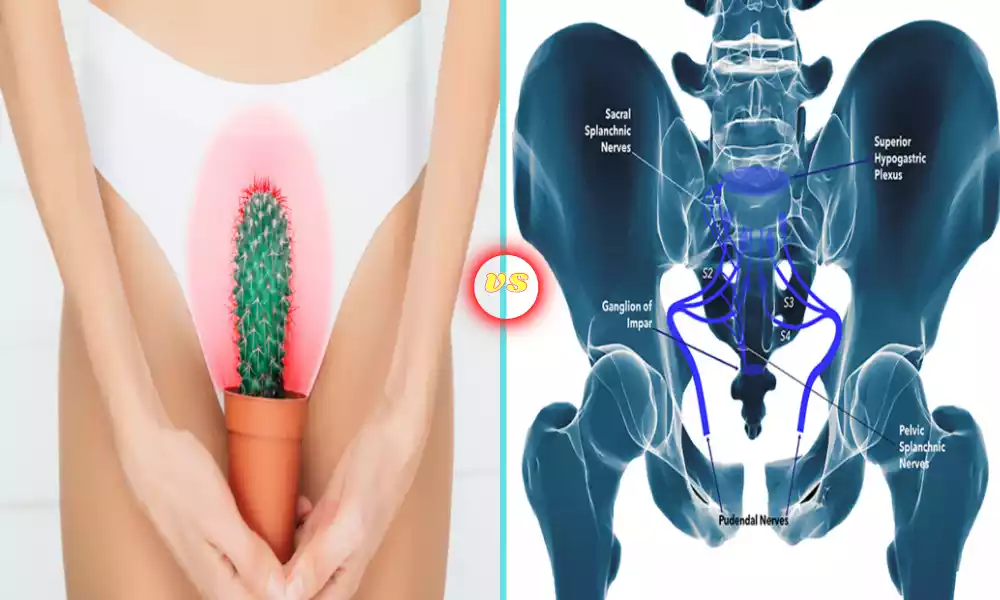
Vulvodynia and Pudendal Neuralgia are two chronic pelvic pain conditions, but they differ considerably in terms of symptoms, causes, and treatment methods.
Vulvodynia involves persistent discomfort in the vulva without identifiable causes while Pudendal Neuralgia involves pain along the path of the pudendal nerve due to nerve entrapment or injury.
Understanding these distinctions is key to accurate diagnosis and effective care that caters specifically to each individual’s specific needs.
Definition of Vulvodynia
Vulvodynia is a chronic pain condition affecting the external female genital organs known as the vulva. It’s characterized by persistent, unexplained discomfort in this region which may either be generalized across its entirety or localized to a particular area.
Whether constant or intermittent with an intensity that ranges between burning, stinging, or raw sensations.
Vulvodynia stands out as an uncommon medical condition because there is no obvious underlying disease or structural abnormality causing its symptoms, making diagnosis and treatment of it more challenging.
With no visible signs or identifiable triggers to ease its discomfort, its severity is sometimes extreme for those living with it – often medication, physical therapy, and lifestyle modifications may help manage symptoms effectively.
Definition of Pudendal Neuralgia
Pudendal Neuralgia is a chronic and painful condition affecting the pudendal nerve, which runs from the pelvis through to the genital and anal regions. This disorder manifests itself with discomfort along its path, producing burning, stabbing, or aching sensations along its route.
Pudendal Neuralgia symptoms often worsen with sitting, and relief can often be found by standing or lying down. Other associated symptoms may include numbness, increased sensitivity, or sexual dysfunction.
Pudendal Neuralgia can be caused by factors including nerve entrapment, compression, or injury sustained from surgery, childbirth, or repetitive strain, among other sources.
Due to its complexity, treating Pudendal Neuralgia often requires multiple approaches including medication, nerve blocks, physical therapy, or surgery in severe cases – all designed to enhance the quality of life for those living with the condition. Proper diagnosis and individualized treatments can significantly increase life quality for those affected by it.
