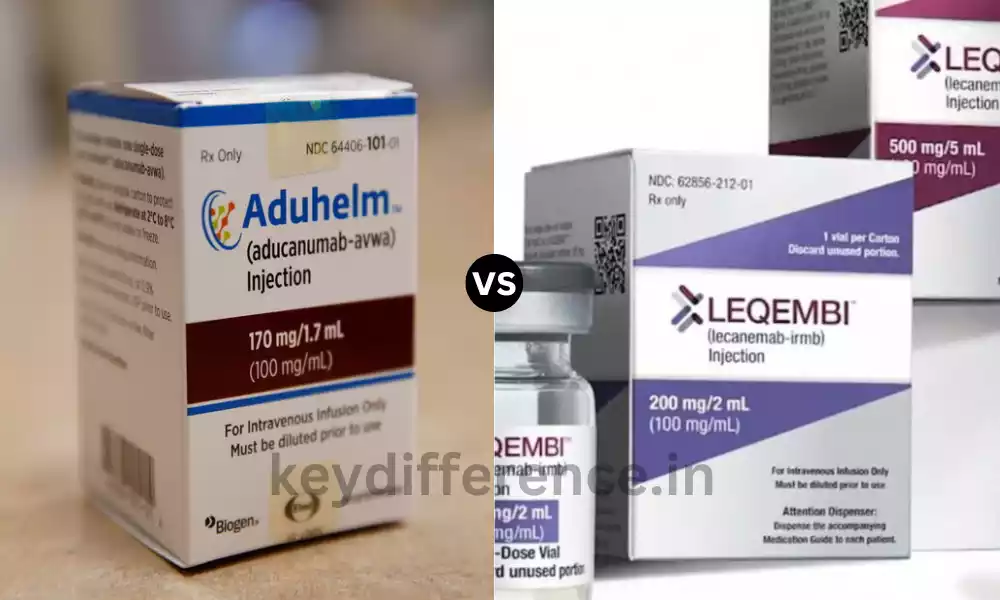
Alzheimer’s Disease is a devastating neurological condition that impacts millions of people across the globe. Despite the increasing incidence of the disease, the effectiveness of treatments has been sporadic. Recently two promising medications, Aducanumab and Lecanemab, are emerging as potential treatments that have distinct actions and clinical outcomes.
The main distinctions in Aducanumab and Lecanemab offer valuable insights into their progress, clinical trials, and regulatory status, as well as safety profiles, and possible positives and negatives. Understanding these differences is vital for healthcare professionals, patients, and researchers who are trying to navigate the maze of Alzheimer’s disease treatment.
What is Aducanumab?
Aducanumab is a monoclonal medication developed to treat Alzheimer’s disease. It targets specifically amyloid beta which is a protein that builds amyloid plaques within the brains of people suffering from Alzheimer’s disease.
Through binding to and aiding in the elimination of amyloid plaques, Aducanumab hopes to stop the progression of Alzheimer’s disease and possibly improve the cognitive functioning of some people. It received a lot of interest and controversy because of its approval by the U.S. Food and Drug Administration (FDA) as well as the inconsistent results of clinical studies.
What is Lecanemab?
Lecanemab (brand name Leqembi) is a monoclonal antigen medication that is used to treat Alzheimer’s disease. This is an amyloid beta-directed antigen which means it binds with and eliminates amyloid beta plaques out of the brain. Amyloid beta plaques can be considered to be one of the most prominent symptoms of Alzheimer’s disease and they are believed to play an important key role in the progression of the disease.
Lecanemab can be administered as an intravenous infusion at intervals of two weeks. It’s approved for the treatment of people suffering from early Alzheimer’s disease, which includes those suffering from moderate cognitive impairment (MCI) as well as mild cognitive impairment caused by Alzheimer’s disease, who have confirmed an increase in beta-amyloid levels in the brain.
Lecanemab was granted an expedited acceptance by the US Food and Drug Administration (FDA) in January 2023. It was fully approved in July 2023. It’s the first Alzheimer’s treatment that has been shown to slow the progress of the illness.
lecanemab was shown to reduce the amyloid beta plaques that are found in the brain and to slow functional and cognitive decline in patients with Alzheimer’s disease in the early stages. The most frequently reported side effects of the drug include headache, infusion-related reactions, and amyloid-related imaging abnormalities.
