Dermatofibroma and dermatofibrosarcoma are distinct skin conditions that have a similar name, however, they differ greatly in terms of their causes and effects. While the dermatofibroma condition is a benign lesion that is often seen at the edges, dermatofibrosarcoma can be an uncommon and deadly cancer that is dangerous and invasive.
The primary features, symptoms, diagnosis, and the key distinctions between the two types of cancer and emphasize the importance of a precise diagnosis and timely medical care.
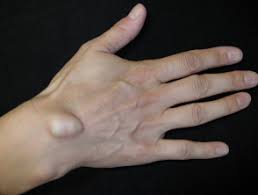
What is Dermatofibroma?
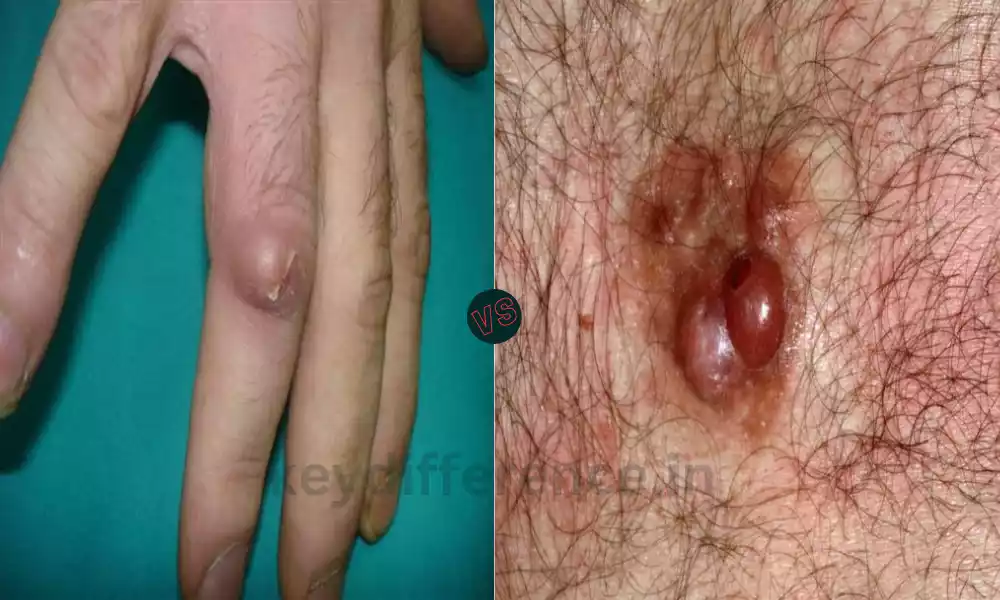
Dermatofibroma is a frequent benign skin condition that is characterized by a bump or nodule on the surface of your skin. The nodules usually develop on the extremities, more often on leg muscles, but are typically present in adults.
Dermatofibromas tend to grow slowly and are considered to be non-cancerous. They may be reddish brown to a purplish shade and typically are firm to the touch. Although generally harmless Dermatofibromas may differ in appearance and texture which makes their diagnosis essential to differentiate them from more dangerous skin conditions.
