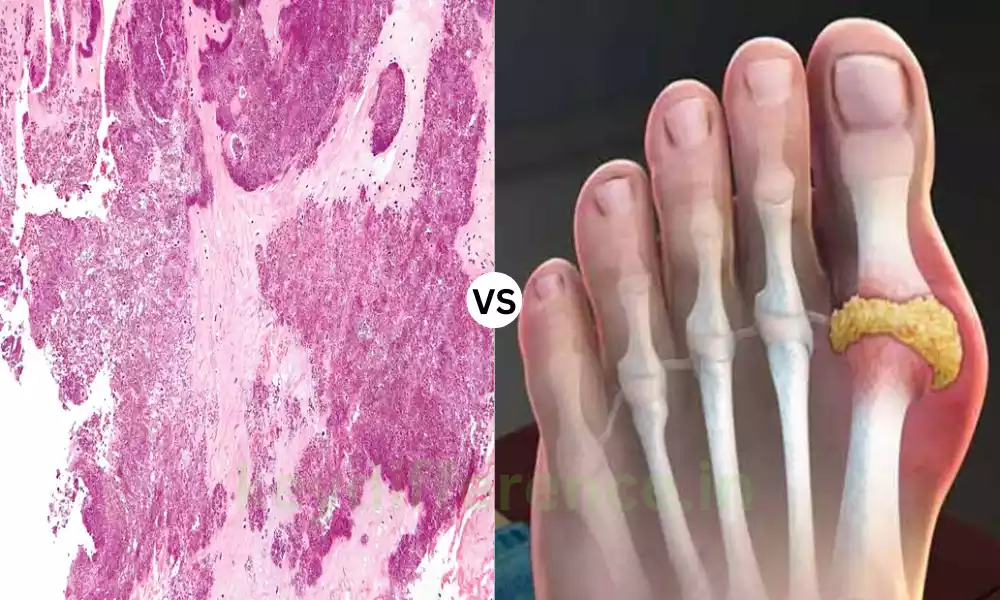
The pseudogout as well as the gout form Pseudogout and Gout different forms of arthritis that have a lot in common in their symptomatology, typically leading to acute joint discomfort and inflammation. However, they differ in their primary causes and treatment methods.
This content outline is designed to give a brief outline of the major distinctions and similarities between these conditions and equip readers with the necessary information to recognize and differentiate between pseudogout and gout.
Explanation of Pseudogout
Pseudogout, also referred to as calcium pyrophosphate deposition disorder (CPPD) is an inflammation-related arthritis that is characterized by the formation of calcium pyrophosphate crystals within joints.
These crystals can trigger an acute and painful joint inflammation that can resemble Gout-like symptoms but they differ by their crystal structure and the root causes. Pseudogout is primarily a problem for joints, primarily the knees.
It can cause acute bouts of swelling, pain, and a decrease in mobility in joints. The most common method of diagnosing pseudogout is an analysis of joint fluid to determine that there are calcium pyrophosphate crystals making it possible to differentiate from other types of arthritis.
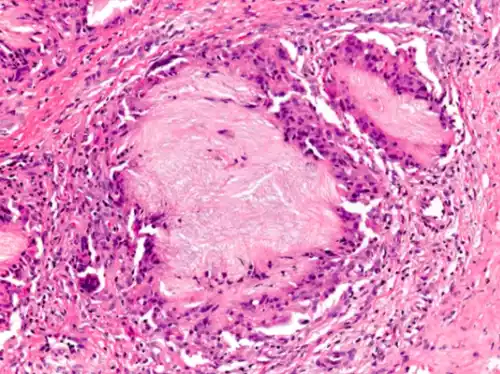
Explanation of Gout
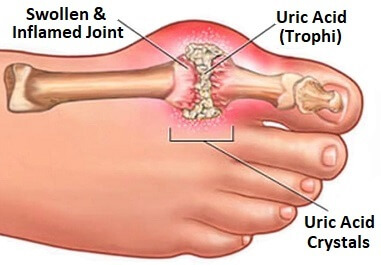
Gout is a kind of inflammatory arthritis, characterized by the build-up of uric acid crystals within joints, which can cause extreme and sudden joint pain inflammation, and discomfort.
