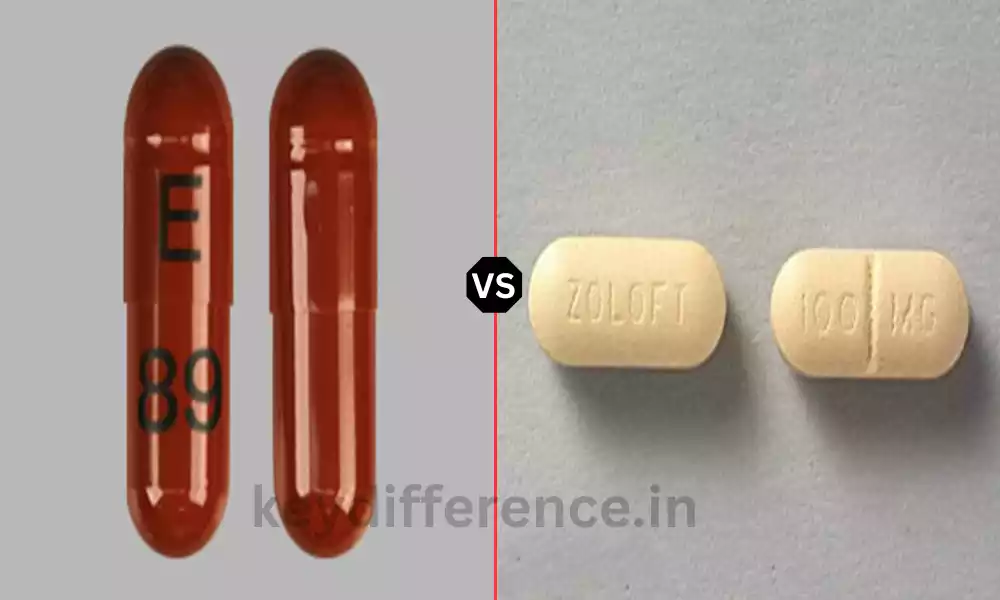
Venlafaxine as well as Sertraline are two frequently prescribed antidepressant drugs each having its own distinct features and advantages. Knowing the distinctions between these medications is vital for healthcare professionals and patients to make informed choices regarding treatment.
The distinct features of Venlafaxine and Sertraline, in terms of effectiveness as well as interactions, side effects, costs, withdrawal preferences, and so on give a thorough review of these drugs to assist in the process of making a decision.
What is Venlafaxine?
Venlafaxine is a medication that belongs to the class of drugs known as serotonin-norepinephrine reuptake inhibitors (SNRIs). It is used primarily as an antidepressant. It can also be prescribed to treat anxiety conditions.
Venlafaxine is a drug that increases the amount of certain neurotransmitters, including serotonin and norepinephrine in the brain. The thought is that this will improve mood and relieve symptoms of anxiety and depression. Venlafaxine comes in a variety of types, including extended-release and immediate-release capsules, and is usually taken in a pill with the guidance of a medical physician.

What is Sertraline?
Sertraline is a drug that is classified as a selective serotonin-reuptake inhibitor (SSRI). It is usually prescribed as an antidepressant. It can also be employed to treat different anxiety and mood conditions.
It works primarily by increasing serotonin levels an important neurotransmitter that is found in the brain. This helps manage mood and ease symptoms that are associated with disorders such as depression as well as obsessive compulsive disorder (OCD) as well as anxiety disorder as well as post-traumatic stress disorder (PTSD) and the disorder of social anxiety.
Sertraline is generally given in oral form generally in liquid or tablet forms and must be administered under the supervision of a medical professional. It is among the most commonly prescribed antidepressant drugs and is recognized as safe in many countries to treat different mental health issues.