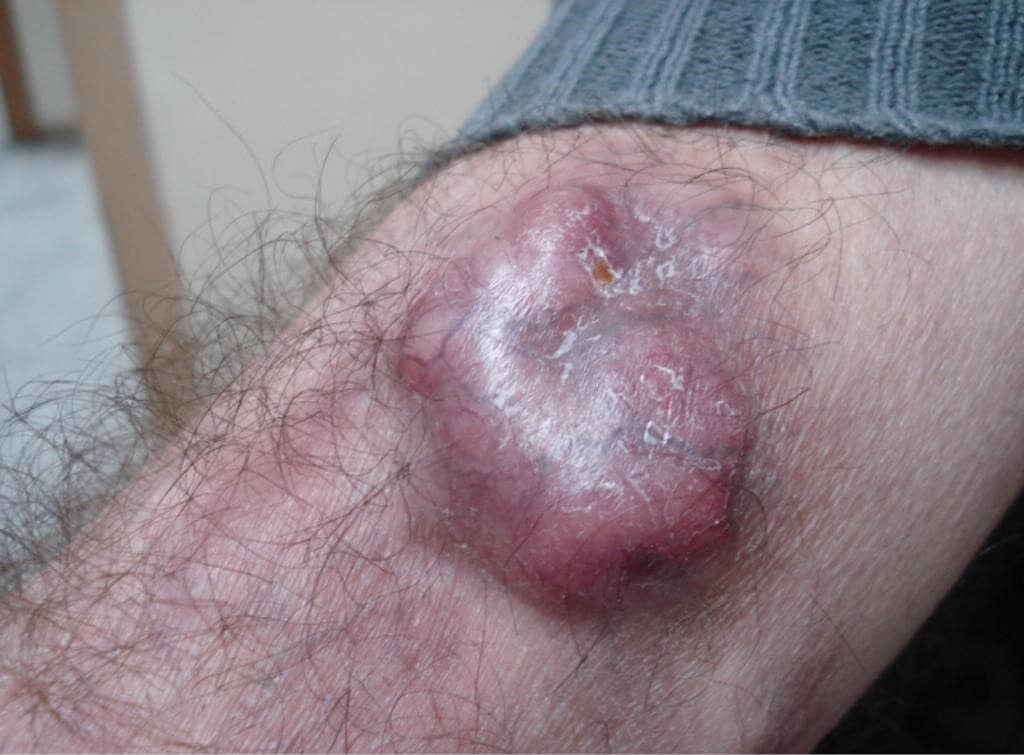
What is Dermatofibrosarcoma?
Dermatofibrosarcoma, also called dermatofibrosarcoma protuberans (DFSP) is a rare, malignant skin tumor that develops from the body’s soft tissue most notably that of the dermis layers of skin. Contrary to dermatofibroma extremely invasive and aggressive.
It grows gradually over time, but it can spread into deeper layers of muscles, skin, and, sometimes, adjacent structures. If it is not treated it is possible for it to spread so early detection and appropriate treatment are essential. Treatment usually involves surgical excision but in rare cases, additional treatments like chemotherapy and radiation might be required.
Importance of distinguishing between Dermatofibroma and Dermatofibrosarcoma
The distinction between dermatofibroma and Dermatofibrosarcoma is crucial because of these reasons:
- Treatment Method: Dermatofibroma is a benign skin lesion that usually doesn’t require aggressive treatment, and typically requires only an observation or simple removal to improve appearance. Contrarily, Dermatofibrosarcoma could be an aggressive tumor that requires more intense treatment, which could include extensive surgery, radiation or chemotherapy. Making the mistake of assuming one is another could result in unnecessary or delayed treatment.
- Prognosis: A precise diagnosis can be vital to determine the likely course of the disease. Dermatofibroma is a well-proven diagnosis and is not a risk for metastasis. Contrarily, Dermatofibrosarcoma could be invasive locally and could recur after the excision, and it could even spread, resulting in uncertain and possibly life-threatening outcomes.
- Psychological Effects: Misdiagnosis or confusion between these two disorders can result in unwarranted stress for patients. Incorrectly classifying benign dermatofibroma into malignant Dermatofibrosarcoma could cause excessive anxiety. However, not recognizing the malignant character of Dermatofibrosarcoma may delay the treatment that is lifesaving.
- Health Resource Allocation: The proper differentiation between the two types of conditions guarantees the efficient utilization of healthcare services. Inadequate tests, treatments, or consultations could cause stress on the healthcare system and add to healthcare costs. This can be avoided by obtaining accurate diagnoses.
- Research and Data Collection: A precise diagnosis is essential to collect reliable medical and epidemiological information. These data can aid in determining the frequency of the condition, risk factors, as well as results of these illnesses and aid in research treatments, as well as medical guidelines.
