Polyhydramnios and Oligohydramnios are two distinct conditions that are related to the amount of amniotic fluid in pregnancy. Knowing the distinctions between them is essential for both fetal and maternal health.
We will explore the definitions and causes, as well as the diagnosis and symptoms, as well as complications, management, and outcomes of polyhydramnios as well as oligohydramnios. We will also highlight their distinct characteristic and the need for prompt diagnosis and treatment.
Definition of Polyhydramnios
Polyhydramnios is a condition that occurs in pregnancy and is characterized by an excess accumulation of amniotic fluid in the amniotic sac. This is the protective shell that surrounds the growing fetus. In this situation it is when the amount of amniotic fluid is greater than the normal range of the gestational age of the individual and typically exceeds 2 Liters or an amniotic-fluid index (AFI) of 25 centimeters or more.
Polyhydramnios can manifest at different phases of pregnancy and could be associated with a variety of maternal and fetal causes that require constant surveillance and intervention to deal with any potential complications.
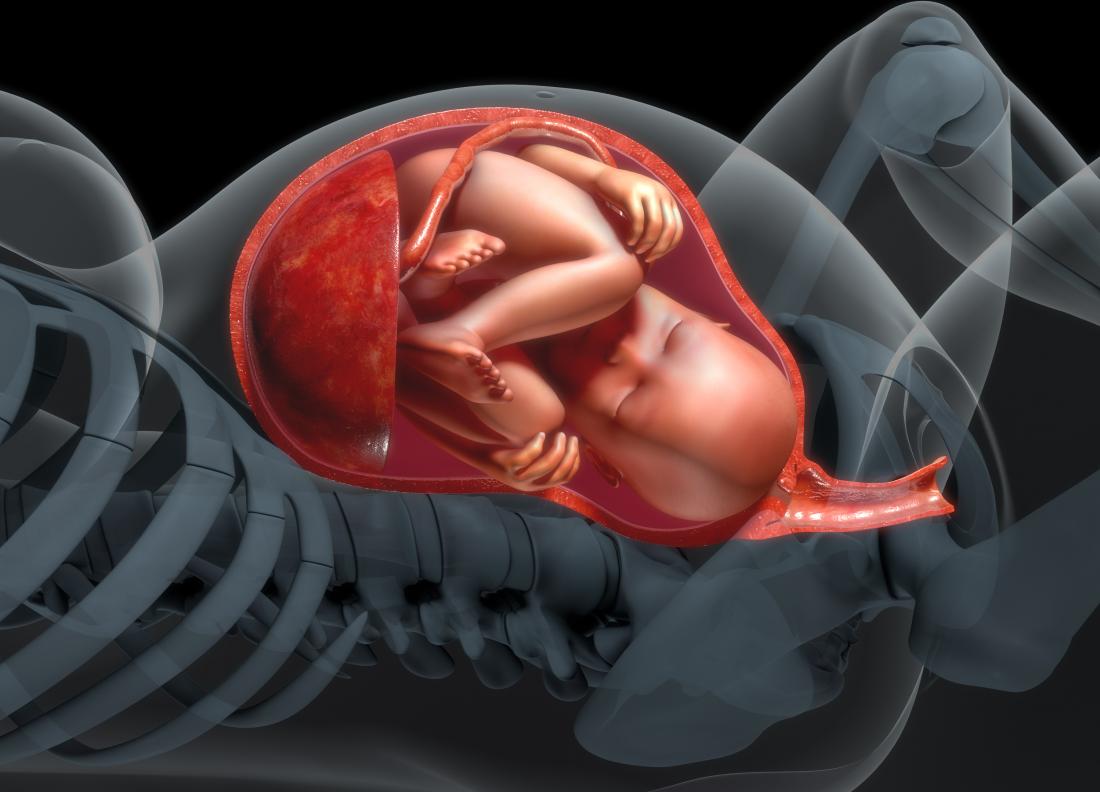
Definition of Oligohydramnios
Oligohydramnios is a medical issue that is present during pregnancy. It is identified by an unusually low amount of amniotic fluid inside the amniotic sac around the fetus that is developing. It is when the amount of amniotic fluid is lower than what is expected for the gestational age at which it can lead to the amniotic liquid index (AFI) that is less than 5 centimeters or an amniotic fluid total quantity below 500 milliliters.