Lecanemab is an exciting new therapy for people suffering from Alzheimer’s however, it is crucial to keep in mind that it’s not an effective cure. It is crucial to discuss the potential risks and benefits of lecanemab with a physician prior to starting treatment.
Comparison Table of Aducanumab and Lecanemab
| Feature | Aducanumab | Lecanemab |
|---|---|---|
| Mechanism of Action | Targets amyloid beta plaques in the brain to reduce their accumulation. | Also targets amyloid beta, aiming to reduce plaques in the brain. |
| Clinical Trials | Underwent Phase I, II, and III trials, with FDA approval (controversial) | Ongoing clinical trials (status may vary). |
| Regulatory Status | Approved by the FDA for the treatment of Alzheimer’s disease. | Status may vary, and may not have received FDA approval (as of 2021). |
| Efficacy | Showed some efficacy in reducing amyloid plaques, but the results were mixed. | Efficacy data and clinical outcomes may vary depending on trials. |
| Safety Profile | Associated with common side effects and adverse reactions. | Safety profiles may differ, with potential advantages or drawbacks. |
| Advantages | Early market availability (conditional) for Alzheimer’s patients. | Potential safety advantages or alternative treatment options. |
| Disadvantages | Controversial approval process and limited clinical evidence. | Uncertain regulatory path and potential differences in efficacy. |
Please note that this is a general comparison and may not reflect the most recent developments or nuanced differences between these two drugs. Clinical trial results and regulatory statuses may have changed since my last update, so it’s crucial to consult the latest medical literature and official sources for the most current information.
Effectiveness in reducing amyloid plaques
At the time of my last information report in the month of September 2021, the two Aducanumab as well as Lecanemab was a drug that had been tested in the lab and designed to treat amyloid beta plaques found in the brains of people suffering from Alzheimer’s disease. The effectiveness of decreasing amyloid plaques differed with these drugs and the clinical trial results are still being studied and discussed.
- Aducanumab:
- The clinical trials conducted with Aducanumab proved that it can effectively decrease amyloid plaques inside the brain. It was created to attach to amyloid beta proteins and assist in the removal of amyloid beta from the brain.
- However, the efficacy of Aducanumab in the reduction of amyloid plaques was the subject of controversy as several studies revealed mixed results with respect to cognitive improvement. The FDA’s approval was given with some conditions and guidelines for further studies.
- Lecanemab:
- Lecanemab is, along with Aducanumab also designed to decrease amyloid beta plaques within the brain.
- Lecanemab’s effectiveness in reducing plaque formation of amyloid can depend on the data from clinical trials and the development stage. Lecanemab could possess its own distinct features and results in this regard. These can be analyzed through clinical studies.
It is important to recognize that the efficacy of these medications for reducing plaques of amyloid as well as how this effect is related to better cognitive performance remains an ongoing subject of studies and discussions.
Results from clinical trials as well as the stages of drug development, and the regulatory decision could have changed in the time since I last updated. To get the most up-to-date and complete details, it is recommended to read the most up-to-date research literature and reliable sources.
How Aducanumab and Lecanemab target amyloid beta plaques differently
At the time of my last information report in the month of September 2021, the two Aducanumab along with Lecanemab were monoclonal antibodies specifically designed to fight amyloid beta plaques that are found in the brains of patients with Alzheimer’s disease. Although both drugs have the same goal they have different ways of working and targeting the amyloid beta system.
This is a general description of why they are able to target amyloid beta plaques in a different way:
- Aducanumab:
- Aducanumab specifically targets amyloid beta aggregates (Ab) proteins that reside in the brain.
- This is an immunoglobulin G1 (IgG1) monoclonal antibody that binds to beta-amyloid protein, primarily the insoluble and aggregated types (amyloid plaques).
- By binding to the clustered Ab Proteins, Aducanumab is believed to assist in the removal of these proteins by the body’s own natural immune systems. It may help in reducing the accumulation of amyloid plaques within the brain.