Discerning between Dermatofibrosarcoma and dermofibroma is crucial to ensure appropriate treatment and improve the patient’s outcomes decrease psychological distress as well as optimize resource allocation, and aid in medical research to enhance our understanding and treatment of these skin diseases.
Comparison Table of Dermatofibroma and Dermatofibrosarcoma
Here is a comparison table of Dermatofibroma and Dermatofibrosarcoma:
| Characteristic | Dermatofibroma | Dermatofibrosarcoma |
|---|---|---|
| Nature | Benign skin lesion | Malignant soft tissue tumor |
| Growth Rate | Slow-growing | Slow-growing but invasive |
| Common Locations | Extremities, often legs | Can occur anywhere on the body |
| Clinical Features | Small, firm nodule Typically painless | Raised nodules, often purplish May be painful or tender |
| Diagnosis | Clinical examination Dermoscopy Biopsy | Clinical examination Imaging (MRI, CT) Biopsy |
| Staging and Prognosis | Not applicable | Staging used for prognosis Good prognosis for localized cases, potential for recurrence and metastasis |
| Treatment and Management | Observation Surgical excision for cosmetic reasons | Surgical excision Radiation therapy Chemotherapy (rarely) |
| Metastasis Risk | Does not metastasize | Can potentially metastasize |
| Psychological Impact | Usually minimal distress | May cause significant distress and anxiety |
| Importance of Accurate Diagnosis | Rule out malignancy | Early detection is critical |
| Research and Data Collection | Important for data collection | Critical for research and treatment guidelines |
This table provides a concise overview of the key differences between dermatofibroma and Dermatofibrosarcoma in terms of their nature, clinical features, diagnosis, prognosis, treatment, and their impact on patients and medical research.
Advantages of Dermatofibroma and Dermatofibrosarcoma
It’s crucial to know that Dermatofibrosarcoma and dermatofibroma are two different types of cancer that are distinct, with dermatofibroma being an innocent skin lesion, and Dermatofibrosarcoma, a malignant cancer of the soft tissues. Neither of them offers any intrinsic advantages.
We can talk about the advantages within the area of medical management as well as understanding:
Advantages of Dermatofibroma:
- Early detection: Dermatofibromas are usually easily diagnosed and identified. Early detection can provide timely relief for the patient and also prevent needless stress.
- low health risks: Dermatofibromas are harmless and do not pose major health risks. They’re usually unnoticeable and do not require a hefty treatment.
- Affordable Medical Prices: Treatment of dermatofibromas can be generally less costly and less resource-intensive than malignant conditions.
- Cosmetic Issues: If the dermatofibroma creates cosmetic issues on the part of the person suffering from it, removal by surgery can enhance the appearance of the patient, offering the opportunity for those looking for improvements in appearance.
Advantages of Accurate Diagnosis of Dermatofibrosarcoma:
- Rapid Treatment: A timely and accurate diagnosis of Dermatofibrosarcoma is crucial since it permits the prompt and efficient treatment of the disease and increases the chances of favorable treatment.
- The most effective treatment planning: Understanding the exact diagnosis allows doctors to design and implement appropriate treatment strategies, like radiation, surgery, or chemotherapy.
- Optimized patient care: Accurate diagnosis facilitates greater communication between healthcare professionals as well as the patient which allows for a more comprehensive approach to care and assistance.
- Improved Research: The ability to identify the cause of the disease is helpful in the collection of data research, as well as the formulation of treatment guidelines increasing our understanding of the disease as well as possible treatment options.
The benefits aren’t inherent to the condition itself but to a precise diagnosis and the appropriate treatment of these conditions. This could ultimately improve the outcomes of patients and decrease unnecessary stress.
Disadvantages of Dermatofibroma and Dermatofibrosarcoma
There are certainly some disadvantages associated with dermatofibroma or the Dermatofibrosarcoma:
Disadvantages of Dermatofibroma:
- Possibility of Misdiagnosis: Dermatofibromas may be misinterpreted as other skin disorders which can lead to misdiagnosis, unneeded tests or treatments as well as distress for patients.
