Introduction
Skin grafting and plastic surgery are two distinct surgical processes with their own set of applications and applications. While both procedures aim to enhance appearance or functionality of the body through surgical interventions, their objectives, indications, techniques, outcomes and benefits vary widely – understanding these differences is vital for patients, healthcare providers and individuals seeking specific treatments.
Skin grafting is a surgical Technique utilized to repair or Restore lost or Damaged skin due to burns, chronic Wounds, or other trauma. This Procedure involves Transplanting healthy skin from one area of the body to Another in order to facilitate wound healing and restore integrity to damaged or lost areas of the skin.
Plastic surgery refers to any procedure performed on either cosmetic or reconstructive individuals to enhance aesthetic appearance or restore form and function following congenital anomalies, injuries or medical conditions.
We will delve into the fundamental aspects of skin grafting and plastic surgery in this content outline, from their definitions and indications to surgical techniques, recovery processes, outcomes and goals.
Furthermore, we will highlight key differences between them, such as goals, patient selection criteria and collaboration among specialties. By developing an in-depth knowledge of both procedures, readers will be more equipped to make informed decisions regarding healthcare needs and treatment options.
Definition of Skin Grafting
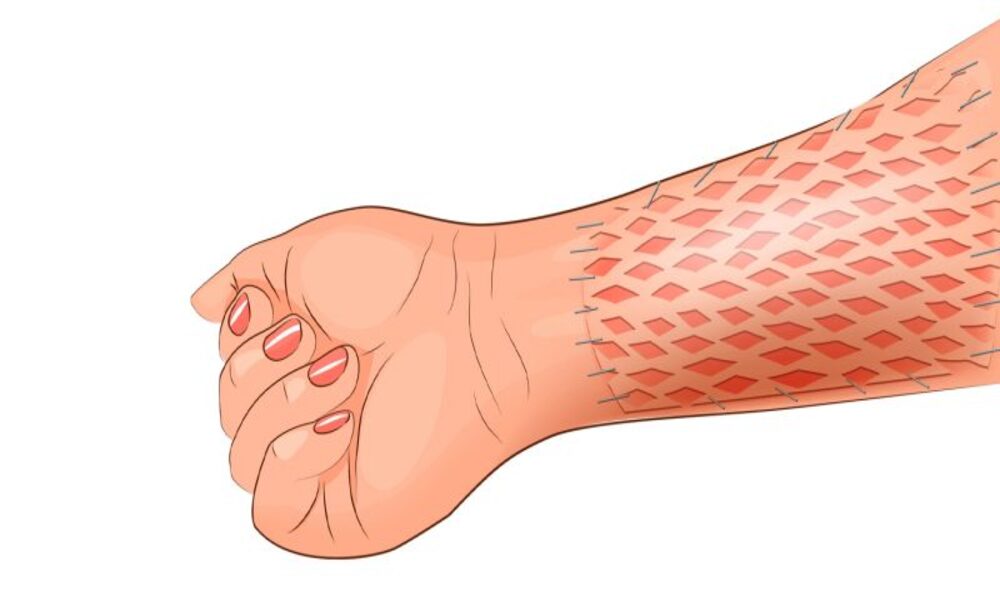
Skin grafting is a surgical procedure in which healthy skin tissue from one area (donor site) of the body (donor site) is transplanted onto another part (recipient site), in need of replacement or repair, to promote wound healing and restore function and aesthetics of recipient site. Its goal is to replace or repair damaged skin while also speeding healing.
At each step, a section of skin is carefully taken from its donor site – either an area within a patient’s own body, or from another individual (allograft). Harvested skin may come either as a thin layer (split-thickness graft), containing epidermis and part of dermis; or as full thickness graft, which includes all dermis. Graft types depend on factors like wound size and location as well as desired outcomes.
Donor skin is then transplanted onto the recipient site and secured into position with surgical adhesive, then allowed to establish blood supply through revascularization. The graft serves as either temporary or permanent cover for wounds; providing protection, speeding healing processes, and supporting regeneration of new tissue growth.