It is usually regarded as a metabolic disorder since it is associated with high levels of uric acid within the blood, which is called hyperuricemia. The crystals of uric acids can accumulate in joints across the body, however, it is more common to see them in the toes which are the largest. Gout attacks can be very painful and are typically associated with swelling, redness, and warmth around the joint that is affected.
Gout is caused by a mixture of genetics, diet choices, as well as other medical conditions. It is usually diagnosed by an evaluation of joint fluid, a clinical exam analysis to determine uric acid crystals, and occasionally imaging tests such as X-rays.
Gout treatment involves changes to your lifestyle such as diet modifications, weight control, and a higher level of hydration and medicines to reduce discomfort, ease inflammation, and reduce uric acid levels in blood. If untreated Gout can cause arthritis-related joint pain and the development of deposits of uric acids known as tophi.
Comparison Table of Pseudogout and Gout
Here’s a comparison table highlighting the key differences and some similarities between pseudogout and gout:
| Characteristic | Pseudogout | Gout |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Form of inflammatory arthritis characterized by calcium pyrophosphate crystal deposition in joints | Form of inflammatory arthritis characterized by uric acid crystal deposition in joints |
| Crystal Composition | Calcium pyrophosphate crystals | Uric acid crystals |
| Underlying Cause | Calcium pyrophosphate crystal deposition | Elevated uric acid levels (hyperuricemia) |
| Common Affected Joints | Knees, wrists, ankles, and other joints | Often the big toe, but can affect various joints (e.g., ankles, knees) |
| Symptoms | – Sudden joint pain and inflammation – Resembles gout symptoms – Pain, swelling, and limited mobility | – Sudden and severe joint pain – Swelling, redness, warmth – Typically affects the big toe |
| Diagnosis | Joint fluid analysis (identifying calcium pyrophosphate crystals) – Imaging (X-rays, CT scans) | Joint fluid analysis (identifying uric acid crystals) – Imaging (X-rays, ultrasound) |
| Treatment | – Pain relief medications (NSAIDs, colchicine) – Joint aspiration for symptom relief – Physical therapy | – Lifestyle modifications (diet, hydration, weight management) – Pain relief medications (NSAIDs, colchicine) – Urate-lowering therapy (allopurinol, febuxostat) |
| Prognosis and Complications | – Recurrent pseudogout attacks – Joint damage over time – Association with other health conditions | – Chronic gout and joint damage – Kidney stones – Tophi formation |
| Similarities | – Acute onset of joint pain and inflammation – Potential for chronic forms of arthritis – Management of symptoms and prevention strategies | – Acute onset of joint pain and inflammation – Potential for chronic forms of arthritis – Management of symptoms and prevention strategies |
Please note that while this table highlights the main differences and some similarities between pseudogout and gout, it is essential to consult with a healthcare professional for an accurate diagnosis and personalized treatment plan if you suspect you have either condition.
Importance of distinguishing between Pseudogout and Gout
The distinction between gout and pseudogout is vital for many reasons since it could greatly impact the diagnosis, treatment, and treatment of these two kinds of arthritis.
Here are a few of the main reasons why it is important to distinguish between pseudogout as well as Gout:
- Treatment Methodology: Treatment for gout and pseudogout may differ in a significant way. Gout is managed primarily by reducing uric acid levels in the blood and dealing with inflammation, whereas treatment for pseudogout is based on managing calcium pyrophosphate crystal inflammation. The proper treatment is crucial for relieving symptoms and preventing complications.
- Medication Choice: The medications that treat these ailments differ. For gout, medicines such as febuxostat or allopurinol are prescribed to reduce the levels of uric acid, whereas medicines like NSAIDs as well as colchicine, are typically employed to treat inflammation and pain. For pseudogout, pain relief drugs like NSAIDs are usually more effective. Furthermore, certain treatments can be targeted at the dissolution of calcium crystals.
- Avoiding mismanagement: The misdiagnosis and confusion between gout and pseudogout can result in the incorrect prescription of medicines that may not be effective in helping relieve symptoms. This could lead to prolonged discomfort and unneeded negative side consequences.
- Preventing complications: Both of these conditions can result in joint damage and other complications if they are not treated appropriately. Gout may cause the formation of deposits of uric acids (tophi) as well as kidney stones. In addition, pseudogout can cause the deposition of crystals that recur and cause joint damage. An early and precise diagnosis is vital to prevent these issues.