- Cosmetic concerns: Though generally benign Dermatofibromas can cause problems with the appearance of some people and can cause distress.
- Diagnostic uncertainty: In some instances, the definitive diagnosis of dermatofibroma could require a biopsy. The procedure can be uncomfortable and result in a tiny wound at the biopsy site.
Disadvantages of Dermatofibrosarcoma:
- Abrupt Nature: Dermatofibrosarcoma is a cancerous soft tissue tumor that has the potential to invade adjacent tissues, which makes it difficult to treat and possibly life-threatening.
- Emotional Stress: The diagnosis of dermatofibrosarcoma may create significant anxiety and stress for both the patient as well as their loved ones due to its malignant character.
- Complex treatment: The treatment for Dermatofibrosarcoma typically involves surgical removal that can be invasive and sometimes disfiguring. Other treatments, like chemotherapy or radiation, could be required.
- The risk of recurrence: After a successful treatment, dermatofibrosarcoma could develop a second time, which requires monitoring for a long time and care for follow-up.
- Metastasis-Risk: Dermatofibrosarcoma has the possibility of spreading to other organs which can drastically reduce the patient’s chances of survival and the quality of their life.
- Health Care Costs: Treatment of dermatofibrosarcoma may be expensive and time-consuming because of the necessity for surgeries, follow-up treatment, and adjuvant therapies that could be used.
The disadvantages of these diseases are mostly due to their clinical features as well as the possibility of misdiagnosis, emotional effects, and the difficulty and expense of treatment. Correct diagnosis and the right treatment are essential to improving the outcomes of patients.
Similarities Between Dermatofibroma and Dermatofibrosarcoma
Dermatofibroma and Dermatofibrosarcoma are distinct skin conditions with different features:
There are, however, some similarities:
- Skin Lesions: The two conditions are characterized by skin irregularities and the appearance of bumps or nodules that appear on the skin’s surface.
- Common Localization: The dermatofibroma tumor can occur in different locations such as the extremities, it’s not restricted to a specific region. Dermatofibrosarcoma is, on the contrary, it’s possible to develop everywhere in the body.
- Clinical Exam: The first assessment of both conditions usually requires a clinical examination conducted by a health professional.
It’s essential to highlight that the character, nature, and consequences of the two conditions are very different in that dermatofibroma is a benign skin lesion, and dermatofibrosarcoma is a malignant, cancer of the soft tissues. A precise diagnosis and distinction between the two is crucial to ensure the proper treatment and outcomes.
What are their clinical features?
The clinical characteristics of dermatofibroma as well as dermatofibrosarcoma can be distinct because of their distinct characteristics. Here’s a brief overview of their clinical characteristics:
Dermatofibroma:
- Description: Dermatofibromas typically present as firm, small bumps or nodules on the surface of your skin. They usually appear either reddish or brownish or a deep purplish color.
- TextureIn the event of contact, Dermatofibromas can feel a bit like they’re hard or spongy. They might also have a slightly depressed or dimpled center when seen from a side, creating an appearance that is “button-like” appearance.
- The pain: Dermatofibromas are generally not painful, however, they could occasionally be tender or itchy when they are irritated or rubbed.
- Localization: They are commonly found on the extremities of the body, especially in the legs. But, they can also be found in other areas of the body too.
Dermatofibrosarcoma:
- appearance: Dermatofibrosarcoma typically presents as a firm, raised, and sometimes purplish-colored bump or nodule within the body. The texture and color of the lesions can differ.
- Texture: Lesions of this kind can feel rough and can be painful or tender when touched, particularly when they’re irritated.
- Development: Unlike dermatofibroma, Dermatofibrosarcoma is characterized by its slow but locally invading growth that can spread into the deeper layers of skin and surrounding tissues.