Skin grafting has become an integral component of medicine in various fields, including dermatology.
Burns: For replacing damaged or burned skin. Chronic Wounds: To help heal ulcers, pressure sores or non-healing wounds. Traumatic Injuries: To reconstruct areas with significant tissue loss due to accidents or surgeries.
Skin grafting success and outcomes depend on factors like viability, wound care protocols, patient health and post-op administration. Complications could include graft failure, infection, poor healing, scarring or changes to color and texture of the recipient’s skin.
Definition of Plastic Surgery
Plastic surgery is a surgical specialty dedicated to reconstructing, restoring or altering human bodies through reconstructive, aesthetic or reconstructive measures. The term “plastic” derives from Greek “plastikos,” meaning to mold or shape; plastic surgery encompasses both cosmetic (aesthetic) and reconstructive procedures to address concerns pertaining to appearance, symmetry and functionality.
Cosmetic plastic surgery aims to enhance or improve a person’s physical appearance, aesthetics and self-confidence through elective procedures on normal body structures that otherwise appear pleasing aesthetically.
Common Cosmetic procedures include breast Augmentation, Rhinoplasty (nose reshaping), facelifting, liposuction and Abdominoplasty (tummy tuck). Individuals often seek these cosmetic Procedures either to enhance their own look, address any specific Cosmetic concerns they have or achieve desired Aesthetic results.
Reconstructive plastic surgery aims to repair or restore bodily structures damaged due to congenital anomalies, developmental abnormalities, trauma, infection, tumors or disease. Reconstructive procedures may include breast reconstruction following mastectomy; cleft lip and palate repair; scar revision surgery; hand surgery or skin grafting as examples of reconstructive treatments.
Plastic surgeons undergo extensive training and possess an array of specialized skills necessary for both cosmetic and reconstructive procedures. They perform comprehensive evaluations on patients, discussing goals and expectations before creating tailored treatment plans using various surgical techniques such as incisions, tissue manipulation, grafting or implant placement – as well as any additional necessary interventions such as incisions.
Recovery and outcomes following plastic surgery procedures vary based on factors related to the procedure itself, the patient, and adherence to post-operative care instructions. Potential complications, though generally minor, may include infection, bleeding, scarring, asymmetry, adverse reactions from anesthesia administration and dissatisfaction with the results.
Plastic surgery must always be conducted by highly qualified, experienced plastic surgeons in accredited medical facilities to ensure patient safety and achieve optimal results.

Comparison Table of Skin Grafting and Plastic Surgery
Here’s a comparison table highlighting the key differences between skin grafting and plastic surgery:
| Aspect | Skin Grafting | Plastic Surgery |
|---|---|---|
| Purpose | Replace damaged or lost skin | Enhance aesthetics or restore form/function |
| Indications | Burns, chronic wounds, traumatic injuries | Congenital anomalies, injuries, conditions |
| Surgical Techniques | Transplantation of healthy skin grafts | Incisions, tissue manipulation, grafting |
| Donor Site | Patient’s own body or donor (allograft) | N/A (no donor site) |
| Outcome Focus | Wound healing, functional restoration | Aesthetic improvement, form/function |
| Recovery | Healing of graft, potential complications | Healing of incisions, potential complications |
| Cost | Variable depending on graft type and size | Variable depending on procedure and scope |
| Collaboration | May involve collaboration with other specialties | May involve collaboration with other specialties |
| Examples | Treatment of burns, chronic wounds | Breast augmentation, rhinoplasty, etc. |
This table provides a concise overview of the primary differences between skin grafting and plastic surgery. It highlights the distinct objectives, indications, techniques, and outcomes associated with each procedure.
It’s important to note that while the table provides a general comparison, individual cases may have unique considerations, and it’s always recommended to consult with a healthcare professional for personalized advice.