- Lifestyle and Dietary Guidelines: Lifestyle changes and dietary suggestions may differ for gout and pseudogout. Gout sufferers are advised to modify their diet to lower the level of uric acids, while pseudogout treatment may be focused more on joint health and managing pain.
- Prognostic implications: Recognizing the particular health issue can help healthcare professionals and patients know the long-term prognosis as well as the anticipated course of the disease. This knowledge will help in making the treatment plan and lifestyle modifications.
- QOL: Accurately identifying the condition will allow the more effective management of symptoms as well as higher health for people who suffer from pseudogout or gout. The right treatment can ease discomfort, ease inflammation, and increase mobility.
knowing the difference between Gout and pseudogout is crucial to ensure that patients receive the most effective and appropriate treatment, avoid complications, and boost their overall health.
Healthcare professionals play a crucial part in correctly diagnosing and managing these diseases however, individuals must seek out medical advice when they are experiencing joint pain and associated symptoms, to ensure they are receiving the appropriate treatment.
How are gout and pseudogout similar?
Gout and pseudogout share a lot in a variety of ways, even though they are distinct forms of arthritis that are triggered by crystals.
Here are a few key similarities between pseudogout and gout:
- Acute Joint Pain: Gout and pseudogout usually present with periods of severe and sudden joint discomfort. These painful episodes can happen abruptly and frequently without prior warning.
- Inflammation: In both instances, the affected joints are painful, with symptoms like redness, swelling, and warmth in the area of the joint. The inflammation is the consequence of your body’s immune reaction to crystals.
- Potential for chronic forms: Although Gout and pseudogout typically present as acute symptoms, both also can develop into chronic conditions if they are neglected or not properly managed. Chronic cases of both conditions may cause joint pain and damage for a long time.
- Strategy for Management: The first treatment for acute attacks in pseudogout and gout involves the use of pain-relieving medication, including nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory medications (NSAIDs) or colchicine. Lifestyle changes, like diet changes and weight control, are recommended for both ailments.
- Preventive Strategies: Both ailments are susceptible to similar strategies to prevent them, including keeping hydrated, maintaining an appropriate weight, and making adjustments to the diet in order to lower the chance of recurring attacks. Eliminating alcohol and foods high in purine are beneficial in both instances.
- Diagnostic imaging: Imaging techniques such as ultrasound and X-rays could be utilized in the diagnosis and monitoring of pseudogout and gout in order to determine the extent of joint damage as well as crystal deposition.
- The importance of early diagnosis: Early diagnosis and treatment are crucial for pseudogout as well as gout to ease symptoms and avoid long-term complications.
It’s crucial to recognize that despite these resemblances, however, there are some distinct differences between pseudogout and gout in regards to their crystal composition, their underlying reasons, and the specific treatments.
A precise diagnosis by a healthcare expert is vital in order to ensure that appropriate management and treatment methods are used for each condition.
High uric acid levels in the blood
The presence of elevated levels of uric acids in the blood, also known as hyperuricemia, may cause a myriad of issues and consequences for health. Uric acid is an inorganic waste product typically excreted by kidneys. When the levels of uric acids in blood levels are high, it could result in a variety of health problems.
Here are some of the most important facts regarding high levels of uric acid:
- Causes of Hyperuricemia:
- Diet: Consuming a high quantity of purine-rich foods like red meats seafood, organ meats, fish and high-fructose corn syrup can lead to an increase in uric acid levels.
- Genetics: Certain individuals are predisposed genetically to produce higher levels of Uric acid.
- Kidney Function: A deficiency in kidney function could hinder the body’s capacity to eliminate uric acid effectively, leading to its accumulation in blood.
- Medicines: Certain medicines like diuretics (water pills) can increase the levels of uric acid.
- Health Conditions: conditions like hypertension, obesity metabolic syndrome, and certain cancers may be linked with hyperuricemia.
- Health Implications:
- The presence of high levels of uric acid is an important risk factor for the development of gout, a form of arthritis that is characterized by pain crystals of uric acids that form within joints.
- Uric acid crystals may build up in the kidneys which could result in the formation of kidney stones.
- A few reports suggest hyperuricemia could be linked to an increased risk of developing cardiovascular diseases which include hypertension as well as heart disease.