- Lecanemab:
- Lecanemab is, just like Aducanumab a different monoclonal antibody designed to attack amyloid beta.
- The precise mechanism of action of Lecanemab could differ in terms of particular regions or types of amyloid beta that it is targeting.
- Lecanemab could also function in conjunction with the clustered Ab proteins, however, it could have distinct properties in relation to its affinity for various kinds of Ab and how it assists in the removal of these proteins.
It’s crucial to keep in mind that the exact methods and goals of these drugs can differ, and the most current research and clinical information are required to determine the exact nature of their distinctions.
The science behind and the development of these drugs could have changed since the last update, and so examining the most current research literature and data from pharmaceutical companies could give you more accurate information on the mechanisms that they work and the way they differ in their approach to amyloid beta plaques.
FDA approval and any regulatory hurdles or concerns
- FDA approval: Aducanumab, developed by Biogen was granted preliminary approval from the U.S. Food and Drug Administration (FDA) in June 2021. The drug was the only medication that was approved to treat Alzheimer’s disease for more than two decades.
- Conditional approval: The FDA gave conditional approval based on the drug’s capacity to decrease amyloid plaques within the brain. However, this approval came with the requirement that Biogen carry out a second clinical trial in order to confirm the effectiveness of the drug and confirm its effectiveness in the treatment of Alzheimer’s disease. The “accelerated approval” pathway was highly controversial since it was based on an alternative measure (reducing amyloid plaques) instead of clinically proven benefits.
- Controversy and debate: The FDA’s decision to approve Aducanumab sparked controversy. Researchers and experts expressed reservations about the medication’s effectiveness in clinical trials and the lack of evidence to prove its ability to enhance cognitive function. The conditional approval as well as the cost-intensive nature of the treatment raised questions about the ethics and economics of the treatment.
- Continuous Research and Monitoring: After approval, the effectiveness and safety of Aducanumab were to be monitored closely in the post-marketing studies that were required. This decision by the FDA to approve the drug conditionally the drug was a unique method of treating Alzheimer’s disease. It also triggered discussions on the process of approving new therapies.
It’s important to know how the situation with Aducanumab and any related regulatory issues could have changed in the time since I last updated. For the most up-to-date information regarding this drug’s FDA approval as well as any subsequent developments or issues, I suggest reviewing these FDA announcements, as well as the most recent medical literature.
Implications for Alzheimer’s disease patients and the healthcare industry
The FDA approval as well as the controversies around medications such as Aducanumab and Lecanemab have important implications for those suffering from Alzheimer’s disease as well as the healthcare industry:
Implications for Alzheimer’s Disease Patients:
- Treatment options: The approval of medicines such as Aducanumab may provide alternative treatments for people suffering from Alzheimer’s disease. This could be a promising way to slow the progress of the disease and potential improvement in cognitive function.
- Uncertainty and Controversies: The debates surrounding the efficacy and approval of these medications could result in uncertainty for patients. Patients may be uncertain about the best way to proceed with these drugs, particularly considering the conditional approval as well as ongoing research.
- Cost and accessibility: The expense of these treatments can be a hurdle for a large number of patients. In-pocket and insurance coverage could be a major concern for families and individuals.
- Monitoring and adverse effects: Patients need to be monitored closely for possible adverse effects or side effects that may be caused by these medications. This requires attentive coordination between caregivers, patients as well and healthcare providers.
Implications for the Healthcare Industry:
- The Regulatory Pathways: Appropriation of Aducanumab as well as similar drugs via the expedited approval process has raised questions about how the future Alzheimer’s treatment options will be assessed and if they will be approved. It could cause modifications to the regulatory process for the approval of new drugs.
- Research and Development: The controversy and the conditional approvals underscore the necessity for ongoing research and advancement in the area of Alzheimer’s disease. Research and development companies can be focused on improving and refining the treatments or looking at other options.
- Healthcare costs: The cost of these medicines could have a significant impact on the cost of healthcare. Insurance companies and healthcare providers will have to think about the implications of this for their business and insurance alternatives for patients.
