Tendonitis and bursitis are two common musculoskeletal ailments that can lead to discomfort and pain, particularly when people engage in sports or perform repetitive movements in their daily lives.
While they are similar in terms of symptoms and treatment strategies, however, they are two distinct conditions with distinct causes and anatomical. This content outline delved into the main differences between tendonitis and bursitis, offering a thorough knowledge of these conditions to aid in better diagnosis, identification, and treatment.
Definition of Bursitis
Bursitis is a condition that’s medical in nature. It’s which is defined by the irritation or inflammation of small sacs that are filled with fluid called bursae. The bursae can be found all over the body, primarily in the areas where movement and friction occur between muscles, bones, tendons, and skin.
The most common cause of bursitis is excessive use, repetitive motion trauma, or infection which can cause swelling, pain, or restricted range of motion in the joint or region affected.
The bursae’s primary function is to lessen friction and cushion between these structures. However, when they are inflamed they may cause pain and pain. Treatment typically involves rest, anti-inflammatory drugs physical therapy, as well as occasionally it is possibly to aspirate the bursa that is inflamed.
Definition of Tendonitis
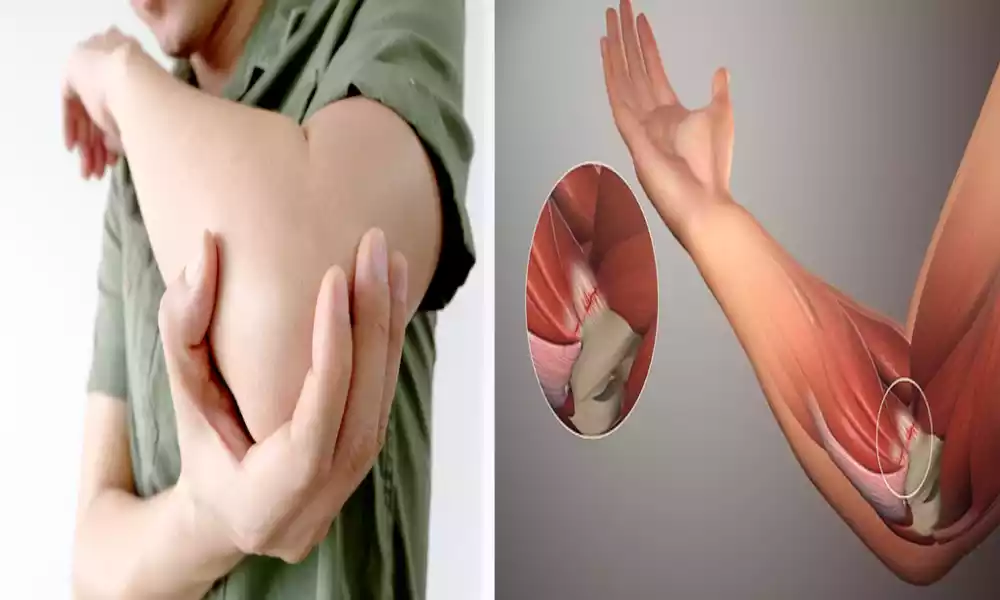
Tendonitis often referred to as tendinitis is a medical condition that is defined by the irritation or inflammation of a tendon. A tendon is the fibrous, thick tissue that connects bones to muscles.
Tendonitis usually occurs as an outcome of excessive strain and repetitive strain, or injuries on the tendon. The condition can cause swelling, pain, and tenderness of the affected area, with possible limitations to the movement of joints and muscles.
Tendonitis is a common problem that affects tendons in regions like wrists, elbows, shoulders as well as the knees and heels. Treatment for tendonitis usually includes rest, ice, or heating therapy, anti-inflammatory medication as well as physical therapy, and, in some instances corticosteroid injections.
A proper management strategy is crucial for relieving symptoms and preventing the occurrence of chronic or repeated tendon issues.