- The elevated levels of uric acid are linked to insulin resistance and an increase in the chance of developing the type 2 form of diabetes.
- Symptoms:
- Hyperuricemia is not the only cause of obvious symptoms. It is usually brought to the forefront when it triggers Gout attacks or other health issues.
- Diagnosis:
- Hyperuricemia is usually detected through an examination of blood that tests levels of uric acids within the bloodstream. If the uric acid level is 7 mg/dL or greater is typically regarded to be elevated.
- Treatment:
- Treatment for high uric acid levels that are high can require changes to lifestyles that include dietary adjustments (reducing purine-rich food items and consumption of alcohol) weight control, and keeping hydrated.
- Drugs such as allopurinol or Febuxostat can be prescribed to reduce the levels of uric acid, particularly when there is any history of kidney attacks or gout stone formation.
- Treatment of medical conditions that have underlying causes and addressing lifestyle issues can help control hyperuricemia.
It is important to remember that not all people with elevated levels of uric acids are likely to develop gout-related health issues. The treatment for hyperuricemia needs to be adapted to the individual’s particular circumstances as well as risk factors.
A doctor can offer advice on how to manage elevated levels of uric acids and related issues.
Formation of calcium pyrophosphate crystals
The development of calcium pyrophosphate crystals is one of the key steps that is involved in the development and progression of pseudogout. which is an arthritis condition that is characterized by the formation of crystals within joints.
Here’s a quick overview of the process by which calcium pyrophosphate crystals develop:
- Synthesis of Pyrophosphate (PPi):
- Pyrophosphate (PPi) is an organic molecule that is found within the human body. It is produced as the result of a variety of metabolic processes, such as the breakdown of the adenosine triphosphate (ATP) that is involved in the cellular energy transfer.
- Role of Chondrocytes:
- Chondrocytes are special cells found in cartilage, the fatty tissue that covers the edges of bones in joints. Chondrocytes play an essential part in maintaining the health of cartilage.
- In pseudogout, there is an unbalance in the breakdown and production of pyrophosphate inside chondrocytes.
- Excess Pyrophosphate Accumulation:
- In pseudogout, there’s an increase in pyrophosphate in chondrocytes. This leads to increased levels of this substance.
- Calcium Binding:
- The excess pyrophosphate found in chondrocytes bonds with calcium ions in joint fluid. This binding creates Calcium pyrophosphate-based complexes.
- Formation of Crystals:
- In time, these calcium pyrophosphate compounds can form crystals in joint spaces. The crystals are microscopic and appear as needle-like or rhomboid structures.
- Deposition in Joints:
- The calcium pyrophosphate crystals that form are then released into synovial fluid, which helps to lubricate the joints. They can then be deposited in and around joints, which triggers an inflammation response.
- Inflammation and Symptoms:
- These crystals within the joint space may trigger an immune reaction, which can lead the joint to become inflamed. This inflammation can cause symptoms of pseudogout which include joint pain redness, swelling, and a warm sensation.
It’s crucial to understand that the exact mechanisms underlying to the formation and crystallization of calcium pyrophosphate in pseudogout are currently not fully understood so research into this field continues.
Pseudogout may affect many joints, with knees being among the most frequently affected joints. A precise diagnosis and treatment for pseudogout generally involve a medical evaluation as well as joint fluid analysis to detect calcium pyrophosphate crystals and the use of medication to control inflammation and pain during acute attacks.
Joint aspiration to relieve symptoms
The procedure, commonly referred to as arthrocentesis, is a medical procedure used to alleviate symptoms arising from particular joint problems, such as pseudogout, gout, arthritis, and infections. It involves removing liquid (synovial fluid) from joints that are swollen with a needle and the syringe.
This is how joint aspiration is done and how it can alleviate symptoms:
Procedure for Joint Aspiration:
- Patient preparation: The patient is generally placed so that it provides easy access to the joint. The joint’s skin will be cleaned as well as sterilized.
- Local anesthesia: to reduce any discomfort that may occur during this procedure the doctor can inject local anesthetic in the skin and surrounding tissues around the joint.
- Needle Injection: A sterile needle is carefully placed into joint space. The healthcare professional may employ the ultrasound device or the fluoroscopy (live radiography) to direct the needle to the proper place in the joint.
