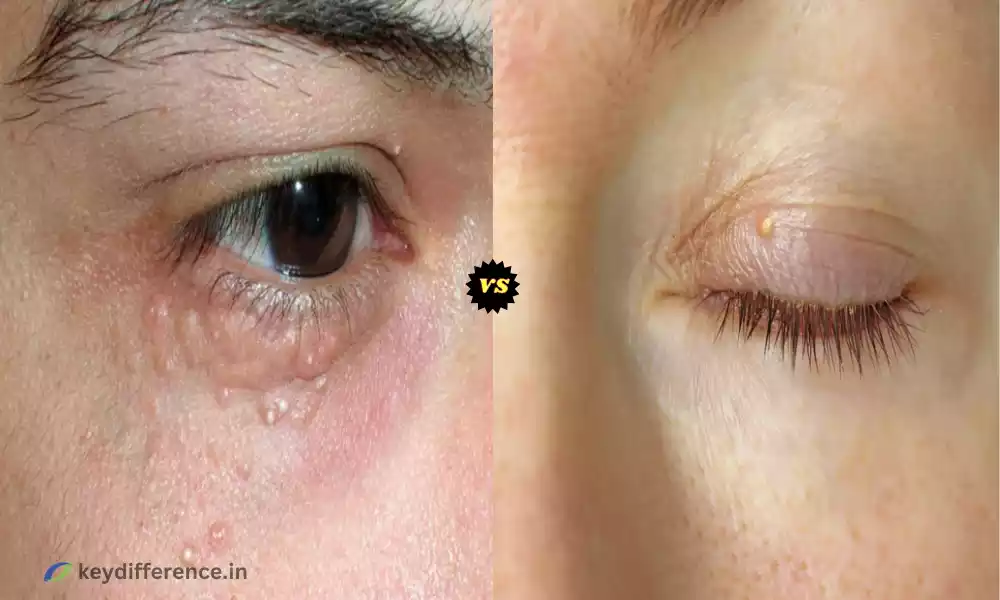
“Milia and Xanthelasma may appear similar at first glance, yet each condition has distinctive causes, symptoms, and treatments. Milia are small white cyst-like bumps often found around the eyes or cheeks of patients diagnosed with Milia, on the other hand, Xanthelasma is usually thickenings of tissue that form cyst-like bulges on its surface that form into solid plaques known as plaquettes or spots on the skin that occur for other reasons than Milia.”
Keratin deposits often result from trapped keratin and are generally harmless. On the other hand, xanthelasma are yellowish plaques typically seen on eyelids that could indicate higher cholesterol levels in your system.
Understanding the distinctions between Milia and Xanthelasma is critical for accurate diagnosis and appropriate treatment. This article will explore their distinct features, focusing on what differentiates them and providing insight into their management.”
Explanation of Milia
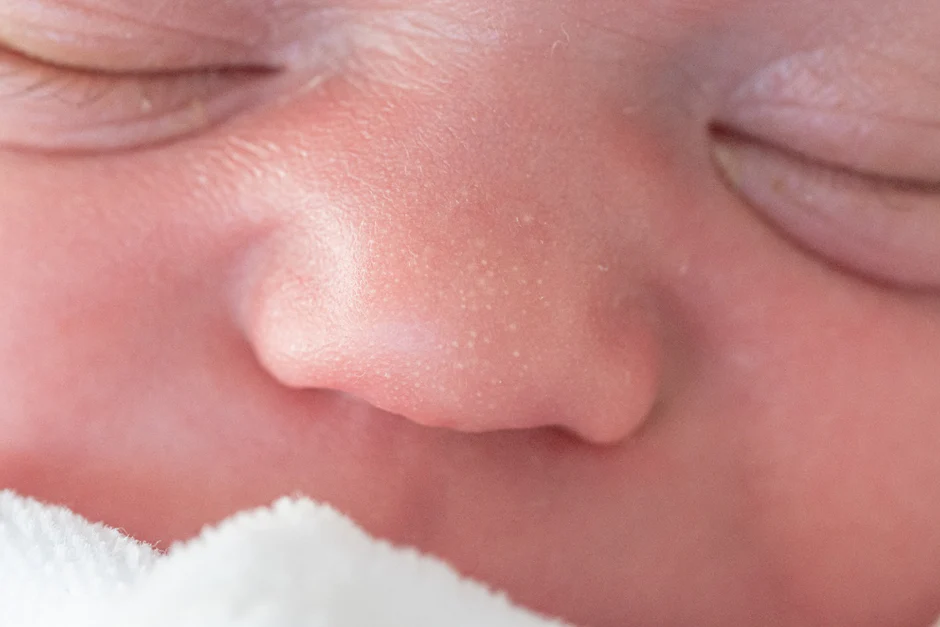
Milia are small white bumps found primarily around the eyes, nose, and cheeks that contain cysts filled with the protein keratin which forms part of our outermost layer of human skin, hair, and nails.