Importance of understanding the differences between Venlafaxine and Sertraline
Knowing the distinctions among Venlafaxine and sertraline can be vital for a number of reasons:
- Individualized treatment: Patients respond differently to medication, and what is effective for one person may have a different effect or be appropriate for the other. Knowing the differences between Venlafaxine and Sertraline can allow healthcare professionals to customize treatment according to an individual’s particular requirements and needs.
- Effectiveness: Venlafaxine and Sertraline might have different levels of efficacy for different conditions or symptoms. Understanding these differences can help healthcare professionals make an informed decision about the right medication that is best for the specific patient’s health condition.
- Safety and Side Effects: Both drugs have distinct adverse effect profiles. Knowing these differences aids healthcare professionals in selecting the drug that is most likely to be tolerated by the patient, and reduces the risk of non-compliance and the need to stop treatment.
- Drug interactions: The two drugs, Sertraline and Venlafaxine may interact differently with other drugs and other substances. Understanding these interactions is vital to prevent potentially negative or harmful effects when using these drugs in conjunction with other drugs or treatments.
- Withdrawal and discontinuation: Patients who have to quit taking these drugs should gradually stop taking them to reduce withdrawal symptoms. Knowing the withdrawal profile that occurs with Venlafaxine as well as Sertraline is crucial to planning safe withdrawal strategies.
- Accessibility and Cost: Medication costs can differ and insurance coverage could be different between Venlafaxine as well as Sertraline. Knowing the price and accessibility of these medicines can assist patients in making informed decisions based on their financial circumstances.
- Preferences of the Patient: Patients may have certain preferences or concerns about medications, including the ease of administration, or concerns regarding certain adverse negative effects. Healthcare professionals can better meet the preferences of patients by having a clear knowledge of the differences between Venlafaxine as well as Sertraline.
- Optimizing Outcomes: The ultimate goal of any medical treatment, which includes treatment for depression, is to maximize the outcomes of patients and improve their quality of life. Understanding the differences between these two medicines could help in making better treatment decisions, increase patient compliance, and ultimately more effective outcomes in managing mental health problems.
Understanding the difference between Venlafaxine and sertraline can be crucial for health professionals as well as patients since it allows the choice of the appropriate medication for a patient’s particular requirements, which ultimately leads to safer and more effective treatments.
Comparison Table of Venlafaxine and Sertraline
Here’s a simplified comparison table of Venlafaxine and Sertraline:
| Aspect | Venlafaxine | Sertraline |
|---|---|---|
| Class | SNRI (Serotonin-Norepinephrine Reuptake Inhibitor) | SSRI (Selective Serotonin Reuptake Inhibitor) |
| Primary Use | Depression, anxiety disorders | Depression, anxiety disorders |
| Mechanism of Action | Inhibits reuptake of serotonin and norepinephrine | Inhibits reuptake of serotonin |
| Efficacy | Efficacy varies among individuals; may be more effective in certain cases | Efficacy varies among individuals; often considered the first-line treatment for depression |
| Common Side Effects | Nausea, dry mouth, constipation, dizziness, sleep disturbances | Nausea, diarrhea, sexual dysfunction, insomnia, headaches |
| Discontinuation Syndrome Risk | Higher risk, especially with immediate-release forms | Possible, but generally milder compared to Venlafaxine |
| Drug Interactions | Potential for significant interactions, especially with other serotonergic drugs | Fewer drug interactions compared to Venlafaxine |
| Dosage Forms | Extended-release capsules, immediate-release tablets | Tablets, liquid solution |
| Availability as a Generic | Available (generic) | Available (generic) |
| Cost | May be more expensive in some cases | Often considered more cost-effective |
| Patient Preferences | The choice may depend on individual preferences and side-effect profiles | The choice may depend on individual preferences and tolerability |
Please note that individual responses to these medications can vary, and the choice between Venlafaxine and Sertraline should be made in consultation with a healthcare provider, taking into account the specific needs and characteristics of the patient.
Populations where each medication is more effective
The efficacy that comes from Venlafaxine and Sertraline is different across different populations, and it depends on the particular mental health issue being treated.