- Fluid Removal: When the needle is properly placed in the joint area, synovial fluid can be extracted by attaching a syringe to the needle, and then gently pulling the plunger. What amount of synovial fluid gets eliminated will depend on the condition that is being treated as well as the judgment of the healthcare professional.
- Analysis: The aspirated synovial fluid goes to a lab to be analyzed. The analysis will help identify the root cause of joint discomfort. For instance, in pseudogout or gout, the presence of crystals that are characteristic in the synovial fluid may confirm the diagnosis.
How Joint Aspiration Relieves Symptoms:
- Treatment for Pain: removing excessive synovial fluid from joints is able to instantly relieve pressure inside the joint. The reduction in pressure typically results in a significant decrease in discomfort and pain.
- Reduplication of Inflammation: in conditions like gout or pseudogout elimination of inflammation and crystals from joints can lessen inflammation as well as the symptoms that accompany it, such as redness, swelling, and warmth.
- Diagnosis: Joint fluid analysis can provide important diagnostic information. It is able to confirm or eliminate specific joint conditions and help guide subsequent treatment choices.
- Therapeutic Impact: In certain instances, joint aspiration can be not just for diagnostic purposes, but can also be used to treat. It can, for instance, be used to drain joints with fluid that has become infected as a result of Septic arthritis.
- Preventing complications: for conditions such as pseudogout or gout, joint aspiration may help to avoid complications that are associated with inflammation and crystal deposition, for example, joint damage.
- Treatment Plan: The results of joint fluid tests may assist healthcare professionals in determining the most effective treatment for the underlying joint issue, whether that is through medication lifestyle changes, or any other treatment.
Joint aspiration is usually considered an effective and safe procedure when carried out by a qualified healthcare professional. However, it might not be appropriate for every patient or for all joint disorders.
Patients must discuss the possible advantages and dangers associated with joint aspiration with their medical physician prior to having the procedure.
Association with other health conditions
Gout and pseudogout can be linked to various health issues, and understanding the connections is crucial for full-scale healthcare management. Here are a few typical health issues that can be linked to gout or pseudogout.
Conditions and symptoms associated With Gout:
- Metabolic syndrome: Gout is typically linked to metabolic syndrome, which is a group of diseases that include hypertension, obesity insulin resistance, and abnormal levels of lipids. These causes can result in an increase in uric acid levels and also the development of gout.
- Hypertension (High Blood Pressure): There is an extensive connection between hypertension and gout. Hypertension can be a contributing factor in the development of gout and gout can worsen hypertension.
- Diabetes: Gout is associated with Type 2 Diabetes. Inflammation resistance and metabolic issues can play a role in both.
- Kidney Disease: Gout is an underlying kidney disease. Kidney disorders can result in diminished excretion of uric acid which can lead to hyperuricemia and Gout.
- Cardiovascular Disease: Gout sufferers have an increased risk of suffering from cardiovascular illnesses like cardiovascular artery diseases, heart attacks, and strokes.
- Obesity: Obesity is a recognized risk cause for both gout and metabolic syndrome. This is because it could cause an increase in the production of uric acids and decrease excretion.
Conditions associated with Pseudogout:
- Aging: Pseudogout is more frequent with age and occurs more often among older adults. The risk of developing pseudogout rises substantially after 60.
- Joint trauma or surgery: Joint injuries, trauma, or surgery could trigger pseudogout attacks in prone people.
- Metabolic disorders: Certain metabolic disorders like hemochromatosis (iron overload disorder) could predispose individuals to pseudogout.
- Hyperparathyroidism: The overactivity of the parathyroid glands could cause an increase in calcium levels in the blood, which can contribute to the development of pseudogout.
- Osteoarthritis: Pseudogout may be a co-occurring condition with osteoarthritis and could cause more pain in joints affected by osteoarthritis.
- Other Rheumatic Disorders: Pseudogout could be a part of other rheumatic diseases including rheumatoid or rheumatoid-like.
- Calcium disorders: Disorders that interfere with the metabolism of calcium within the body may increase the chance of deposition of calcium pyrophosphate crystals and can cause pseudogout.
It is important to remember that, while there are associations not all people with gout or pseudogout are likely to develop these health conditions, and having these conditions isn’t a guarantee of the growth of gout or pseudogout.