Oligohydramnios may be caused by different fetal, maternal, or placental issues and can cause problems for the mother and the growing baby. Monitoring and management are vital when oligohydramnios are discovered to identify potential risks and ensure the most favorable outcome for the baby’s development.

The importance of distinguishing between Polyhydramnios and Oligohydramnios
Differentiating between polyhydramnios as well as oligohydramnios in the course of pregnancy is vitally important due to a variety of reasons:
- Clinical Management: The accurate identification of these conditions allows healthcare professionals to offer appropriate and customized medical treatment. The strategies to manage polyhydramnios as well as oligohydramnios vary and a proper diagnosis is crucial to determine the best procedure to take.
- Fetal Well-Being: Polyhydramnios and oligohydramnios may be a source of distinct effects on the health of a fetus. Polyhydramnios may cause complications like preterm birth or macrosomia (abnormally large fetus) and fetal malposition. the oligohydramnios may cause cord compression, growth restriction, and developmental problems. An accurate diagnosis can ensure that proper measures are implemented to manage and reduce the dangers.
- Maternal Health: The two conditions could affect the health of an expectant mother. Polyhydramnios can cause discomfort, and tension in the diaphragm, as well as other organs. It could also be related to conditions such as preeclampsia and gestational diabetes. Oligohydramnios may cause complications such as preterm birth which can pose risks to the mother’s health. A precise diagnosis is crucial for managing these maternal issues efficiently.
- Plan of Delivery: Knowing if a pregnant woman is impacted by polyhydramnios or the oligohydramnios condition is essential to plan the method and time of delivery. Polyhydramnios could increase the risk of cesarean sections due to the possibility of cord prolapse or other complications. Likewise, an oligohydramnios pregnancy may require the induction of labor earlier or other procedures to avoid distress of the fetus during labor.
- Identifying the Root Causes: Finding out the root causes of polyhydramnios and the oligohydramnios condition is essential to address any medical issues that could contribute to these ailments. An accurate diagnosis can be the basis for proper investigations and treatment for fetal and maternal factors like the presence of gestational diabetes or renal anomalies that require care.
- All-Purposes Pregnancy Outcomes: An accurate and timely distinction between these conditions could greatly affect the overall outcomes during the course of pregnancy. Early detection and proper treatment can reduce the risk of complications increase the health and wellbeing of both mother and baby, and improve the odds of a healthy birth and pregnancy.
Discerning between polyhydramnios and oligohydramnios is crucial to providing the best healthcare during pregnancy. This ensures that healthcare professionals are able to identify particular risks, develop management strategies, and make well-informed decisions to improve the safety and health of the mother-to-be as well as the fetus in development.
Comparison Table of Polyhydramnios and Oligohydramnios
Here is a comparison table highlighting the key differences between polyhydramnios and oligohydramnios:
| Aspect | Polyhydramnios | Oligohydramnios |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Excessive amniotic fluid accumulation (>2 liters or AFI > 25 cm) | Insufficient amniotic fluid (<5 cm or total volume <500 mL) |
| Occurrence | Uncommon | Less common |
| Gestational Timing | Can occur at any stage of pregnancy | Can occur at any stage of pregnancy |
| Potential Causes | Maternal factors (diabetes, multiple gestation) – Fetal factors (gastrointestinal or renal abnormalities) – Placental factors | Maternal factors (hypertension, preeclampsia) – Fetal factors (poor fetal kidney function) – Placental factors |
| Maternal Symptoms | Discomfort, abdominal distension | Concern about fetal well-being |
| Fetal Symptoms | Macrosomia (large baby) | Growth restriction |
| Fetal Complications | Preterm birth | Cord compression |
| Delivery Considerations | This may increase the likelihood of a cesarean section | May require early induction or other interventions |
| Monitoring and Diagnosis | Ultrasound evaluation – Amniotic fluid index (AFI) measurement | Ultrasound evaluation – Amniotic fluid index (AFI) measurement |
| Potential Long-term Effects | Risk of preterm birth | Developmental issues (due to compression) |
| Impact on Maternal Health | Discomfort, potential gestational diabetes, or preeclampsia | Risk of preterm labor |
| Impact on Fetal Health | Potential macrosomia and related complications | Growth restriction, risk of fetal distress |
| Management | Monitoring, and treating underlying causes – Potential amnioreduction (removing excess fluid) | Monitoring, and addressing underlying causes – Potential amnioinfusion (adding fluid) |
| Prognosis | Generally favorable with proper management | The prognosis depends on the cause and severity of oligohydramnios |
| Delivery Planning | May require careful planning due to increased risks | May necessitate early induction or other interventions |
Please note that both polyhydramnios and oligohydramnios can have varying degrees of severity and associated complications, so individual cases may differ in terms of their management and outcomes. Consultation with a healthcare provider is essential for proper diagnosis and management.