Comparison Table of Bursitis and Tendonitis
Certainly, here’s a comparison table outlining the key differences and similarities between bursitis and tendonitis:
| Aspect | Bursitis | Tendonitis |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Inflammation of the bursae (fluid-filled sacs) located near joints. | Inflammation of a tendon, the fibrous tissue connecting muscle to bone. |
| Common Affected Areas | Joints like shoulders, hips, knees, and elbows where bursae are located. | Often occurs at joints with frequent movement, such as shoulders, elbows, wrists, knees, and heels. |
| Primary Cause | Overuse, repetitive motion, trauma, or infection leads to bursa irritation. | Overuse, repetitive strain, aging, or injury causes tendon inflammation. |
| Symptoms | Pain, swelling, tenderness, limited joint movement. | Pain, swelling, stiffness, and potential muscle weakness. |
| Diagnostic Methods | Physical examination, imaging tests (ultrasound, MRI). | Physical examination, imaging tests (ultrasound, MRI). |
| Treatment Options | Rest, ice or heat therapy, anti-inflammatory medications, physical therapy, aspiration (in severe cases). | Rest, ice or heat therapy, anti-inflammatory medications, physical therapy, corticosteroid injections (if necessary). |
| Complications | Chronic bursitis, septic bursitis (infection). | Tendon rupture, chronic tendonitis. |
| Prevention | Proper ergonomics, gradual exercise progression, and protective gear. | Proper technique, warm-up, stretching, strength training. |
This table highlights the distinctions between bursitis and tendonitis in terms of their definitions, common affected areas, causes, symptoms, diagnosis, treatment, complications, and prevention strategies.
Understanding these differences is essential for accurate diagnosis and effective management of these conditions.
The importance of distinguishing Difference Between Bursitis and Tendonitis
Differentiating between tendonitis and bursitis is essential for a variety of reasons since the two conditions have different reasons, treatments, and possible complications.
Here are the primary reasons to consider distinguishing between tendonitis and bursitis:
- Accurate Diagnosis:
- Being able to identify the exact issue is vital to ensure successful treatment. A misdiagnosis could lead to ineffective treatments, causing delays in the recovery process or worsening symptoms.
- Targeted Treatment:
- The tendonitis and bursitis conditions often require different methods of treatment. An accurate diagnosis can ensure that patients receive treatment tailored to their specific condition, increasing the likelihood of recovery.
- Medication Selection:
- Anti-inflammatory medicines used to treat these conditions can differ. Tendonitis and bursitis require specific dosages and medications and knowing the right situation is crucial for the most effective and safe treatment.
- Rehabilitation:
- Exercise and physical therapy differ depending on the structure that is affected. The correct identification aids in designing the right rehabilitation programs to build the muscles that are affected and increase mobility.
- Prevention Strategies:
- Knowing the distinctions between tendonitis and bursitis could aid patients in preventing these diseases. Knowing the risks and prevention actions specific to each condition will lower the chance of developing symptoms.
- Avoiding Complications:
- Tendonitis and bursitis can result in complications if not properly treated. An early and accurate diagnosis can facilitate prompt intervention, which reduces the possibility of developing chronic diseases or serious complications such as tendon ruptures.
- Quality of Life:
- Correct and timely treatment improves the quality of life for patients by reducing pain, increasing the mobility of patients, as well as avoiding disability. An accurate diagnosis is essential to achieving these results.
- Cost-Effective Care:
- Preventing misdiagnosis or inappropriate treatment can reduce the cost of healthcare for both patients as well as healthcare systems. A targeted approach to care is more efficient and cost-effective.
- Patient Education:
- Understanding the particular condition allows patients to take an active role in their healing. Patients can make informed choices regarding treatment options and lifestyle modifications.
Discerning between tendonitis and bursitis is vital for accurate diagnosis, customized treatment, and best outcomes. This ensures that patients receive the proper treatment and reduces the burden of disability, and pain as well as the costs of healthcare that are associated with these ailments.
Comparison of location and role in joints
The Role of Joints and Location:
Bursitis vs. Tendonitis
- Location:
- Bursitis:
- Bursae are small sacs of fluid found throughout the body, near joints.
- The most common areas for bursitis are those in which bursae are present for example, the shoulder knee, hip, elbow, or heel.
- The most commonly affected bursae are the subacromial sulcus bursa in the shoulder, the olecranon bursting at the elbow, and the prepatellar bursa inside the knee.
- Tendonitis:
- Tendons are strong, flexible cords connecting muscles to bones.
- Tendonitis can be found in a variety of areas of the body, mostly at sites in which tendons are exposed to strain and repetitive movement.
- The most common places for tendonitis are the tendons of the rotator cuff in the shoulders, the Achilles tendon on the heel as well and the tendons that run through the elbow and wrist.
- Bursitis:
- Role in Joints:
- Bursitis:
- Bursae are cushions that lubricate ease friction and permit easy movement between muscles, tendons, and bones.
- They reduce wear and tear in joint movements through the effect of cushioning.
- Tendonitis:
- Tendons play an important function in transmitting the power generated by muscles to bones, which allows joint motion.
- Tendonitis is a condition that occurs when tendons become damaged or inflamed due to injuries or overuse, which affects their ability to transfer force efficiently.
- Tendonitis can restrict the mobility of the joint, causing discomfort during movement.