Healthcare professionals consider these relationships when assessing and managing patients with joint problems in that addressing the underlying health conditions is essential to the effective management of gout and pseudogout and minimizing the risk of complications.
Calcium pyrophosphate crystals in pseudogout
Calcium pyrophosphate crystals are essential to the pathogenesis and development of pseudogout, which is also called calcium pyrophosphate deposition condition (CPPD). These crystals are microscopic and form inside and around joints, and constitute a characteristic feature of pseudogout.
Here’s an examination of the calcium pyrophosphate crystals that are found in pseudogout:
- Crystal Composition: Crystals of calcium pyrophosphate comprise calcium and the ions of pyrophosphate. They are distinct from the uric acid crystals that are found in the gout.
- Synovial Fluid Deposition: In pseudogout, calcium pyrophosphate crystals build up within the synovial fluid which is used to lubricate joints. The crystals may develop in the event of an imbalance in the amount of calcium and pyrophosphate within the synovial fluid.
- Synovial Membrane Inflammation: the presence of calcium-pyrophosphate crystals could cause an inflammation response in the synovial membrane in the joint affected. The resulting inflammation causes typical symptoms of pseudogout which include swelling, pain as well as redness, and warmth in the joint.
- Joint Injury: As time passes repeated episodes of inflammation resulting from calcium pyrophosphate crystal deposition could cause joint damage and the emergence of chronic pseudogout. This could lead to chronic joint pain and deformities.
- Pseudogout-related Attacks: The attacks occur when crystals are removed from the synovial fluid to the joint space causing an inflammation response. The attacks may be sudden and painful to the point of being painful.
- Diagnosis: The diagnosis of pseudogout usually involves the analysis of joint fluid. In this method, the synovial fluid is extracted from the joint affected and studied under the microscope. The detection that calcium pyrophosphate crystals are present inside the joint fluid is an essential characteristic of diagnosis.
- Treatment: Treatment for pseudogout typically involves treating acute attacks using pain-relieving medications (such as NSAIDs and colchicine) and, sometimes, joint aspiration to eliminate crystal-laden fluids and alleviate symptoms. The long-term treatment could involve medication to ease inflammation and avoid further crystal formation.
- Other Deposition Sites: While pseudogout typically affects joints calcium pyrophosphate crystals could sometimes be found within other organs, like cartilage or tendons.
- Associations: Pseudogout is more prevalent in older adults and certain metabolic disorders such as hyperparathyroidism or hemochromatosis could increase the chance of calcium pyrophosphate crystal deposition.
It’s crucial to understand that although gout and pseudogout have similarities in the sense of acute joint inflammation and pain, the nature of the underlying crystal (calcium pyrophosphate when pseudogout is present as well as uric acids in Gout) and the risks and treatment strategies are distinct.
A precise diagnosis by a healthcare specialist is vital for the proper treatment.
Similarities Between Gout and Pseudogout
Gout and pseudogout despite being distinct types of arthritis based on crystals, have some similarities, especially in their clinical presentation and how they are treated.
Here are the most significant similarities between gout and:
- Acute Joint pain: Gout and pseudogout are characterized by the abrupt onset of severe joint pain. The episodes of pain typically appear quickly and may be extremely severe.
- Inflammation: In both cases, the affected joints are damaged, causing symptoms like heat, redness along swelling in the area of the joint. This inflammation is a result of the body’s immune reaction to crystals that are present in the joint.
- Unexpected Onset: The attacks of pseudogout or gout usually occur without warning. Patients could change from not experiencing symptoms to suffering from acute pain and inflammation in an hour.
- Commonly affected joints: While they could be a problem for any joint Both gout and pseudogout usually concentrate on certain joints. Gout most often affects those with the biggest toe (podagra) as well and pseudogout is often a problem for knees. However, they can also affect other joints too.
- Overlap of Symptoms: The symptoms of pseudogout and gout could be similar, including the sensation of warmth, redness, pain, and swelling of the joint that is affected. The overlap may make it difficult to distinguish between the two based only on the symptoms.
- Diagnose Methods: Both of these conditions usually require joint fluid tests to confirm the diagnosis with certainty. The identification of the kind of crystals that are present in synovial fluid can help identify Gout (uric acid crystals) and pseudogout (calcium pyrophosphate crystals).