Amniotic fluid volume levels in each condition
Here are the levels of amniotic fluid volume related to polyhydramnios and Oligohydramnios:
- Polyhydramnios:
- Polyhydramnios is a condition that occurs when the volume of amniotic fluid is high in an abnormal way.
- Amniotic Fluid Index (AFI) is a standard measure to measure the volume of amniotic fluid usually higher than 24 centimeters.
- Another test used to determine the presence of polyhydramnios is the single-depth vertical pocket (SDVP) measurement that is greater than 8 cm.
- Polyhydramnios can be described as the presence of excessive amniotic fluid inside the uterus. This can result in the uterus expanding greater than what is normal for gestational age.
- Oligohydramnios:
- Oligohydramnios is identified when the volume of amniotic fluid in the body is unusually low.
- An AFI measurement that is less than 5 centimeters is typically interpreted as an indication of the oligohydramnios.
- A single deepest vertical pocket less than 2cm could also indicate oligohydramnios.
- Oligohydramnios is distinguished by a decrease in amniotic fluid that is found in the uterus that can result in a uterus that is smaller than the normal size for gestational age.
It is important to remember that the thresholds and measurements may differ a little bit based on the healthcare professional and the guidelines that are used in various healthcare environments. The correct diagnosis and assessment of the amniotic fluid level must be done by a certified medical expert.
Common causes of polyhydramnios and oligohydramnios
There are many most frequently occurring causes of polyhydramnios and Oligohydramnios:
Common Causes of Polyhydramnios:
- Maternal Factors:
- Diabetes: Poorly controlled maternal diabetes can cause excess urine production in the fetus leading to polyhydramnios.
- Obesity: The mother’s obesity has been associated with a greater probability of having polyhydramnios.
- Maternal Hydrops: Heart dysfunction or kidney disease could influence the regulation of amniotic fluid.
- Fetal Factors:
- Fetal Anomalies: Certain fetal anomalies like gastrointestinal or central nervous system problems may result in an increase in the production of amniotic fluid.
- The Twin-to-Twin Transfusion Syndrome (TSS): When twins are identical in their conception the blood flow imbalance between twins could cause polyhydramnios in one twin, and oligohydramnios in the other.
- Fetal Infections: Infections such as congenital cytomegalovirus (CMV) can impact the fetal swallowing process and production of urine which can lead to polyhydramnios.
- Idiopathic (Unknown) Causes:
- In certain instances, polyhydramnios can be present without a clear basis, and this is known as an idiopathic case of polyhydramnios.
Common Causes of Oligohydramnios:
- Maternal Factors:
- Dehydration: The dehydration that mothers experience, usually due to inadequate drinking of fluids or health conditions such as preeclampsia can result in reduced levels of amniotic fluid.
- Hypertension: Preeclampsia or chronic hypertension can impact placental blood flow and levels of amniotic fluid.
- Smoking, and Substance Abuse: These habits can decrease the flow of blood to the placenta, and can lead to oligohydramnios.
- Fetal Factors:
- Fetal Renal Issues: Issues with the kidneys in the fetus, for example, renal dysplasia, or renal agenesis may result in a decrease in the production of urine and, in turn, an increase in oligohydramnios.
- Post-Term Pregnancy: When pregnancies continue to grow past due dates the risk of developing the oligohydramnios condition may increase.
- Umbilical Cord Problems: Compression or restriction of the umbilical line can decrease the flow of blood to the fetus and levels of amniotic fluid.
- Placental Factors:
- Placental Insufficiency: Placental issues such as placental abruption or insufficiency can affect the amount of oxygen and nutrients to the fetus, thereby reducing the amniotic fluid volume.