Importance of understanding the differences between the Skin Grafting and Plastic Surgery
Deliberating between skin grafting and plastic surgery is crucial for various reasons:
Accurate Treatment Selection: Understanding the distinctions between skin grafting and plastic surgery helps individuals and healthcare professionals select the most appropriate intervention to meet a patient’s condition or desired result. Understanding their differences allows patients to receive care that matches up with their needs – be that functional impairment or aesthetic enhancement.
Patient Education and Informed Decision-Making: Knowledge about the differences empowers patients to make educated healthcare decisions. By understanding the nature, goals, potential outcomes of skin grafting and plastic surgery procedures as well as recovery time frames and expected results of each option they can be actively involved in the decision making process and actively make their healthcare choices informedly.
Collaboration Between Healthcare Professionals: Understanding the differences between skin grafting and plastic surgery allows healthcare professionals to work effectively together. Interdisciplinary cases that combine both techniques help healthcare providers coordinate their efforts more efficiently while sharing expertise for optimal patient results.
Knowledge of Skin Grafting and Plastic Surgery Contributes to Superior Patient Care and Safety: Healthcare providers who understand the differences between skin grafting and plastic surgery contribute significantly to improved patient care and safety.
They can accurately evaluate patients, select the most effective treatment approach and anticipate potential complications or limitations associated with each procedure, enabling them to create personalized treatment plans, provide comprehensive pre- and post-operative care and mitigate risks.
Realistic Expectations and Patient Satisfaction: Understanding the differences between skin grafting and plastic surgery helps set realistic expectations for patients, so they understand what each procedure can achieve, its limitations, and potential outcomes. Realistic expectations foster patient satisfaction as they reduce chances of unrealistic or misguided hopes about the results they should expect from their chosen procedure.
Understanding the differences between skin grafting and plastic surgery is critical to informed decision-making, proper treatment selection, collaborative healthcare delivery, patient safety, and realistic expectations. By understanding their respective differences, patients and healthcare providers can work together toward optimal outcomes while improving overall care quality.
Healing process and potential complications
Healing Process: Skin Grafting:
After skin grafting, the healing process typically includes multiple steps. At first, revascularization relies on existing blood flow at the recipient site in order to form new vessels (reepithelialization).
Over time, however, attachment occurs and new blood vessels form at various points around it; finally reepithelialization takes place and new skin cells cover its surface as the wound closes over. Healing times vary depending on its size and location as well as patient health factors; duration can also depend on size as well as overall health factors of each patient as well.
Plastic Surgery: Recovery time after plastic surgery will depend on the specific procedure performed, with incisions taking time to heal and close before eventually scarring over time and improving in appearance. Patients are advised to follow post-operative care instructions, including wound care advice, to facilitate proper healing. Swelling and bruising are usually minimal after plastic surgery procedures; usually subsiding within weeks to months.
Possible Complications of Skin Grafting:
These procedures may present potential risks that include:
Graft Failure: Unfortunately, sometimes grafts fail due to insufficient blood supply, infection or improper placement. These factors could include inadequate blood supply, infection or improper placement.
Infection: Graft sites can become susceptible to infections that compromise healing and necessitate medical intervention, potentially hindering their effectiveness and leading to additional bleeding or bleeding at either donor or recipient sites that requires additional measures to control.
Plastic Surgery: Potential complications related to plastic surgery vary depending on the procedure but could include:
Infection: Surgical sites can become infected and require antibiotics or further medical intervention to resolve. Poor Wound Healing: Factors like smoking, certain medical conditions or poor post-operative care may contribute to delayed or impaired wound healing.
Scarring: Plastic surgery incisions may leave visible scars behind, though every effort will be made to minimize their visibility.
Adverse Reactions of Anesthesia: Though complications from anesthesia may be uncommon, they do occasionally arise and could include allergic reactions, respiratory problems or adverse drug interactions.
Important to keep in mind is that complications are possible risks of medical procedures; however, they don’t happen every time. Adherence to pre- and post-operative care instructions as well as close monitoring by healthcare professionals is vital in order to minimize complications and facilitate successful healing.
It is recommended that any concerns or unusual symptoms be shared promptly with their healthcare provider for evaluation and management.
