lead to confusion and a misdiagnosis. Hay Fever and Sinusitis of the most commonly reported conditions that are commonly seen, hay fever (allergic rhinitis) as well as sinusitis have some of the same symptoms, however, they differ in causes as well as treatment and treatment.
We will look at the major differences between sinusitis and hay fever to help patients and healthcare professionals know the causes of these conditions to ensure the most accurate diagnosis and treatment.
Explanation of Hay Fever
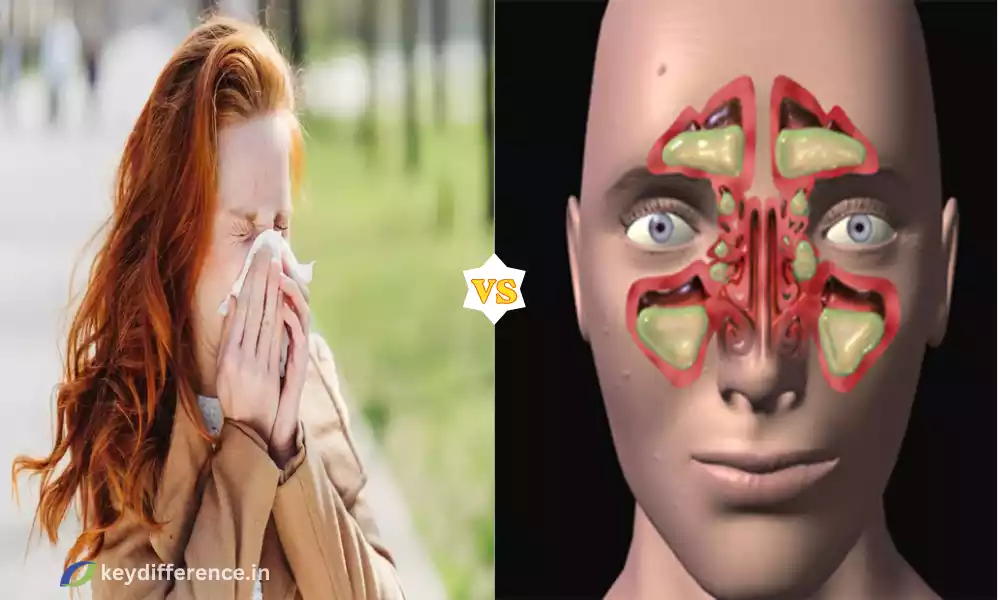
Hay fever, also known as allergic rhinitis is an allergic reaction that is primarily affecting the nasal passages and, occasionally, the throat and eyes. It is caused by exposure to allergens like pollen, dust mites, or pet dander, which can cause a range of symptoms such as running or nasal stuffiness watery or itchy eyes as well as postnasal drip.
Hay fever generally manifests as seasonal or perpetual patterns, based on the particular allergen, and is not triggered through an underlying infection. It is among the most frequent allergies in the world and can have a significant impact on the quality of life of an individual especially during allergy season.

Explanation of Sinusitis
Sinusitis, also referred to as rhinosinusitis is a medical disease that manifests as swelling and inflammation of the tissues that line the sinus cavities inside the skull. The sinuses are air-filled areas found within the facial bones, around the eyes and nose. Sinusitis can result from many factors, including bacteria, viruses allergies, and other irritants that cause the obstruction of sinus openings and the build-up of mucus.
The blockage may cause symptoms like facial pressure and pain nasal congestion, thick nasal discharge, and in some instances, it can cause fever. Sinusitis may become acute (short-term) chronic (lasting longer than twelve weeks) or persistent (multiple episodes in a single year). The correct diagnosis and treatment are crucial to ease symptoms and avoid complications.