Here are some guidelines on the groups in which each medication could be more effective:
Venlafaxine:
- Treatment-resistant depression: Venlafaxine can be considered as a treatment-resistant depression when other antidepressants, such as SSRIs such as Sertraline are not providing enough relief.
- Anxiety and Norepinephrine-related Involvement: Venlafaxine’s dual mechanism of action, which includes serotonin and norepinephrine can increase its effectiveness in people suffering from anxiety disorders in which norepinephrine dysregulation plays an important role.
- Chronic Depression and Pain: Venlafaxine is employed to treat disorders where chronic pain and depression coexist including neuropathic pain and fibromyalgia.
- Special Symptom Profiles: There are instances where Venlafaxine might be the best choice in cases where specific symptoms such as fatigue or lack of concentration are evident since it could produce a stimulant effect because of its norepinephrine-related activity.
Sertraline:
- Generalized Anxiety Disorder (GAD): Sertraline is commonly regarded as the first-line treatment for GAD because of its effectiveness in reducing anxiety symptoms as well as having fewer adverse effects than Venlafaxine.
- Obsessive-Compulsive Disease (OCD): Sertraline is an FDA-approved medication that treats OCD and is the most preferred option for this particular disorder.
- Panic disorder: Sertraline is known to be effective in treating panic disorder, which makes it an ideal choice for people suffering from this condition.
- Social Anxiety Disorder: Sertraline can also be an efficient treatment option for social anxiety disorders and is commonly used in these situations.
- Mild depression: The medication sertraline has been commonly prescribed to people suffering from milder depression due to the favorable side effects of its profile.
It’s crucial to understand that the decision between Venlafaxine and Sertraline must be taken on a case-by-case basis, taking into account the patient’s specific diagnosis, severity of symptoms as well as medical history and individual preferences.
Healthcare professionals carefully evaluate the individual’s specific circumstances to determine which one is most likely to be efficient, while minimizing any risk of side effects and pitfalls.
Severity and prevalence of side effects in each drug
The adverse effects of Venlafaxine and Sertraline are different in their severity and frequency. It’s important to keep in mind that each person’s response to these drugs may differ and therefore not all patients will experience the same adverse effects.
Here’s a general overview of the severity and frequency of common side effects associated with every medication:
Venlafaxine:
- Common side effects: Common adverse reactions of Venlafaxine include dry mouth, nausea dizziness, constipation, and sweating as well as sleep disorders (such as vivid or insomnia).
- Severity: A few of the adverse effects, such as dizziness and nausea, can be very serious, particularly when beginning to take the drug or increasing the dosage. The severity can decrease in time as your body adjusts.
- Incidence Nausea can be a frequent side effect of beginning Venlafaxine however, it usually gets better over time. Other side effects are not as often reported, yet they still cause a lot of patients.
- Discontinuation syndrome: Venlafaxine’s use is associated with a greater risk of causing discontinuation-related syndrome which may manifest as nausea, dizziness, irritation as well as “brain zaps.” The intensity of these symptoms could differ, however, they tend to be more prominent when using immediate-release formulations.
Sertraline:
- The most common adverse side effects: Common Sertraline side effects include nausea, diarrhea infertility (e.g. diminished sexual libido, or difficulties in arousal orgasm) as well as insomnia and headaches.
- Severity: These side effects can vary from moderate to mild, and often they improve over time as your body adapts to the drug. Sexual adverse effects can be especially troubling for certain people.
- The prevalence of HTML0 is: Nausea can be a common side effect that occurs when you start Sertraline However, it generally diminishes as you continue to use it. Sexual dysfunction, when it is experienced may persist throughout treatment.
- Discontinuation symptoms: While Sertraline can cause discontinuation-related symptoms when it is abruptly stopped, they tend to be less severe than Venlafaxine. The symptoms could include flu-like symptoms, dizziness as well as mood disorders.