Long-term outcomes and cosmetic considerations
Long-Term Outcomes of Skin Grafting:
The long-term outcomes of skin grafting depend on factors like its size and location, patient health, post-operative care compliance, as well as any functional and aesthetic improvements gained through successful transplants that restore skin integrity and promote wound healing.
Nevertheless, it should be remembered that transplanted tissues may not exactly resemble surrounding skin in terms of color, texture, or hair growth characteristics.
Cosmetic Considerations: While skin grafting’s primary goal is to restore function and promote healing, its cosmetic aspects should not be neglected. Healthcare providers take into account factors like placement of the graft relative to natural skin lines or contours and alignment with natural lines or contours for maximum cosmetic outcomes.
Furthermore, efforts may be undertaken to minimize visible scarring while matching color and texture perfectly between graft and surrounding skin.
Long-Term Outcomes of Plastic Surgery:
The long-term outcomes of plastic surgery depend on which procedure was undertaken. Cosmetic plastic surgery aims to make aesthetic improvements which have lasting positive impacts on one’s appearance and self-confidence, while reconstructive plastic surgery seeks to restore form, function and quality of life; though aging and other factors could diminish these results over time.
Cosmetic Considerations: Cosmetic concerns are at the core of plastic surgery procedures such as breast augmentation, rhinoplasty and facelift procedures. Each procedure’s goal is to enhance or modify specific features to achieve an ideal aesthetic outcome; plastic surgeons carefully consider factors like symmetry, proportion, balance and individual preferences to achieve results that look natural yet align with patient goals.
Discussion of realistic expectations regarding potential scarring or changes over time during pre-operative consultation meetings are vitally important steps toward reaching successful results.
At skin grafting and plastic surgery practices, long-term outcomes and aesthetic considerations depend on several individual variables including healing response, lifestyle choices and post-op care adherence.
Therefore, it’s vital for patients to have open conversations with their healthcare providers regarding expectations, desired outcomes and any limitations or risks associated with the procedures.
Pre-operative evaluation and planning
Pre-Operative Evaluation and Planning:
Pre-operative evaluation and planning are integral parts of both skin grafting and plastic surgery procedures, ensuring patient safety, optimizing results and setting realistic expectations. This process Typically includes:
Medical History Review: Healthcare providers will Perform a review of a patient’s Medical history, such as any Preexisting medical Conditions, surgeries, allergies, Medications and current Health status.
This assessment allows healthcare providers to identify any potential risk factors as well as assess suitability for procedures as well as plan any necessary modifications or precautions before proceeding with surgery or procedures.
Physical Examination: To properly assess a patient’s overall health and address specific areas of concern, healthcare providers conduct comprehensive physical exams which encompass skin checks, anatomical features, measurements and any relevant functional considerations. This helps them better understand individual patient needs as well as develop effective treatment solutions.
Patient Goals and Expectations: Healthcare providers engage in an in-depth dialogue with their patients to understand their goals, expectations, motivations for seeking procedures, potential outcomes as well as any concerns or misconceptions they might have about this process.
Through this dialogue they help set realistic expectations as well as address any misconceptions or misunderstandings they might encounter during treatment.
Imaging and Diagnostic Tests: Depending on the nature of the procedure, imaging studies such as X-rays, MRIs or CT scans may be needed to assess underlying structures and help with surgery planning. Furthermore, diagnostic tests such as blood tests or biopsies may be administered to evaluate overall health or assess areas of concern.
Informed Consent: Informal Consent is an essential step in the pre-operative process. Healthcare providers will present all information related to the procedure, its potential risks and complications, expected outcomes, alternative treatment options available and recovery process; then patients have an opportunity to ask any pertinent questions and give informed consent for it.
Pre-Operative Instructions: In order to ensure optimal outcomes during surgery, healthcare providers provide specific pre-operative instructions in the form of fasting guidelines, medication management guidelines, smoking cessation advice and skincare preparation instructions. Patients should adhere to all these instructions to reduce risks and maximize surgical outcomes.