- Patient and caregiver education: Healthcare providers will require investment in education for caregivers and patients to ensure that patients are informed about the benefits, dangers, and drawbacks of these procedures. This is crucial to the sharing of decisions.
- Monitoring Post-Marketing: Monitoring on a regular basis of the effectiveness and safety in real-world environments will be crucial. Healthcare industry players will play an important role in acquiring and analyzing data to determine the long-term effects of these therapies.
The apprehension of approval for drugs such as Aducanumab and Lecanemab offers both benefits and challenges for Alzheimer’s patients as well as for the healthcare industry.
The approval of these drugs could open up alternative treatments while raising concerns about the regulatory process, cost, and the necessity for continuous research and patient education. The changing nature of Alzheimer’s disease treatment will likely continue to influence the approach of healthcare professionals to control this disease.
Similarities Between Aducanumab and Lecanemab
- Targeting Amyloid Beta: Both drugs target Amyloid Beta (Ab) plaques that are found in the brain. These plaques are a characteristic of Alzheimer’s disease. They are designed to decrease the amount of plaques that accumulate.
- Mechanism of action: Aducanumab and Lecanemab are both monoclonal antibodies that is, they are designed to bind specific proteins, specifically, Ab proteins, and help in the removal of them from the brain.
- Clinical Studies: The two drugs were or were in the process of undergoing clinical trials to test their effectiveness and safety in Alzheimer’s patients. The majority of these trials comprise phases to evaluate safety, efficacy, and long-term effects.
- Potential Impact upon Disease Progression: The main purpose of the two drugs Aducanumab as well as Lecanemab is to slow down the progress of Alzheimer’s disease and possibly conserve cognitive function and living quality in patients with the disease.
- The Regulatory Process: The two drugs were subjected to review by regulators for example, an FDA procedure for approval within the United States, which involves the evaluation of their safety and effectiveness.
- Continuous research and Development: The advancement of these drugs reflects continuous research efforts to discover efficient treatments for Alzheimer’s. This is a sign of a commitment to address a critical medical need.
It is important to note that the specific characteristics as well as the clinical results and the regulatory status of these medications may have changed from my previous update. For the most up-to-date information on the differences and similarities between Aducanumab and Lecanemab.
It is recommended to check out the most recent research, results of clinical trials, and official information that is provided by pharmaceutical companies as well as regulatory bodies.
References books
Here are some general recommendations by category:
Fiction:
- “To Kill a Mockingbird” by Harper Lee
- “1984” by George Orwell
- “Pride and Prejudice” by Jane Austen
- “The Great Gatsby” by F. Scott Fitzgerald
- “The Catcher in the Rye” by J.D. Salinger
Non-Fiction:
- “Sapiens: A Brief History of Humankind” by Yuval Noah Harari
- “Becoming” by Michelle Obama
- “Thinking, Fast and Slow” by Daniel Kahneman
- “The Immortal Life of Henrietta Lacks” by Rebecca Skloot
- “Educated” by Tara Westover
Science and Technology:
- “The Selfish Gene” by Richard Dawkins
- “Cosmos” by Carl Sagan
- “The Innovators” by Walter Isaacson
- “The Gene: An Intimate History” by Siddhartha Mukherjee
- “The Emperor of All Maladies” by Siddhartha Mukherjee
History:
- “A People’s History of the United States” by Howard Zinn
- “The Guns of August” by Barbara W. Tuchman
- “The Wright Brothers” by David McCullough
- “Genghis Khan and the Making of the Modern World” by Jack Weatherford
- “The Second World War” by Sir Winston Churchill
Conclusion
Aducanumab and Lecanemab as possible Alzheimer’s disease treatment options, bring both potential and uncertainty to the world of healthcare. Both drugs, though sharing the aim of reducing the amyloid plaques that accumulate in the brain, show differences in their regulatory routes and safety profiles as well as their clinical effectiveness.
The debates and doubts regarding their approval can have implications for patients suffering from Alzheimer’s disease and the overall healthcare industry. Research, education of patients, and monitoring with care are crucial in navigating this complicated landscape, and also in providing the urgent need to develop effective treatments for Alzheimer’s disease.