- Localization: Dermatofibrosarcoma can occur everywhere on the body, and isn’t restricted to a specific area. It is located on the limbs, trunk, and neck, as well as the head.
Though both of them can manifest as skin nodules, their medical characteristics, such as appearance, texture, and the characteristics of growth, differ. Dermatofibromas are generally benign and stable, while dermatofibrosarcoma can be a malignant soft tissue cancer that has invasive characteristics.
A precise diagnosis, which often involves biopsy, is essential in determining the difference between these two types because of their distinct clinical characteristics and implications.
How are they diagnosed and treated?
The treatment and diagnosis for Dermatofibroma as well as dermatofibrosarcoma vary significantly due to their distinct characteristics.
Here’s a brief overview of the way these conditions are generally diagnosed and treated:
Dermatofibroma:
Diagnosis:
- Clinical Examining: Dermatofibromas are often identified based on a physical exam conducted by a health professional. They are distinguished by features like their appearance and appearance.
- Dermoscopy: Dermoscopy is a safe diagnostic procedure that can be utilized to look at the specifics of the lesion more precisely.
- Biopsy: When there’s doubt as to what the cause is or to exclude any other issues, a biopsy could be conducted. It involves the removal of a small tissue sample from the site of injury to be examined microscopically.
Treatment:
- Note: Dermatofibromas are typically benign and don’t require treatment. If the lesion is not symptomatic and does not cause cosmetic issues or cause any concern for the appearance, a “watch and wait” approach could be suggested.
- Surgery Excision: If a dermatofibroma causes discomfort or cosmetic concern it is able to be surgically eliminated, which is usually done with local anesthesia. The procedure involves the removal of the lesion and the margin that is healthy.
Dermatofibrosarcoma:
Diagnosis:
- Clinical Exam: Dermatofibrosarcoma is initially diagnosed by a clinical exam however, it is required to undergo additional evaluation to confirm the diagnosis.
- Imaging: Imaging studies such as MRI (Magnetic Resonance Imaging) or CT (Computed Tomography) scans are utilized to evaluate the extent of tumors and their possible involvement in the deeper tissues.
- A biopsy: Biopsy is essential for a precise diagnosis. A tissue sample is collected from the area of the lesion for histological analysis. This can verify the diagnosis of Dermatofibrosarcoma.
Treatment:
- Surgery Excision: The most common treatment for dermatofibrosarcoma involves wide surgical excision. The goal of surgeons is to eliminate the tumor and an area of healthy tissue in order to reduce the chance of recurrence. Reconstruction is sometimes required for more extensive removals.
- Treatment with Radiation: The use of radiation therapy is suggested to ensure the total removal of remaining cancerous cells and to reduce the possibility of repeat cancer.
- Chemotherapy: Chemotherapy has not been widely utilized to treat dermatofibrosarcoma. However, it can be thought of in cases of an aggressive or metastatic disease.
- Therapeutic Targeting: Emerging treatments, such as targeted therapy, or immunotherapy are being studied for the treatment of dermatofibrosarcoma, in certain cases.
While the diagnosis of dermatofibroma is usually made through the examination of the patient and treated with the use of surgical excision or observation Dermatofibrosarcoma needs a more thorough diagnosis.
Which includes biopsy and imaging and typically requires a combination of surgical excision as well as radiation therapy and sometimes treatment with targeted or chemotherapy. An early and accurate diagnosis is essential for the treatment of dermatofibrosarcoma, to maximize its effectiveness and improve the prognosis.
Summary:Dermatofibroma vs Dermatofibrosarcoma
Dermatofibrosarcoma and dermatofibroma are two distinct skin disorders with distinct clinical features behavior, symptoms, and methods of treatment. Dermatofibroma is typically benign, usually requiring only surgery or even a minor one.
Dermatofibrosarcoma is an untreated tumor that requires urgent and aggressive medical care to ensure the highest possible result. An accurate diagnosis and differentiation between the two types of cancer is crucial to ensure proper care and support for patients.