Anesthesia Evaluation: When required for a procedure, an anesthesiologist or other anesthesia provider will perform an initial evaluation to ascertain your overall health, determine which anesthesia technique would best meet your needs and discuss risks and recovery.
Pre-operative evaluation and planning sessions provide healthcare providers and patients an opportunity to develop trust, set clear expectations, address any concerns, and ensure the patient is adequately prepared for an upcoming procedure.
Open communication, comprehensive assessments, and teamwork between healthcare provider and patient are key ingredients of successful pre-operative evaluation and planning sessions.
Surgical techniques specific to each procedure
Skin Grafting:
Harvesting of Grafts: Split-Thickness Grafts: When harvesting split-thickness grafts, using a dermatome (a surgical instrument), carefully remove a thin layer of skin from either the donor site (usually thigh or buttock) using surgical instruments such as dermatomes until enough has been taken to make up an acceptable graft, according to your intended use and wound depth.
Full-Thickness Grafts: Extraction of an entire thickness of skin from the donor site – epidermis and dermis alike. This form of grafting is most frequently used to repair small wounds or for cosmetic enhancement purposes.
Preparing the Recipient Site:
Preparing the recipient site involves cleaning and debriding to remove necrotic tissue or debris, followed by dressings, topical agents or specialized techniques that promote healthy wound beds for the graft to adhere to.
Securing and Monitoring the Graft:
Grafts must be carefully placed onto a prepared wound bed and secured in place using sutures, staples or adhesive dressings. In some instances, protective coverings such as dressings or bolsters may also be applied in order to safeguard them, provide compression support, and promote adhesion between graft and body tissue. Grafts must be carefully monitored during their first post-operative phase to ensure viability, adequate blood supply, and successful healing.
Plastic Surgery:
Incision Techniques
Plastic surgery procedures involve incisions at specific spots to gain access to the tissues beneath and make necessary modifications. The choice of incision technique depends on both the surgical procedure and goals for its success. Common options may include linear incisions, curved incisions or hidden ones in natural skin creases or hairlines to minimize visible scarring.
Tissue Manipulation and Reshaping:
Plastic surgeons employ various techniques to reshape tissues. This may involve the excision (removal) of excess skin, fat, or other tissues; or use of sutures, grafts or implants to enhance or modify desired areas. Reconstructive tissue flaps such as local flaps or microvascular free flaps may be utilized for reconstructive procedures to help restore form and function in areas suffering from significant tissue loss.
Grafting and Implantation:
Plastic surgery procedures often utilize grafts or implants to augment or reconstruct specific areas of the body, including autologous fat grafting or synthetic implants (e.g. silicone implants). Skin grafting and plastic surgery procedures vary based on each procedure, patient needs and surgeon expertise. Surgeons carefully plan and execute these techniques in order to produce desired functional or aesthetic outcomes while protecting patient safety and minimizing complications.
Expected Outcomes and long-term results
Skin Grafting: Expected Outcomes: The primary objective of skin Grafting is to promote wound Healing and restore skin integrity, with its Expected outcomes including Improved wound closure, Decreased risk of infection, and Potential for Improved function in affected areas.
A successful skin graft should provide coverage, protection and support for an existing wound while simultaneously encouraging regeneration. Long-term success and outcome depend on various factors including viability of graft material used, healing capacity of affected tissues as well as individual patient factors.
Long-Term Results: Successful skin grafting can yield long-term Improvements to wound healing, Functional Restoration and aesthetic Appearance. As time progresses, the graft integrates with its Surroundings until its Appearance more closely matches that of Surrounding skin – though color, texture, hair growth patterns or scarring may still exist in grafted areas despite efforts made to minimize their visibility.
Plastic Surgery:
Expected Outcomes:
Expected outcomes of plastic surgery can vary widely depending on the procedure and patient goals. With cosmetic plastic surgery, expected outcomes generally consist of improving or altering aesthetic appearance through measures such as improving symmetry, contour, or size; in reconstructive plastic surgery these goals include restoring form, function and quality of life via improvements such as increased functionality or correcting structural abnormalities.