Importance of distinguishing between Vulvodynia and Pudendal Neuralgia
Distinguishing between Vulvodynia and Pudendal Neuralgia is essential for various reasons:
Both conditions involve chronic pelvic pain, but they each affect different anatomical areas and have distinct causes. Vulvodynia affects primarily the vulvar region while Pudendal Neuralgia targets the pudendal nerve knowing which area you experience pain will assist in diagnosing which condition applies.
Diagnostic Challenges: Both conditions may exhibit similar symptoms, including pain and discomfort in the pelvic region. A comprehensive examination must take place to accurately diagnose one or both conditions.
Treatment Approaches: Vulvodynia and Pudendal Neuralgia treatment approaches can vary considerably, for Vulvodynia this might include medication, physical therapy, lifestyle modifications, or surgery while Pudendal Neuralgia might necessitate specialty procedures like nerve blocks or surgery – incorrect treatment can result in unnecessary suffering and expenses.
Psychological Impact: Sufferers of chronic pain conditions often find them emotionally taxing. A proper diagnosis allows the individual to better comprehend their condition and fosters a more positive mental state as they engage in targeted treatments for it.
Misdiagnosis Prevention: Misdiagnosing one condition as another can result in ineffective or inappropriate treatments, potentially worsening the condition and delaying appropriate therapy, prolonging discomfort and other symptoms for longer than necessary.
Personalized Care: Healthcare providers who understand a patient’s specific condition can tailor a tailored care plan that is specific to his/her unique needs, which promotes more effective management and may result in improved quality of life for each patient.
As previously discussed, distinguishing Vulvodynia and Pudendal Neuralgia is key to providing accurate diagnosis, effective treatments, and overall better patient care.
Both conditions share characteristics in common, such as chronic pelvic pain, however, their management requires specialization of knowledge and focus.
Comparison Table of Vulvodynia and Pudendal Neuralgia
Certainly! Here’s a comparison table that highlights the key differences and similarities between Vulvodynia and Pudendal Neuralgia:
| Aspect | Vulvodynia | Pudendal Neuralgia |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Chronic pain in the vulva, without an identifiable cause | Chronic pain affecting the pudendal nerve |
| Pain Location | Vulvar region | Areas supplied by the pudendal nerve (e.g., anus, perineum) |
| Symptoms | Burning, stinging, raw sensation | Burning, stabbing, aching, possibly numbness |
| Causes | Unknown, no clear underlying disease | Nerve entrapment, injury, surgery |
| Diagnostic Challenges | Lack of visible signs, identifiable triggers | Need for specialized tests and criteria |
| Treatment Approaches | Medication, physical therapy, lifestyle changes | Medication, nerve blocks, surgery |
| Relief Factors | Varies widely, and may include positional changes | Often relieved by standing or lying down |
| Impact on Daily Life | Can affect daily activities, relationships, mental health | May restrict sitting, and affect sexual function |
This table provides a concise overview of how these two conditions differ and also their similarities.
Proper understanding and differentiation are vital for healthcare providers to ensure appropriate diagnosis and effective treatment.
Pain in the areas supplied by the pudendal nerve
Pudendal Neuralgia can be identified by symptoms in areas served by the pudendal nerve, specifically around its terminals and roots.
The pudendal nerve supplies sensations to various parts of the pelvic region including:
Perineum (the area between the anus and genitals), lower buttocks, anal region, and vulvar area in females).
Male Scrotal Region Whilst compression, irritation, or damage of the pudendal nerve can cause chronic and severe pain in this region of male genitalia,
Often described as burning, stabbing, or aching, it may also be accompanied by symptoms like numbness or tingling activities which put pressure on it such as sitting may exacerbate it while standing or lying down often provides respite from such discomfort.
Pudendal Neuralgia can have an immediate and devastating impact on an individual’s daily life, interfering with sitting activities, sexual function, and emotional well-being due to the persistent nature of its pain.
Treatment for Pudendal Neuralgia may include medication, pelvic floor physical therapy sessions, or nerve blocks, in severe cases, surgical intervention may also be needed in order to release nerve entrapments.
Understanding the specific areas and characteristics of pain are vital in correctly diagnosing Pudendal Neuralgia and differentiating it from other pelvic pain conditions like Vulvodynia.
