Introduction Obstructive and Central Sleep Apnea
Sleep Apnea (OSA and CSA) are serious sleeping disorders that disrupt breathing during rest. There are two categories of Sleep Apnea Obstructive Sleep Apnea (OSA) is more frequently encountered while Central Sleep Apnea (CSA).
OSA occurs when throat muscles relax excessively, blocking airway passages; in contrast CSA results from insufficient signals being transmitted between the brain and muscles controlling breathing – both types can have serious repercussions for health and daily life.
Therefore understanding their differences is critical for diagnosis and management; this article explores their symptoms, causes, management strategies as well as management approaches.
What is Obstructive Sleep Apnea?
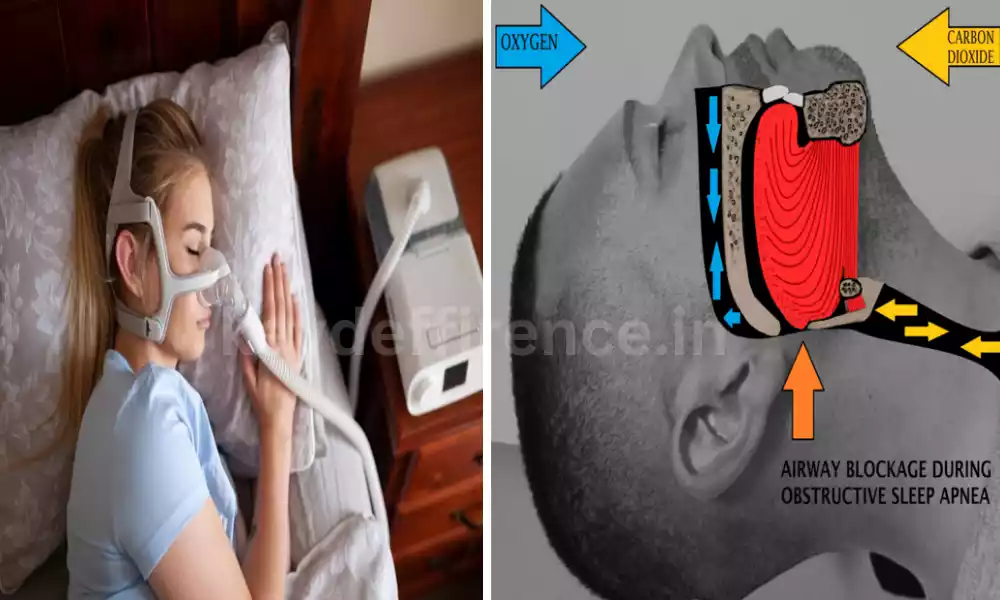
Obstructive Sleep Apnea (OSA) is the most prevalent form of sleep apnea and occurs when throat muscles relax too deeply during sleep, temporarily blocking airway passageways.
This obstruction results in brief stops in breathing that occur throughout the night, often with abrupt awakenings with choking sounds or daytime fatigue as symptoms. Untreated OSA can lead to serious health problems which require lifestyle adjustments, medical devices like CPAP machines, or surgery as treatment options.
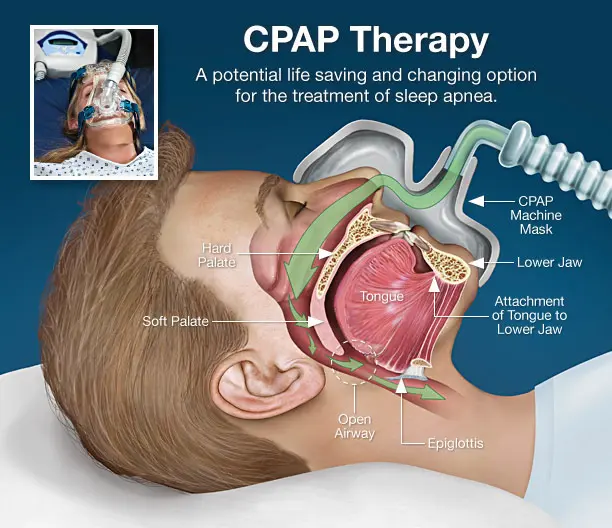
What is Central Sleep Apnea?
Central Sleep Apnea (CSA) is a type of sleep apnea in which the brain fails to send proper signals to muscles controlling breathing, leading to brief interruptions during sleep.