It is true that the two medications Venlafaxine and Sertraline may produce side effects, however, the degree and severity of these adverse effects may vary.
The decision to choose between the two medicines is usually based on taking into consideration the patient’s medical history along with the severity and nature of the symptoms they experience, as well as their tolerance to possible adverse effects.
Healthcare providers collaborate with patients to identify the drug that provides the most effective balance of efficiency and tolerance.
Likelihood and severity of withdrawal symptoms
The severity and likelihood of withdrawal symptoms following the discontinuation of Venlafaxine and Sertraline may vary, and it is important to remember that each person’s experience may be different.
Here’s a general overview of the probability and severity of withdrawal symptoms for each drug:
Venlafaxine:
- Probability of Symptoms of Withdrawal: Withdrawal symptoms are more likely to happen when taking Venlafaxine, particularly after discontinuing the immediate release form. The symptoms may also be present in the absence of doses or when reducing the dosage.
- The severity of withdrawal symptoms: Withdrawal symptoms from Venlafaxine can be very intense for certain individuals. Common withdrawal symptoms include dizziness nausea as well as irritability “brain zaps” (a sensation of electrical shocks to the head) or flu-like symptoms. The degree of the symptoms varies, but they are usually more severe when you take higher doses or immediate-release formulations.
- Tapping: Tapering off Venlafaxine under the supervision of a physician is generally suggested to lessen the possibility and the severity of withdrawal-related symptoms. Reducing the dosage gradually can aid in adjusting the body more efficiently.
Sertraline:
- Probability of Symptoms of Withdrawal: While Sertraline can be a trigger for withdrawal symptoms when abruptly stopped these withdrawal symptoms are typically milder and less frequent when compared to Venlafaxine.
- Seriousness of Symptoms of Withdrawal: Sertraline withdrawal symptoms can include nausea as well as flu-like symptoms and mood swings. The symptoms of withdrawal are generally less severe than those encountered when taking Venlafaxine. However, the individual’s responses may vary and some people might still feel uncomfortable.
- The process of tapering: It is recommended to ensure an easier and more pleasant transition. This is particularly crucial for those who have been taking the medication for a prolonged time.
Withdrawal symptoms are more frequent and may be more severe if you stop taking Venlafaxine in particular the immediate release version. It is vital to adhere to an appropriate tapering schedule and medical advice to reduce the effects.
Although Sertraline can cause withdrawal symptoms, they tend to be more mild and less frequent and therefore it is a little simpler for some people to quit the medication when it is appropriate. Always consult a medical doctor before discontinuing any antidepressant medication.
Doctor-patient communication regarding medication choice
Communication between the doctor and patient regarding the choice of medication especially when it comes to antidepressants such as Venlafaxine and Sertraline is crucial to make informed choices that are compatible with the patient’s wishes and preferences.
These are some of the most important aspects of this communication:
- Patient Education:
- The doctor should inform the patient of the treatments available, which include Venlafaxine as well as Sertraline. This should include explaining how these drugs work, their possible advantages, as well as potential adverse negative effects.
- Diagnosis and Treatment Goals:
- The physician and patient must discuss the specific diagnosis of the patient and treatment objectives. This involves knowing the nature and severity of the illness and what the patient is hoping to achieve through treatment.
- Risks and Benefits:
- Healthcare professionals should be able to provide information on the possible dangers and benefits of each drug, including the possibility of adverse effects, withdrawal symptoms, and the anticipated timeframe for the therapeutic effects.
- Patient Preferences:
- Patients might have their own preferences about the kind of medication they’re willing to take, for example, dosage frequency or formulation (e.g. capsules, tablets and liquid) and the potential adverse reactions they are most worried about. Healthcare providers must be aware of these preferences.
- Medical History and Coexisting Conditions:
- It’s crucial to discuss the medical history of the patient and any medications or co-existing conditions they’re taking. Certain health conditions or interactions with drugs could affect the selection of antidepressants.