An accurate diagnosis enables healthcare providers to implement the most appropriate strategies for relieving symptoms and improving the quality of life for their patients.
Common misconceptions
Misunderstandings surrounding Vulvodynia and Pudendal Neuralgia can often cause unnecessary confusion, misdiagnosis, and ineffective treatment.
Here is a breakdown of common misconceptions for each condition:
Vulvodynia is Psychological: Some may assume Vulvodynia to be solely psychological in origin, however, emotional factors may exacerbate symptoms, Vulvodynia remains a real physical condition with real pain associated with it.
Vulvodynia Doesn’t Just Affect Sexually Active Women: Vulvodynia affects women of all ages and sexual activity levels – not just sexually active ones.
Visible Signs Ought to Be Present: Since Vulvodynia doesn’t usually exhibit visible symptoms, people may assume the absence of visible symptoms means the pain isn’t real.
Vulvodynia is Difficult to Treat: Treating Vulvodynia can require multiple approaches and can often take an extensive period of time and patience.
Pudendal Neuralgia
Only Affects Women: Although Pudendal Neuralgia most often affects female pelvic pain sufferers, men can also be affected.
Sexual Activity Caused Pain: People often assume Pudendal Neuralgia is caused directly by sexual activity, while sexual activities may aggravate symptoms, they typically aren’t the root of the issue.
Though similar in symptoms, Pudendal Neuralgia should not be confused with sciatica, and misdiagnosing one can lead to mistreatment of either.
Surgery is the Only Answer: Some may perceive surgery to be the primary or sole solution to Pudendal Neuralgia, overshadowing more effective forms of therapy such as medication and physical therapy that may also provide relief.
Understanding and correcting these misperceptions are of utmost importance for healthcare providers, patients, and the general public alike.
Knowledge helps with early diagnosis, effective treatments, reducing stigmatism surrounding these conditions as well as creating a more compassionate and supportive environment for those experiencing chronic pain disorders.
Lack of well-defined cause
Vulvodynia’s absence of an easily identified cause presents several diagnostic and treatment challenges,
here is an exploration of this aspect:
What Does Vulvodynia Indicate?
Unlike many medical conditions where there is an obvious underlying cause or pathology to pinpoint, Vulvodynia lacks an identifiable root cause, there may not be visible injuries, infections, or structural abnormalities yet the patient still experiences persistent pain in the vaginal region.
Diagnostic Complexity: Without an obvious cause for Vulvodynia, diagnosis can often involve ruling out other possible conditions as potential sources. This makes the diagnostic process both lengthy and time-consuming.
Treatment Challenges: Failing to understand its underlying cause makes treating Vulvodynia a trial-and-error process, many therapies focus on managing symptoms rather than curing an underlying condition.
Psychological Consequences: Patients suffering from lack of a clear cause often feel frustrated and helpless in the face of this mystery illness, often leading to feelings of isolation or despair.
Misunderstanding and Stigma: Without tangible causes to explain a condition like ADHD, healthcare providers, and others can misinterpret symptoms as “all in the mind.”
Anatomical areas affected
Vulvodynia and Pudendal Neuralgia both affect different regions of the pelvic area, as distinct conditions.
Here’s a breakdown of what regions these conditions affect:
Labia Majora and Labia Minora: the outer and inner “lips” surrounding the vaginal opening, respectively. Clitoris can sometimes become sensitive areas for pain localization. And finally, Vestibule may also become problematic areas.
Perineum: Vulvodynia can also affect the area between the vagina and anus, with pain that radiates across this space or localizing to particular parts.
Pudendal Neuralgia: What to Know and Expect (PNN) Pudendal Nerve dysfunction may result in symptoms affecting areas that the nerve supplies, including:
Perineum: This region lies between the anus and genitals. Anal Regions include the anal canal and surrounding tissues.
Vulvar Region in Females includes the clitoris, labia, and vaginal opening, Scrotal Region can impact the male scrotum as well.
The pudendal nerve, which supplies sensation to this region, may become compressed, inflamed, or damaged and lead to chronic discomfort in these regions. Any compression, irritation, or damage could trigger chronic discomfort in these locations.