- Bursitis:
- Function in Joint Health:
- Bursitis:
- Bursae are primarily responsible for joint health by reducing friction which helps prevent excessive wear on adjacent structures.
- If bursitis is present it may cause small-scale swelling and pain, however, it doesn’t usually alter the overall functioning of the joint.
- Tendonitis:
- Tendons are a crucial part of joint function and play a role in smooth and controlled movement.
- Tendonitis can affect joint function, creating pain and restricting the capacity to perform tasks that require the tendon’s functions.
- Bursitis:
- Interaction:
- Bursitis and Tendonitis :
- Tendonitis and bursitis may be present together, particularly in areas where tendons as well as bursae are tightly linked.
- In these cases, irritation of the tendon (tendonitis) could result in an increase in friction and irritation of the surrounding bursa, leading to bursitis.
- Bursitis and Tendonitis :
Knowing the position and function of tendons and bursae in joints is crucial to diagnosing and managing ailments like tendonitis and bursitis. Both can cause discomfort and pain however, they have distinct anatomical structures as well as mechanisms that affect their appearance and treatment.
Typical symptoms of tendonitis
Tendonitis also referred to as tendinitis is a condition that is characterized by irritation, inflammation, or microtears within the tendon. It is the fibrous tissue that connects muscles and bones. The symptoms of tendonitis differ depending on the affected tendon as well as its location within the body.
Here are a few typical signs of tendonitis:
- Pain: Pain is the most frequent symptom of tendonitis. The pain is usually described as the sensation of tenderness or ache in the affected region. It can be a little mild at first but may become more severe over time with the use of the injured tendon.
- Swelling: The inflammation of the tendon may cause localized swelling in the area of the tendon that is affected. The swelling can be apparent and can cause discomfort.
- Tenderness: The area surrounding the tendon affected can be a bit tender. The pressure or the palpation of the area could cause pain.
- Stiffness: Tendonitis can lead to an increase in stiffness of the joint or the muscle around the tendon affected. The stiffness is usually apparent in the morning or after a period of rest.
- Insufficiency: A few people suffering from tendonitis might feel weaker in the muscle group affected. This weakness may make it difficult to perform tasks that require an affected tendon.
- limited range of motion: Tendonitis can restrict the range of motion for the joint that’s associated with the tendon affected. This restriction can impact everyday activities and athletic performance.
- Crepitus or Cracking: In certain instances, the movement in the tendon affected could result in popping or cracking sounds, also known as crepitus. It may also cause discomfort.
- Warmth: The area that is affected could feel warm to the area due to an increase in the circulation of blood and swelling.
- Pain during Activity: Tendonitis pain usually is aggravated by activity or movement that involves the tendon affected. The repetition of motions, for example, throwing, typing, or lifting, could cause more discomfort.
- Pain at rest: When it is more severe instances, the pain caused by tendonitis could persist even at rest, causing disruption to sleeping and activities.
It’s important to know that the symptoms specific to tendonitis will vary according to the tendon affected along with the extent of the problem. Getting a medical diagnosis and evaluation is vital when you suspect tendonitis.
The proper treatment, rest, and rehabilitation are required to ease symptoms and avoid further injury in the tendon. In addition, your healthcare professional might suggest imaging studies such as ultrasound or MRI in order to verify the diagnosis as well as determine the severity of damage to the tendon.
Medical history and physical examination
Physical and medical histories are the most important elements of a healthcare practitioner’s assessment procedure. They are vital for gathering data about the health of a person identifying health concerns that could be a cause for concern and determining the most appropriate treatment plan, which may include any additional diagnostic tests and treatments.
Here’s a brief overview of these two essential aspects of an assessment of a patient:
- Medical History:
- Patient interview: A healthcare professional typically starts with an extensive interview of the person. During the interview, the patient will share details about their health issues of the present and past medical history as well as family medical history and lifestyle-related factors (such as exercise, diet, and alcohol or tobacco consumption).
- Chief complaint: The main reason to seek medical attention, referred to as the primary complaint is recognized. The complaint aids in the exam and investigation.
- Present illness: The physician requests the patient to describe the condition they are experiencing in full, including the date of onset, the time, duration, as well as any other factors that cause or lessen the symptoms.
- Medical Histories: The patient is required to provide information on their health conditions, surgeries hospitalizations, allergies medication (including supplements and over-the-counter medications), and vaccinations.
- Family history: Information about any important medical condition or disease that affects the family of the patient is gathered. This assists in determining genetic predispositions to a variety of diseases.
- Lifestyle and Social Histories: A record of the daily routine of a patient such as food, exercise as well as alcohol and drug usage, and smoking is gathered.