- Monitoring and Follow-up:
- The doctor and patient should create plans for monitoring the progress and subsequent appointments. This will include discussions regarding how often patients is scheduled to see their doctor to evaluate the effectiveness of their treatment as well as any needed adjustments.
- Tapering and Discontinuation:
- Patients should be aware of the importance of reducing the medication when it is not required anymore or if they wish to stop treatment. Healthcare providers should give instructions on how to safely decrease the dose.
- Questions and Concerns:
- Patients are incentivized to inquire and share any concerns they may have regarding the medication or potential consequences. Communication that is transparent and honest is crucial.
- Informed Decision-Making:
- The final decision about treatment should be made jointly with the patient’s full participation. The patient should be at ease and confident in making the right choice that is in line with their values and needs.
- Informed Consent:
- When a decision has been made it is important to obtain informed consent. Patients must understand the implications of their chosen treatment including the potential advantages and potential risks and give their consent to treatment.
- Documentation:
- Healthcare providers must document the discussions with patients in their health records in order to make sure the process of making decisions is documented and clear.
Effective communication between doctors and patients is an essential element of patient-centered healthcare, making sure that treatment decisions aren’t just medically correct, but also in line with the patient’s wishes and values. It fosters trust and cooperation which can lead to better outcomes when managing mental health problems.
Similarities Between Venlafaxine and Sertraline
Venlafaxine as well as Sertraline are antidepressant medicines, and although they are in different classes (Venlafaxine can be described as an SNRI as Sertraline can be described as an SSRI) Both have a lot in common:
- Indices: Two Venlafaxine and Sertraline are prescribed to treat similar disorders which include major depression generalized anxiety disorder social anxiety disorder, as well as panic disorder.
- Mechanism of Action: Though they both have distinct primary mechanisms of action (Venlafaxine blocks the reuptake of norepinephrine and serotonin in a similar manner, while Sertraline is primarily a stimulant of serotonin reuptake) The end consequence is a rise in the levels of serotonin in the brain. This is believed to be the primary factor responsible for relieving symptoms of anxiety and depression.
- Antidepressant Effect: Both medicines can be effective in reducing symptoms of anxiety and depression. They are considered to be among the first-line treatments for these ailments.
- Oral Administration: Venlafaxine as well as Sertraline are available as oral formulations generally in capsules or tablets making them easy to take.
- Prescription Medicines: Both drugs require an order from a healthcare professional, and the dosages are generally determined by the patient’s particular needs and responses to treatment.
- Tapering to Stop: For both Venlafaxine and Sertraline, it is usually recommended to decrease the dosage at the time of discontinuation to reduce withdrawal symptoms or signs of discontinuation.
- Possible Side Effects: Although the exact adverse effects can vary between the two medications they all can cause common side effects that are associated with SSRIs and other SNRIs. These include nausea, digestive issues, and sexual dysfunction.
- The beginning of action: Both medicines can require several weeks of consistent use to achieve their full therapeutic effectiveness. Patients may not notice instant relief from their ailments.
It is important to remember that, despite the fact that Venlafaxine and Sertraline have many similarities, however, they differ regarding their effects on the body’s possible interactions, as well as withdrawal symptoms.
The decision to choose between these two medications is often based on patients’ characteristics, symptoms, and degree of tolerance to medication, and must be determined in consultation with a medical physician.
Conclusion
Venlafaxine as well as Sertraline are antidepressant medicines frequently used for treating anxiety and depression disorders. Although they have some similarities in their uses and mechanisms in action, these two medications have distinct characteristics in regard to withdrawal risks, side effects as well and patient preferences.
The decision between these drugs must be made with careful consideration of the specific needs of the patient that are accompanied by open dialogue between healthcare professionals and patients. The most appropriate treatment is a joint decision that aims to maximize the effectiveness of treatment and ensure that patients are well.