Encouragement for those experiencing symptoms to seek professional medical help
Absolutely! If you or anyone in your circle is experiencing symptoms indicative of Vulvodynia or Pudendal Neuralgia, it’s crucial to take them seriously and seek professional medical assistance immediately.
Here is some hope:
Chronic pelvic pain from Vulvodynia or Pudendal Neuralgia doesn’t have to be something you suffer through alone and quietly your suffering deserves proper consideration and care from medical professionals trained in pelvic health.
They are here for support if this situation becomes confusing or distressful for you.
Do Not Ignore Your Symptoms: Symptoms can be used by your body as a warning system – ignoring them could result in greater problems and greater suffering.
Speak to Professionals: Consulting a healthcare provider specializing in pelvic pain can conduct a comprehensive assessment, offer a diagnosis and suggest treatment solutions tailored to you and your concerns.
They’ll work closely with you to create a customized care plan and listen to any worries that come up along the way.
Not All in Your Head”: Lacking visible symptoms does not diminish the truth of chronic pelvic pain conditions, which require careful management with multiple treatment approaches to be effective.
Explore Different Treatment Options: There is no single, universal cure, treatment could involve various therapies, medications, physical therapy sessions, or lifestyle adjustments that work for each individual patient.
Establish an open line of communication with your healthcare provider so they can find out which solution will be most successful in treating you.
Establish a Support System: Connecting with others who understand your condition through support groups or personal relationships can make a huge difference on your journey. Don’t hesitate to reach out to friends, family, or support networks when needed.
Remember You’re Not Alone: Many have successfully overcome chronic pelvic pain with the proper support and care, offering hope for improved quality of life through appropriate interventions.
Your health and well-being are worth making an effort for. Trust your instincts, prioritize your health, and take the necessary steps to obtain support and treatment.
Understanding and managing chronic pelvic pain can be difficult, but with professional medical assistance, empathy, and determination improvement is possible.
If you are experiencing these symptoms please seek medical assistance as soon as possible and be assured of receiving the care and support that you require.
Reference Books
Certainly! If you’re looking for more in-depth knowledge on Vulvodynia and Pudendal Neuralgia, the following reference books and resources may be helpful:
Vulvodynia
- “The V Book: A Doctor’s Guide to Complete Vulvovaginal Health” by Elizabeth G. Stewart and Paula Spencer
- A comprehensive guide to vulvar health, including Vulvodynia.
- “Healing Painful Sex: A Woman’s Guide to Confronting, Diagnosing, and Treating Sexual Pain” by Deborah Coady and Nancy Fish
- Focuses on sexual pain disorders, including Vulvodynia.
- “The Vulvodynia Survival Guide: How to Overcome Painful Vaginal Symptoms and Enjoy an Active Lifestyle” by Howard I. Glazer and Gae Rodke
- A practical guide for those living with Vulvodynia.
Pudendal Neuralgia
- “Pelvic Pain Explained: What You Need to Know” by Stephanie A. Prendergast and Elizabeth H. Rummer
- Covers various pelvic pain issues, including Pudendal Neuralgia.
- “Pudendal Nerve Entrapment: A Clinician’s Guide” by Stanley J. Antolak Jr.
- A clinical guide focused on Pudendal Neuralgia, its diagnosis, and treatment.
- “Secret Suffering: How Women’s Sexual and Pelvic Pain Affects Their Relationships” by Susan Bilheimer and Robert J. Echenberg
- Addresses the emotional aspects and relationship challenges of chronic pelvic pain, including Pudendal Neuralgia.
Conclusion
Vulvodynia and Pudendal Neuralgia are complex conditions of chronic pelvic pain that pose unique obstacles to diagnosis, treatment, and day-to-day living. They present unique difficulties when diagnosing, treating, or living with them.
Though they share similar effects in terms of location, each disease’s causes, symptoms, and management strategies differ substantially.
Misconceptions and an unknown cause may make managing these conditions challenging, but with professional medical guidance, accurate information, and supportive care available individuals suffering from these disorders may find relief and an improvement in quality of life.