Comparison Table of Hay Fever and Sinusitis
Here’s a comparison table highlighting the key differences between Hay Fever (Allergic Rhinitis) and Sinusitis:
| Characteristic | Hay Fever (Allergic Rhinitis) | Sinusitis |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Allergic reaction to allergens affecting the nasal passages and sometimes the eyes and throat. | Inflammation of the sinus cavities in the skull causes various sinus-related symptoms. |
| Causes | Exposure to allergens like pollen, dust mites, pet dander, etc. | Viral or bacterial infections, allergies, irritants, or anatomical issues. |
| Symptoms | Sneezing, runny or stuffy nose, itchy or watery eyes, postnasal drip. | Facial pain and pressure, nasal congestion, thick nasal discharge, fever (in some cases). |
| Timing of Symptoms | Seasonal (e.g., during specific pollen seasons) or perennial (year-round, due to indoor allergens). | Can be acute (short-term), chronic (lasting over 12 weeks), or recurrent (multiple episodes within a year). |
| Fever | Typically no fever is associated with hay fever. | Fever can occur in some cases of bacterial sinusitis. |
| Diagnosis | Based on medical history, physical examination, and allergy testing (if needed). | Clinical evaluation, sometimes requiring imaging (CT scan, MRI). |
| Treatment | Allergen avoidance, antihistamines, decongestants, immunotherapy (allergy shots). | Antibiotics (for bacterial sinusitis), decongestants, pain relievers, nasal irrigation, and sometimes surgery. |
| Duration of Symptoms | Symptoms typically come and go with allergen exposure. | Duration varies, acute cases resolve within a few weeks, and chronic cases last over 12 weeks. |
| Contagious | Not contagious; allergic response to allergens. | Not contagious; typically caused by infections. |
| Prevention | Avoiding allergens or allergen immunotherapy for long-term management. | Proper hygiene, avoiding irritants, and treating underlying conditions (e.g., allergies). |
This table provides a concise overview of the key differences between hay fever (allergic rhinitis) and sinusitis, helping individuals and healthcare professionals distinguish between these two common respiratory conditions.
Importance of distinguishing between hay fever and sinusitis
Differentiating between hayfever (allergic nasality) and sinusitis is vital for a number of important reasons:
- The most appropriate treatment: Accurate diagnosis ensures that patients receive the most efficient and specific treatment. The sinusitis and the hay fever require different methods of management and relief. The treatment of one issue using the wrong remedy could lead to ineffective outcomes and long-term suffering.
- Treatment of Symptoms: Knowing the specific situation allows for better management of symptoms. For instance, hay fever symptoms are usually treated by avoiding allergens or using antihistamines. However, sinusitis could necessitate antibiotics and other therapies to treat the root of the infection.
- Preventive: Understanding the root of the problem can assist people in taking preventive actions. If it’s hay fever, staying clear of allergens during peak times will help reduce the symptoms. The prevention of sinusitis might involve addressing allergies underlying as well maintaining good hygiene in the nasal area, and treating the infection promptly.
- Preventing Complications: The inability to treat sinusitis appropriately could lead to complications such as sinus polyps, chronic sinusitis, or the spread of the infection to other structures such as the brain or eyes. An accurate diagnosis and treatment could assist in preventing these problems.
- Health and Quality: Both conditions can affect a person’s overall level of living. Differentiating between them will allow for more specific interventions, which leads to faster relief and enhanced health.
- Health Resource Allocation: Accurate diagnosis aids healthcare professionals in efficiently allocating resources. It helps reduce unnecessary treatments, tests, and doctor’s appointments, thereby reducing time and money on healthcare.
- Reducing the use of antibiotics: Overuse of antibiotics is a growing issue because of resistance to antibiotics. The distinction between hay fever and sinusitis could help prevent unnecessary prescriptions for antibiotics in cases of sinusitis that is viral, and where antibiotics will not be effective.
- Educational Purposes: Informing patients about the causes of their illness aids them in understanding their condition and plays an active part in controlling it. The knowledge gained allows patients to make informed decisions about treatments and lifestyle decisions.
In the end, knowing the difference between sinusitis and hay fever is vital to ensure the proper treatment, symptom control, and prevention of complications. It also aids in the efficient utilization of healthcare resources and minimizes the risk associated with misdiagnosis and mistreatment.
Medical history and physical examination
Physical examination and medical history are essential elements of diagnostic procedures in the field of medicine. They give healthcare professionals vital information regarding the patient’s health, symptoms, and the possibility of illnesses.
Here’s a quick overview of the medical history and physical exam:
Medical History:
- Patient Information: Get started by gathering basic demographic information, like the patient’s age gender, gender, and contact details of the patient.
- The most common complaint: Ask the patient to provide the reason for the visit, as well as the primary symptoms. This will help you determine the primary problem or issue.
- Present Infection: Gather a detailed detail of the condition currently and when it first began the progress of symptoms and the causes which can cause them to worsen or ease.
- Medical Histories: Inquire about the patient’s medical history such as hospitalizations, surgeries, and any other chronic illness or ailments they suffer from. This can give insight into the health concerns that could be underlying.