- Psychosocial factors: The health professional might inquire about psychological or emotional factors that may affect the patient’s health, including depression or stress problems.
- Physical Examination:
- General Appearance: The doctor examines the patient’s general appearance, including indications of stress, anxiety, posture, and nutritional status.
- Vital Signs: Measurements like breathing rate, blood pressure, and body temperature are recorded.
- Head-to-Toe Evaluation: An in-depth assessment of different body systems is performed. It involves inspecting and palpating (feeling) as well as percussing (tapping) inculcating (listening) to various organs and body parts. The most important components of the physical examination could include:
- Lung and heart sounds
- Examen of the abdomen
- Musculoskeletal Evaluation
- Evaluation of the Neurologic System
- Skin examination
- Examining specific problems or complaints (e.g. joint irritation or rashes, respiratory symptoms)
- Specialized Exams: Depending on the symptoms of the patient and their medical history, the doctor can carry out specialized tests or exams like an ophthalmoscopic examination, an otoscopic examination, or a neurological exam.
- Diagnostic tests: Based on the results of the physical examination along with medical information, the physician might recommend additional diagnostic tests, including blood tests and images (X-rays, CT scans, MRI) electrocardiograms (ECG and EKG), or other tests that are specific to the patient.
The medical history as well as the physical examination are crucial to developing a thorough knowledge of the patient’s health situation. They provide the foundation to make a precise diagnosis and establish a suitable treatment plan.
The data collected during these procedures helps healthcare professionals determine health risks and risk factors and decide on the best method to improve the health of the patient.
Prognosis and Complications
The prognosis and the potential for complications differ according to the particular health issue or condition the patient is battling. We’ll present an outline of what “prognosis” means and the common factors that affect it, along with some instances of the complications that may arise from medical circumstances.
Prognosis:
Prognosis refers specifically to the expected result or the course of a medical issue or disease. It gives an estimate of the probability of recovery, the anticipated duration of the disease, and the possibility of complications. A variety of factors may affect your prognosis.
- The severity of the condition: How severe the illness or injury is an important aspect. The mild cases could have better outcomes than those with a more severe or advanced case.
- Type of The condition: Certain diseases have various prognoses. Certain diseases are acute, which means they tend to have a shorter and good course. Other conditions are chronic and have an extended and more unpredictable course.
- Reaction to Treatment: The response of a patient to treatment could significantly affect the outcome. Patients who respond well to treatment options tend to have a better chance of surviving.
- Age and General Health: The patient’s age and overall health may affect the prognosis. People who are younger and healthier typically have better chances to recover from injury or illness.
- Speed of diagnosis and Treatment: A diagnosis that is made early and prompt treatment can enhance the chances of success in several cases, and could stop the condition from getting worse.
- Comorbidities: The presence of any other existing health conditions (comorbidities) can affect the treatment plan, particularly when they interfere with the primary health condition.
- Patient Adherence: A patient’s compliance with prescribed treatments and lifestyle modifications can affect the prognosis. Inadequate compliance with medical advice could make things worse.
- Genetics: In some instances, genetic factors can affect the prognosis. Certain genetic markers can predispose patients to have greater or less favorable outcomes for certain ailments.
Complications:
Complications are secondary conditions and adverse reactions that may occur as a result of an illness, medical condition, or treatment.
The severity of complications can differ based on the particular condition, however, they can include:
- Infections: Infections may occur as a result of various ailments in particular those whose immune systems are weak.
- Organ damage: Certain ailments can result in damage or dysfunction of body organs and systems. For instance, diabetes may result in eye, kidney, or nerve damage.
- Pain and disability: Chronic illnesses or injuries could cause chronic disabilities or pain that impact the quality of life of a person.
- Surgical complications: The procedure of undergoing surgery may result in complications like bleeding, infection, and adverse reactions to anesthesia.
- Side effects of medications: The medicines prescribed to treat a problem can cause negative side effects that require to be controlled.
- psychological impact: A variety of medical conditions can cause psychological effects, like anxiety, depression, or shifts in mood.
- Recurrence: In some instances, it is possible for the condition to recur necessitating additional treatment or treatment.
- Lifestyle Changes: Certain illnesses require major lifestyle changes that can be difficult for patients.
It is important to remember that the prognosis and severity of complications may differ widely among individuals regardless of the same medical condition because of the distinct mix of factors that affect every patient.
Healthcare professionals play a vital part in assessing the prognosis of patients as well as monitoring for potential complications and offering advice to patients on how to maximize their outcomes and improve their quality of life.