- Strategy for Management: The initial treatment of acute attacks of both gout and pseudogout is to use medications for pain relief, like nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory medications (NSAIDs) as well as colchicine. Lifestyle changes, like diet changes and weight control, are also suggested for both ailments.
- Preventive Strategies: Both ailments are susceptible to similar prevention strategies, including drinking enough water, maintaining an appropriate weight, and making adjustments to the diet in order to decrease the chance of developing attacks in the future. Eliminating alcohol and foods high in purine is advantageous in both instances.
- Possibility of Chronic Forms: Both gout and pseudogout could become chronic conditions if they aren’t properly treated or if the risk factors remain. Chronic versions of both conditions may cause joint injuries and chronic pain.
While there are similarities it’s important to recognize that the reasons (crystal structure and composition) as well as some aspects of treatment may differ in significant ways between pseudogout and gout.
A precise diagnosis by a medical professional is essential to determine the best treatment and management strategy for every situation.
Management of symptoms and prevention strategies
The management of symptoms associated with pseudogout or gout as well as implementing prevention strategies is crucial for those suffering from these ailments.
Here are some guidelines to manage symptoms and prevent pseudogout and gout:
Management of Gout:
- Medications for Acute Attacks:
- Nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory medicines (NSAIDs): NSAIDs like naproxen and ibuprofen are able to decrease inflammation and pain Gout attacks.
- Colchicine: Colchicine is another medicine that is used to treat symptoms of gout. It can be especially effective if taken at the beginning of an attack.
- Corticosteroids: In certain instances, corticosteroids can be prescribed to decrease inflammation and discomfort.
- Lifestyle Modifications:
- Diet: Reduce intake of foods with high levels of purine, like red meat, seafood, organ meats, and alcohol, as they could cause elevated levels of uric acids.
- Hydration: Ensure that you are hydrated to flush out uric acids from your body.
- Weight Management: Getting and maintaining a healthy weight will lower the risk of suffering from gout attacks.
- Medications for Long-term Management:
- Urate-lowering therapy: If suffer from frequent gout attacks, or chronic hyperuricemia, your physician may prescribe medications such as allopurinol and febuxostat for lowering the level of uric acids.
- Prophylaxis when starting the urate-lowering treatment: To avoid flares of gout when beginning medications to lower urate levels, such as colchicine or NSAIDs are often prescribed.
- Pain Relief:
- Over-the-counter pain relievers can help manage mild pain between gout attacks.
- Rest and Elevation:
- The joint that is affected should be rested and elevating it will reduce swelling and pain in an attack of gout.
Prevention of Gout:
- Dietary Changes:
- Reduce the intake of purine-rich foods.
- Beware of drinking alcohol, particularly spirits and beers.
- Hydration:
- Keep yourself hydrated by drinking plenty of water throughout the day.
- Weight Management:
- Maintain and achieve your weight in a healthy way through exercising and diet.
Management of Pseudogout:
- Medications for Acute Attacks:
- Nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory medications (NSAIDs) as well as colchicine assist in relieving pain and inflammation that occurs during pseudogout attacks.
- Lifestyle Modifications:
- Regularly exercise to maintain joints’ flexibility, strength and mobility.
- Physical therapy is a possibility to help improve joint mobility.
- Management of Underlying Conditions:
- If it is connected to metabolic disorders, like hyperparathyroidism, addressing the root condition is vital.
Prevention of Pseudogout:
- Lifestyle and Dietary Measures:
- Keep a healthy weight by exercising and eating a balanced diet.
- Keep hydrated by drinking enough water.
- Avoid excessive alcohol consumption.
- Be aware of trauma to the joints since they could cause pseudogout-related attacks.
- Treatment of Associated Conditions:
- If the condition is related to specific metabolic disorders be sure to consult a doctor and follow the advice of a physician.
Gout and pseudogout are treatable people who suffer from they can live a normal life by taking care of themselves and adhering to the prevention strategies.
It’s essential to work with your doctor to create a customized management plan that’s tailored to your particular requirements and risk factors.
Conclusion
Although gout and pseudogout share the same joints and symptoms, they’re two distinct diseases with distinct underlying reasons and treatment options. The ability to differentiate between them is essential to prevent and manage the risk of complications among affected patients.