- Medicines: Document the patient’s current medication, which includes prescription drugs, over-the-counter medications as well as supplements. Make sure you ask questions about any allergies or adverse reactions to medications.
- Family Histories: Determine if there are any familial or genetic health conditions that are pertinent to the patient’s present symptoms or general health.
- Social Background: Discuss the patient’s lifestyle, which includes habits such as drinking alcohol, smoking cigarettes, and drug use as well as exercising. This data is crucial to determine the risk factors.
- Environmental and occupational exposures: Explore the patient’s workplace and home environments to determine the possibility of exposure in the form of allergens, toxic substances, or other hazardous substances.
- Allergies: List any allergy that is known to you, particularly those that are caused by food, medication, or environmental allergens.
Physical Examination:
- Vital Signs: Begin by taking a look at the vital signs of the patient, which include blood pressure as well as respiration rate as well as body temperature.
- general appearance: Pay attention to the patient’s general appearance, manner of speaking, and level of discomfort or distress.
- The Head and Neck: Take a look at the face and neck to determine signs of abnormalities including the ears, eyes, throat, nose as well and lymph nodes.
- Lungs and Chest: Examine the lung and chest function through auscultating breath sounds, and assessing chest motion. Check for symptoms of respiratory discomfort.
- Heart: Pay attention to the heart’s sounds to identify any irregular rhythms, murmurs, or other abnormalities.
- Abdomen: Auscultate and palpate the abdominal area to look for any swelling, tenderness, or organ swelling.
- Extremities: Examine the legs and arms for swelling, deformities, or circulation problems. Check joint mobility.
- Neurological Examining: Assess the patient’s mental state and cranial nerves, sensory and motor function reflexes, coordination, and.
- Skin Examining: Inspect the skin for rashes lesions discolorations, and indications of infection.
- Specialized Exams: Depending on the patient’s history and symptoms of the patient, conduct specialized tests that are specific to their complaints. For instance, an otoscope could be used to look into the ear, or a fundoscope for assessing the eyes.
Physical examination and medical history offer healthcare professionals with complete knowledge of the health of the patient and provide the basis for treatment and diagnosis. They can help determine the cause of symptoms, exclude certain ailments, and help guide further diagnostic tests or refer to specialists when required.
Overlapping Symptoms and Challenges in Diagnosis
Hay fever (allergic rhinitis) and sinusitis can present multiple symptoms that could make it difficult to discern from the different conditions.
Here are a few typical symptoms and issues they face in the diagnosis:
Common Symptoms:
- Nasal Congestion: Hay fever as well as sinusitis can result in nasal congestion and congestion which makes it difficult for people to breathe through their noses.
- Nose: Runny Nose: Both conditions can result in a swollen nose that is clear or thick mucus discharge.
- Snorting: Frequent sneezing can be a sign of sinusitis and hay fever because of irritation to the sinuses.
- Postnasal drip: Both of these conditions can cause postnasal drip in which mucus from the nose drips into the throat’s back which can cause irritation of the throat or cough.
- Face Pressure or Pain: Sinusitis is often the cause of facial pressure or pain, however, hay fever may cause facial discomfort as a result of sinus congestion.
- Headache: It is possible for headaches to be an indication of both conditions, especially when pressure or sinus congestion is present.
- The cause of Fatigue is: The combination of sinusitis as well as hay fever can cause fatigue because they can disrupt sleep and can cause discomfort.
Challenges in Diagnosis:
- Similar symptoms: The overlap in symptoms can make it difficult for patients to diagnose themselves and for healthcare professionals to distinguish between two diseases based solely on symptoms.
- Misdiagnosis: Because of the common symptoms, misdiagnosis of the condition is not unusual. People suffering from hay fever may be misdiagnosed as having sinusitis or the reverse, leading to inadequate treatment and long-term discomfort.
- Substantiating Causes: While hay fever is mostly due to exposure to allergens, sinusitis may have a myriad of causes that include bacterial or viral irritations, allergies, or anatomical concerns. Finding the root causes is vital to ensure effective treatment.
- Diagnostic tests: If the situation warrants it further diagnostic tests like images (e.g., CT scans) or allergy testing could be required to distinguish between the two conditions with certainty. They add complexity and expense to the process of diagnosing.
- Timing and duration: The duration of symptoms can be different. The symptoms of hay fever typically are permanent or seasonal, based on the allergen that was exposed and the severity of sinusitis. It can become acute (short-term) chronic (lasting longer than 12 weeks) or persistent.