- Membrane rupture: A rupture of amniotic membranes (premature rupture of membranes, or PROM) could result in the slow leakage of amniotic fluid, leading to oligohydramnios.
It is important to remember that the underlying causes of these ailments can overlap. Healthcare professionals will conduct a thorough examination to identify the underlying causes and appropriate treatment for each individual case.
A prompt diagnosis and early intervention are essential to ensure the most favorable results for the mother as well as the embryo.
Diagnostic methods for each condition
These are diagnostic techniques that are commonly used to assess and treatment of polyhydramnios, as well as oligohydramnios:
Diagnostic Methods for Polyhydramnios:
- Ultrasound: Ultrasound can be described as the most commonly used imaging technique to determine the volume of amniotic fluid and to diagnose polyhydramnios. Two major ultrasound measures are used:
- Amniotic Fluid Index (AFI): This method is based on taking measurements of the depth of the largest amniotic fluid pocket in the four quadrants of the uterus before taking these measurements and summing them. AFI greater than 24 cm and AFI over 24 cm is typically deemed to be indicative of polyhydramnios.
- One The Deepest Vertical Pocket (SDVP): This technique determines the deepest amniotic fluid that is found in the uterus. If the measurement is greater than 8 centimeters could suggest polyhydramnios.
- Amniotic Volume Assessment: Apart from AFI and SDVP Certain clinicians could employ other ultrasound-based methods such as an ultra-wide vertical pouch or the subjective assessment to assess the volume of amniotic fluid.
- Detail Fetal Anomaly Scan: A detailed ultrasound exam can reveal anomalies in fetal development or conditions contributing to polyhydramnios. This includes central nervous system or digestive anomalies.
Diagnostic Methods for Oligohydramnios:
- Ultrasound: Ultrasound also serves as the main diagnostic tool used to determine the amniotic fluid’s volume in the case of oligohydramnios. The same tests used to diagnose polyhydramnios may be used to:
- Amniotic Fluid Index (AFI): An AFI measurement of less than 5 centimeters is typically indicative of oligohydramnios.
- The Single deepest vertical Pocket (SDVP): Any measurement that is less than 2 centimeters could indicate the existence of oligohydramnios.
- Fetal Biophysical Profil (BPP): This test uses ultrasound in conjunction with an un-stress test to assess the health of a fetus. The volume of amniotic fluid is among the elements of the test, and decreased amniotic fluid levels are regarded as a negative sign.
- Amniocentesis: In certain cases especially when the reason for oligohydramnios is not clear or if the need is for more examination, amniocentesis can be conducted. Amniocentesis is the procedure of aspirating amniotic fluid with a needle. It may provide details about the condition of the fetus as well as the possible reasons.
- Monitor: Regular monitoring of the fetus ‘ health and the maternal with regular evaluations of fetal heart rates, will help detect indications of distress or other complications associated with oligohydramnios.
In both polyhydramnios as well as oligohydramnios an accurate diagnosis and monitoring is crucial to ensure the proper treatment and management all through the course of pregnancy. Healthcare professionals will employ the combination of these diagnostic techniques to assess the volume of amniotic fluid as well as its effect on maternal and fetal health.
Management and treatment approaches
The treatment and management for polyhydramnios and other oligohydramnios aim to tackle the root cause to alleviate symptoms and provide the most favorable results for both the mother and fetus.
Here are the typical approaches for each of the conditions:
Management and Treatment of Polyhydramnios:
- Monitoring: Continuous monitoring of Amniotic Fluid and the well-being of the fetus via ultrasound, as well as heart rate measurement is crucial to monitor the progress of polyhydramnios.
- Lifestyle Modifications:
- Dietary Changes: Cutting down on the intake of carbohydrates and sugar can aid in managing polyhydramnios that are related to gestational diabetes.
- Hydration: It is essential to avoid dehydration which can lead to excess amniotic fluid.
- Medicines: Medical professionals can prescribe drugs such as indomethacin or diuretics in order to lower amniotic fluid production.
- Amnioreduction: The procedure involves removing excess amniotic fluid via amniocentesis. It is usually reserved for the most severe cases of polyhydramnios accompanied by severe maternal discomfort or other complications.
- Treatment of the Causes: If polyhydramnios is caused by an abnormality or condition in the fetus the management strategy could focus on addressing the problem that could involve surgeries or specialized treatments.