Similarities Between Bursitis and Tendonitis
Both tendonitis and bursitis are commonly occurring musculoskeletal ailments that affect soft tissues and around joints.
While they are distinct there are many similarities between the two conditions:
- Inflammation: Bursitis and tendonitis cause inflammation of soft tissues. In the case of bursitis, inflammation is triggered by the bursae (small sacs filled with fluid), and in tendonitis, it affects the tendon (fibrous tissues that connect muscles and bones).
- Pain: The feeling of pain is a common symptom for both of the conditions. People suffering from tendonitis or bursitis typically experience pain in a specific area near the area of inflammation. The pain may be mild or extreme, depending on the degree of inflammation.
- Swelling: Swelling is a frequent symptom that is common to tendonitis and bursitis. The inflammation causes the accumulation of fluid within the affected area, which leads to noticeable swelling, tenderness, and an impression of tightness or fullness.
- Limitation of Range: Tendonitis and bursitis can limit the motion range of the joint in question. This makes it difficult to carry out activities or movements that require the injured bursa or tendon.
- Aggravation due to movement: Both conditions are more likely to get worse when you move or engage in activities that strain the affected tendons or bursa. Repetitive movements or activities that exert pressure on the injured area can increase pain and discomfort.
- Common Affected Areas: Tendonitis and Bursitis can be found in similar anatomical locations. For instance, they frequently target the shoulders (rotator cuff tendonitis, subacromial bursitis) and elbow (tennis elbow and olecranon symphysis) and in the hip (trochanteric bursitis) and knee (patellar tendonitis and prepatellar bursitis) and the heel (Achilles tendonitis and retrocalcaneal syphilis).
- Possible causes: Both conditions may be caused by similar causes like overuse or repetitive strain on the affected region injuries or trauma, and degeneration due to the age of the soft tissues.
- Diagnosis: Healthcare professionals generally utilize similar diagnostic strategies for both tendonitis and bursitis that may involve an examination of medical history physical examination, as well as imaging tests (e.g. radiographs, X-rays ultrasound as well as MRI) in order to establish the cause and evaluate the severity of damage to tissues.
- Conservative treatment: Treatment for the initial stage of both ailments typically entails moderate measures, like rest and ice, anti-inflammatory medication physical therapy, adjustments to activity, or ergonomics.
- Possibility of complications: If untreated, or if the root cause is not addressed the tendonitis and bursitis could lead to complications, including chronic joint pain, reduced joint function, and the possibility of frequent flare-ups.
Although there are some similarities it’s crucial to realize that tendonitis and bursitis are distinct conditions that differ in the particular tissues affected and the locations of their affected tissues.
An accurate diagnosis by a medical specialist is essential to customize treatments and strategies to meet the distinct particularities of each disease.
Reference Books
Certainly! Here are some reference books across various genres and subjects that you may find valuable. These books cover a wide range of topics, from literature and science to history and self-help. Keep in mind that the selection is not exhaustive, but it offers a diverse list of books that can serve as excellent references:
Science and Nature:
- “Cosmos” by Carl Sagan – A classic exploration of the universe, its origins, and our place within it.
- “The Selfish Gene” by Richard Dawkins – A groundbreaking work on evolutionary biology and the concept of the gene’s role in evolution.
- “A Brief History of Time” by Stephen Hawking – An accessible exploration of complex cosmological concepts, including black holes and the nature of time.
- “The Immortal Life of Henrietta Lacks” by Rebecca Skloot – An examination of the ethical and scientific implications of the HeLa cell line, derived from Henrietta Lacks.
Literature and Fiction:
- “The Norton Anthology of American Literature” (Various Editors) – A comprehensive collection of American literary classics from various time periods.
- “The Elements of Style” by William Strunk Jr. and E.B. White – A timeless guide to clear and effective writing.
- “The Oxford English Dictionary” – A comprehensive reference work on the English language, providing historical and etymological insights.
History:
- “A People’s History of the United States” by Howard Zinn – An alternative perspective on U.S. history that focuses on the experiences of everyday people.
- “Guns, Germs, and Steel” by Jared Diamond – An exploration of the factors that contributed to the success of certain civilizations throughout history.
- “Sapiens: A Brief History of Humankind” by Yuval Noah Harari – A thought-provoking examination of the history and impact of Homo sapiens on the world.
Conclusion
Reference books are valuable resources that provide information, direction, and information on many different subjects. If you’re interested in the world of literature, science, or pursuing personal growth an appropriate reference book is a reliable companion on your search for knowledge and understanding.
These books are the base for writing, learning, or critical analysis, which makes them vital tools for academic and personal development.