Unlike Obstructive Sleep Apnea where physical blocks prevent airflow, CSA occurs when there’s no effort made whatsoever by your body during short periods.
It is usually associated with medical issues and treatments may need to focus on these conditions as symptoms include difficulty staying or falling asleep and daytime fatigue.
Comparison Table of Obstructive and Central Sleep Apnea
Certainly! Here’s a comparison table that highlights the differences and similarities between Obstructive Sleep Apnea (OSA) and Central Sleep Apnea (CSA):
| Feature | Obstructive Sleep Apnea (OSA) | Central Sleep Apnea (CSA) |
|---|---|---|
| Cause | Blockage of the airway by relaxed throat muscles | Lack of signals from the brain to muscles controlling breathing |
| Common Symptoms | Loud snoring, abrupt awakenings, daytime fatigue | Difficulty falling/staying asleep, daytime fatigue |
| Risk Factors | Excess weight, narrowed airway, chronic nasal congestion | Heart disorders, opioid medications, age |
| Treatment Options | CPAP, lifestyle changes, surgery | Treatment of underlying conditions, CPAP, adaptive servo-ventilation |
| Diagnosis Methods | Sleep study, physical examination | Sleep study, examination of underlying conditions |
| Prevalence | More common | Less common |
This table provides an at-a-glance comparison of the two types of sleep apnea, emphasizing their distinctive features.
While they share some common symptoms, their causes, risk factors, and treatment options differ significantly, reflecting the unique nature of each condition.
Importance of Understanding Different Types
Understanding the different types of sleep apnea is vital both to healthcare providers and those affected or at risk by it, for a variety of reasons.
Here’s why:
1. Accurate Diagnosis Tailored Assessments: Different forms of sleep apnea require different diagnostic approaches, so understanding which kind you have can assist in selecting appropriate tools and procedures for diagnosis.
Identification of Underlying Causes: Different types of sleep apnea may be linked with other medical issues. By understanding which kind you have, medical professionals may be able to uncover any underlying issues which require treatment.
2. Effective Treatment
Personalized Plans: Therapy plans may differ for Obstructive and Central Sleep Apnea; by understanding which type exists, treatment can be tailored specifically to an individual’s unique needs.
Avoid Ineffective Therapies: Utilizing ineffective or harmful treatment approaches is often detrimental. By accurately diagnosing sleep apnea types and their types of treatments, unnecessary interventions, and potential side effects are minimized.
3. Prevention Strategies
Targeted Lifestyle Changes: By understanding which type of sleep apnea an individual has, healthcare providers and individuals alike can implement lifestyle changes designed specifically to reduce its associated risks.
Monitoring and Management: Gaining an understanding of sleep apnea allows for ongoing monitoring and adjustments to treatment plans that promote long-term management and avoidance of complications.
4. Educating Patients and Families
Empowering Self-Care: Gaining knowledge about sleep apnea gives patients a voice in their care, making informed decisions regarding treatment, lifestyle changes, and ongoing management.
Family Support: In order to offer effective assistance for sleep apnea sufferers, their loved ones must understand its unique challenges and needs. This knowledge allows them to offer better support.
5. Research and Development
Targeted Research: Gaining an understanding of different forms of sleep apnea drives targeted research and development efforts that produce innovative diagnostic tools and treatments specific to each form.
Improved Public Health Strategies: Differentiation among types of sleep apnea provides vital insight for public health initiatives, allowing more targeted awareness campaigns, early detection programs, and community support services to be carried out more effectively.
What are the Similarities Between Obstructive and Central Sleep Apnea?
Obstructive Sleep Apnea (OSA) and Central Sleep Apnea (CSA) are both types of sleep apnea that each has unique causes and symptoms, yet both share several similarities:
1. Overlapping Symptoms
Both OSA and CSA can cause disruptions to breathing during sleep, leading to similar symptoms including daytime fatigue, morning headaches, difficulty concentrating, and disrupted restful slumber.
2. Impact on Quality of Life
Both conditions can significantly diminish a person’s quality of life, leading to issues like poor work performance, an increase in accident risk, and straining personal relationships due to chronic fatigue and mood changes.
OSA and CSA pose serious health risks if left untreated, including cardiovascular issues, hypertension, diabetes, and increased stroke risks.
4. Diagnosis
Diagnosing both types typically involves conducting a polysomnography study, in which various physiological functions during sleep are monitored in order to distinguish between the two conditions and measure severity.