Long-Term Results: Plastic surgery can produce long-lasting effects, but it’s important to keep in mind that factors like the aging process, lifestyle factors and other elements could potentially alter their long-term success.
While plastic surgery may make significant improvements over time, its effects are bound to fade as time progresses naturally. As such, realistic expectations and understanding that maintenance or additional procedures may be necessary in the future to maintain or enhance results may be key factors to maximizing long-term outcomes. Adherence to post-operative instructions is also vitally important in optimizing long-term outcomes.
Note that results and long-term outcomes depend on factors unique to each patient, the procedure performed, and post-operative care adherence. Patients should have open and honest discussions with healthcare providers about their goals, expectations, and potential outcomes to get an understanding of what realistically can be accomplished.
Regular follow up visits and communication with their provider are vital in overseeing progress while addressing any concerns that may arise during recovery and healing processes.
Future developments and advancements in both fields
Future advancements and developments in skin grafting and plastic surgery could involve innovative techniques, technologies, and approaches that aim to further improve patient outcomes while expanding treatment options. Here are some areas where advancement may take place:
Skin Grafting:
modificari Tissue Engineering: Advances in tissue engineering and regenerative medicine may lead to the creation of artificial or lab-grown skin substitutes which closely resemble natural skin properties, providing more readily available and standardized grafting materials.
Researchers are studying biomaterials and scaffolds that may assist with the growth and integration of skin grafts, improving viability and functional outcomes.
Cellular Therapies: Stem cells or other cellular therapies to accelerate skin graft healing is an area of active research. Such treatments have the potential to promote survivability, wound healing and regeneration of skin tissues – all elements that could improve outcomes of skin transplantation procedures.
Scar Management: Recent advances in scar management techniques such as laser therapy, topical medications, and advanced wound dressings may help minimize scarring after skin grafting procedures and improve aesthetic outcomes.
Surgical Techniques: Refining surgical techniques can improve outcomes, reduce complications and speed healing. Improved harvesting methods, microsurgical approaches and specialized instrumentation may all contribute to enhanced results while speeding healing time.
Plastic Surgery: Its
The trend towards minimally invasive procedures is expected to grow over time, thanks to advances in technologies and techniques like endoscopic, robotic-assisted surgery, and non-surgical treatments that offer less invasive alternatives with reduced scarring, faster recovery times and improved patient comfort.
3D Printing Technology: 3D printing has the power to revolutionize plastic surgery by creating patient-specific implants, customized surgical tools and anatomical models for pre-operative planning. This revolutionary technology may increase surgical precision while improving outcomes.
Virtual and Augmented Reality (VR/AR) technologies: VR and AR technologies offer surgeons a powerful pre-operative planning tool, allowing them to visualize and simulate procedures within an immersive virtual environment for increased precision, patient education and team communication among surgical teams.
Developments in Aesthetic Procedures: Ongoing research and development efforts in facial rejuvenation, body contouring, non-invasive aesthetic treatments, and non-surgical aesthetic procedures could result in new techniques, devices, or products which provide enhanced and more natural-looking results.
Patient Safety and Outcome Monitoring: By using digital health technologies and data analytics together, digital health technologies can facilitate improved patient monitoring, outcome evaluation, post-operative care and recovery services utilizing wearable devices, telemedicine platforms and artificial intelligence algorithms to maximize safety and speed recovery times.
Important to keep in mind is that although these potential advancements hold promise, they remain subject to ongoing research, testing and regulatory approval. The future landscape of skin grafting and plastic surgery will likely be determined by scientific breakthroughs, technological innovations and ever-evolving patient needs.
Conclusion
Understanding the differences between skin grafting and plastic surgery is vitally important for patients, healthcare providers, and individuals seeking treatments of any kind. Skin grafting involves the transplantation of healthy skin to replace damaged or lost tissue; its primary goal being wound healing and functional restoration.