Management and Treatment of Oligohydramnios:
- Identify and address the root Ursaches: The treatment of the condition is often about diagnosing and treating the primary cause, which could be the mother’s hypertension fetal kidney disorders, or problems with placental development.
- Fluid Supplementation: In some instances intravenous (IV) fluid hydration of the mother could be utilized to boost the levels of amniotic fluid temporarily. However, this is usually only a temporary solution that doesn’t tackle the root of the problem.
- Regular Monitoring: Healthcare professionals closely track fetal health by regularly performing ultrasounds and monitoring fetal heart rate to identify symptoms of distress.
- Fetal Evaluation: When oligohydramnios has been identified, further fetal tests like biophysical profile (BPP) could be conducted to determine the general health of the fetus.
- Preterm Delivery Considerations: In severe cases or when there are indications of distressing fetal development Healthcare professionals may suggest initiating labor or performing an emergency cesarean section to ensure the health of the fetus.
- Amnioinfusion: In the event that the oligohydramnios cause distress for the fetus in labor, an amnioinfusion can be administered. This is the process of injecting a sterile uterus-based fluid during labor in order to relieve stress on the umbilical cord and increase the oxygen levels of the fetus.
It’s crucial to understand that the treatment and management of oligohydramnios and polyhydramnios needs to be customized based on the particular situation and causes of each pregnancy.
Healthcare professionals will collaborate with women who are pregnant to create an individualized care plan that is based on their particular situation and the requirements of the baby. Regular prenatal visits and constant communication with a medical team are essential during the entire pregnancy.
Similarities Between Polyhydramnios and Oligohydramnios
Polyhydramnios, as well as oligohydramnios, are distinct conditions relating to the amniotic fluid volume in pregnancy. Although they differ in their features and consequences.
There are some commonalities between the two conditions:
- Maternal Monitoring: Both polyhydramnios and oligohydramnios need constant monitoring by the mother throughout the pregnancy. Regular visits to the prenatal clinic ultrasounds, prenatal visits, and fetal evaluations are crucial in both instances to monitor amniotic fluid levels as well as the well-being of the fetus.
- Potential Complications: Both conditions could result in complications for the mother as well as the fetus. These issues could be caused by preterm birth, growth restrictions, and an increased chance of a cesarean birth.
- Higher Risk of Cesarean Section: In extreme instances, both polyhydramnios and oligohydramnios can increase the risk of having a cesarean. Polyhydramnios may result in an increase in the size of the uterus making vaginal delivery more difficult, whereas oligohydramnios can require Cesarean birth because of concerns over fetal distress.
- Fetal Monitoring: It is vital to monitor the fetal health to assess the health of the infant. It could include the electronic monitoring of fetal heart rate as well as other tests such as biophysical profile (BPP) to evaluate the baby’s movements as well as breathing, tone, and levels of amniotic fluid.
- Potentially need for intervention: Based on how severe these ailments are and their effect on the fetus’ development, healthcare professionals might need to intervene. It could be amnioreduction (for polyhydramnios) or amnioinfusion (for the oligohydramnios) to maintain the amniotic fluid level during labor.
- Higher Risk of Underlying Conditions: Both polyhydramnios and oligohydramnios are often associated with an underlying condition that affects the mother or the child. For instance, diabetes in the mother is an important risk factor for both conditions, but differently.
- A Close Co-operation with Health Care Providers: Women who are pregnant and suffering from either condition should collaborate closely with their healthcare professionals to ensure proper treatment and care throughout the pregnancy. Communication is open and frequent appointments with the doctor prior to birth are vital.
Even though these features are similar, it is important to understand that polyhydramnios and oligohydramnios are caused by distinct diagnoses, causes, and management strategies. So, an accurate diagnosis and customized treatment are crucial to treat the condition in a timely manner and provide the most favorable results for the mother and the fetus.
Conclusion
Although polyhydramnios, as well as oligohydramnios, have certain commonalities, they’re two distinct conditions with distinct consequences for pregnant women. Both require constant surveillance and could cause complications, however, a precise diagnosis and an individualized treatment are essential in addressing the specific features and reasons for each.
Early intervention and thorough prenatal care play an important part in maximizing the outcomes of both mommy as well as the fetus, in cases of polyhydramnios as well as oligohydramnios.