- response to treatment: The response to treatment may occasionally give clues. Hay fever usually responds to antihistamines. However, they might not be effective against sinusitis. Contrary to this antibiotics are usually used to treat sinusitis due to bacterial causes however they are not effective for hay fever.
To tackle these issues and ensure a precise diagnosis, healthcare professionals often use a mix of elements, such as an extensive health history, a physical exam as well as the duration of symptoms, and, if required further diagnostic tests.
A consultation with a healthcare specialist is crucial for those with persistent or serious respiratory issues to ensure they receive the correct assessment and therapy.
What are the Similarities Between Hay Fever and Sinusitis?
It is known as Hayfever (allergic nasal inflammation) as well and sinusitis though distinct, share a few similarities in terms of symptoms and impacts on the respiratory system. This can make it difficult to differentiate from the other conditions.
Here are the most significant similarities:
- Nasal Congestion: Both sinusitis and hay fever cause nasal congestion and nasal congestion. The reason for this is swelling and inflammation of nasal passages.
- The runny Nose: Individuals with sinusitis or hay fever can have an irritated nose. The nasal discharge may be clear or thicker depending on the underlying reason.
- Snore: Frequent sneezing is a typical symptom in both of the conditions. It is a reaction to remove irritants and excessive mucus from nasal passages.
- Postnasal Drip: Both sinusitis and hay fever may cause postnasal drip where the excess mucus that has accumulated in the nasal passages drips down to the lower back of your throat. This can trigger irritation in the throat or cough.
- Face Pain or Pressure: While facial pain and pressure are typically connected to sinusitis, hay fever can also cause facial discomfort, especially if there is significant congestion in the sinuses.
- Headache: The headaches can occur as an indication of both conditions and are particularly common when there is sinus involvement. The swelling and pressure inside the sinuses can trigger headaches.
- fatigue: Both hay fever and sinusitis may cause fatigue. Sleep disturbances due to constriction, postnasal drip, or any other symptoms may contribute to fatigue.
- Eyes that are irritated: While it’s not the most common sign of sinusitis, symptoms of sinusitis can result in irritation to the eyes. But, itchy, watery, or red eyes are typically connected with hay fever.
- Difficulty Breathing: Both of these conditions can make it difficult for people to inhale through their noses. This can lead to breathlessness in the mouth.
It is important to remember that although both sinusitis and hay fever share these symptoms, they are caused by distinct causes, and require different approaches to treatment.
Hay fever is typically an allergic reaction to allergens such as dust mites, pollen, or pet dander. sinusitis can be caused by a variety of reasons, such as infections, allergies, irritants, and structural problems.
A precise diagnosis by medical professionals is vital in determining the root reason for these symptoms and then tailoring a treatment plan for the particular health issue.
Reference Books
Certainly, here are some reference books on various topics that you might find useful, depending on your area of interest or study. Please note that the availability of these books may vary depending on your location and the most recent publications.
General Reference:
- “The Oxford English Dictionary” – A comprehensive dictionary of the English language.
- “The Encyclopedia of World History” by Peter N. Stearns – Offers a comprehensive overview of world history.
- “The World Almanac and Book of Facts” – An annual publication providing up-to-date information on a wide range of topics.
Science and Technology:
- “Cosmos” by Carl Sagan – A classic exploration of the universe and our place in it.
- “The Feynman Lectures on Physics” by Richard P. Feynman – A series of lectures by the Nobel laureate that covers the fundamentals of physics.
- “Sapiens: A Brief History of Humankind” by Yuval Noah Harari – A thought-provoking examination of the history and impact of Homo sapiens on the world.
Medicine and Health:
- “Gray’s Anatomy” by Henry Gray – A renowned anatomy textbook used by medical students and healthcare professionals.
- “The Merck Manual of Diagnosis and Therapy” – A comprehensive medical reference book for diagnosis and treatment.
- “The Immortal Life of Henrietta Lacks” by Rebecca Skloot – Explores the intersection of medical ethics, race, and the history of cell culture in medicine.
Conclusion
Reference books are a great tool to expand your knowledge, examine different subjects, as well as delve further into specific topics of particular interest. If you’re a student a professional, or a keen learner the appropriate reference book can be an authoritative source and source of guidance.
Through these reference books to gain insight as well as access information and expand your horizons to enable you to understand what’s happening around you and make educated choices in your personal as well as professional.