5. Some Treatment Solutions
Although the treatment approaches for each condition differ significantly, certain solutions like Continuous Positive Airway Pressure (CPAP) and adaptive Servo-Ventilation (ASV) machines may be used for both conditions.
6. Need for Professional Care
Both OSA and CSA require professional medical assessment, diagnosis, and management from healthcare providers who specialize in sleep disorders. Involvement from healthcare providers in caring for OSA/CSA cases typically takes the form of consultation services as a healthcare provider specializing in this condition may provide the care needed.
7. Lifestyle Considerations
Lifestyle modifications that contribute to managing both OSA and CSA such as maintaining a healthy weight and limiting alcohol consumption may be effective ways of combatting both conditions.
How Do You Treat Sleep Apnea?
Treating sleep apnea depends on both its type and severity, as well as individual patient factors like overall health, underlying conditions, and lifestyle considerations.
Here is an overview of how sleep apnea might be treated; with emphasis on Obstructive Sleep Apnea (OSA), Central Sleep Apnea (CSA), and Complex Sleep Apnea Syndrome (CompSAS):
Lifestyle Changes for Obstructive Sleep Apnea (OSA): Weight loss, limiting alcohol before bedtime, quitting smoking, and altering sleeping positions may all help alleviate symptoms of OSA.
CPAP (Continuous Positive Airway Pressure) Machine: A device that delivers a steady stream of air in order to maintain open breathing during sleep.
Dental Appliances: Custom-made devices which reposition the lower jaw and tongue so as to help open breathing passageways during slumber.
Surgery: For severe cases, surgeries to remove excess tissue or correct structural abnormalities may be considered as options for correcting Central Sleep Apnea (CSA).
Treat Underlying Conditions: Managing heart failure or changing medications that contribute to CSA could reduce symptoms.
ASV or Bilevel Positive Airway Pressure (BiPAP): These devices can adjust airflow according to breathing patterns.
Medication: Medication that stimulates breathing might also be prescribed in some instances, especially with Complex Sleep Apnea Syndrome (CompSAS).
Combination Therapies for OSA and CSA: These may include CPAP therapy, ASV therapy, lifestyle changes, and managing any underlying conditions that contribute to OSA/CSA symptoms.
Close Monitoring and Adjustments: Follow-up visits with healthcare providers are crucial in order to make any necessary modifications to treatment plans as necessary. General Recommendations
Sleep Hygiene: Ensuring good practices like setting an adequate bedtime schedule and creating an inviting sleep environment are implemented, along with regular medical follow-ups for monitoring and adjusting treatment as required.
Regular Medical Follow-Ups: Monitor treatment as necessary before reaching any conclusions about improving restful slumber.
Reference Books
Certainly! If you’re looking to deepen your understanding of sleep apnea, including both Obstructive and Central Sleep Apnea, here are some reputable reference books that may be of interest:
- “Sleep Disorders Medicine: Basic Science, Technical Considerations, and Clinical Aspects” by Sudhansu Chokroverty
- A comprehensive guide to sleep disorders, including an in-depth look at sleep apnea.
- “Principles and Practice of Sleep Medicine” by Meir H. Kryger, Thomas Roth, and William C. Dement
- A well-respected reference covering all aspects of sleep medicine, including detailed sections on different types of sleep apnea.
- “Sleep Apnea: Pathogenesis, Diagnosis, and Treatment” by Allan I. Pack
- Focused on sleep apnea, this book covers the pathogenesis, diagnosis, and various treatment options for both Obstructive and Central Sleep Apnea.
- “Fundamentals of Sleep Medicine: Expert Consult” by Richard B. Berry
- An introductory text suitable for medical students, residents, and practitioners, offering a broad overview of sleep disorders, including sleep apnea.
- “Clinical Handbook of Insomnia” by Hrayr P. Attarian
- While primarily focused on insomnia, this book also discusses other sleep disorders, including sleep apnea, and offers practical insights into diagnosis and tr
Conclusion
Understanding the intricacies of sleep apnea – including differences and similarities between Obstructive and Central Sleep apnea – is vital for accurate diagnosis, effective treatment, and improved quality of life for those affected.
Both conditions share similar symptoms and potential health risks, yet each condition varies in its underlying causes and treatments. Education, professional care, and tailored approaches are essential in managing these prevalent sleep disorders.
Recognizing the complexity of sleep apnea can help healthcare providers, patients and anyone interested in the subject begin to take steps toward better restful nights and overall wellbeing.