Milia are most often found among newborns, though it can affect people of any age. While babies’ cases typically resolve on their own, adults’ cases may continue to linger longer.
Milia cysts are generally harmless and considered cosmetic concerns rather than serious health concerns. Milia differ from pimples and other skin conditions in that they do not signal infection or inflammation, depending on its cause and population affected, Milia can be classified into primary, secondary, or even third milia types.
Milia are usually harmless, though for aesthetic purposes some may seek treatment for them. Professional skincare procedures may help but often these symptoms will simply go away on their own over time.
Explanation of Xanthelasma
Xanthelasma refers to yellowish, soft plaques or patches found commonly on eyelids near their inner corners, typically near cholesterol deposits. These plaques may vary in size and shape as they develop over time.
Xanthelasma differs from Milia in that it can often indicate specific health issues. It might indicate high levels of cholesterol or lipids in your bloodstream.
Not everyone with Xanthelasma will have these underlying conditions, rather genetic disorders or liver diseases might cause it.
Xanthelasma is generally harmless to eye health and does not often impair vision, however, many individuals choose treatment for cosmetic reasons as its appearance can be bothersome.
Once diagnosed with Xanthelasma, individuals should conduct a complete analysis of their lipid profile and overall health to ascertain potential cardiovascular disease risks.
Treatment options could range from cholesterol management, diet modifications, and surgical removal procedures depending on the cause and the individual’s preferences.
Comparison Table of Milia and Xanthelasma
Certainly! Below is a comparison table that highlights the differences and similarities between Milia and Xanthelasma:
| Feature | Milia | Xanthelasma |
|---|---|---|
| Appearance | Small, white, cyst-like bumps | Yellowish, soft plaques or patches |
| Common Locations | Face, especially around the eyes | Eyelids, near inner corners |
| Causes | Trapped keratin | Cholesterol deposits, liver issues |
| Associated with Age | Common in newborns & adults | Typically older adults |
| Symptoms | Cosmetic concern, no discomfort | Cosmetic concern, no eye issues |
| Risk Factors | Skin type, age, skin trauma | High cholesterol, genetics |
| Treatment | Often resolves on its own | Cholesterol management, removal |
| Indication of Health Issues | Generally not related | This may indicate underlying health problems |
This table provides a concise overview of the main features of Milia and Xanthelasma, allowing for a quick comparison of these two skin conditions.
While they may appear similar in some respects, the differences in causes, risk factors, and potential health implications highlight the need for accurate diagnosis and appropriate treatment.
Importance of Correct Identification
Accurate identification of Milia and Xanthelasma is of crucial importance, for several reasons. These include:
Treatment Approach: While Milia typically resolve themselves on their own and are mostly aesthetic concerns, treating Xanthelasma may require medical intervention and precise diagnostics in order to take an effective course of treatment. Achieving accurate diagnosis will allow for proper management.
Undiagnosed Underlying Health Conditions: Xanthelasma can be an indicator of serious health conditions like high cholesterol or liver dysfunction; misdiagnosing it as Milia could mean missing an opportunity to identify and address potentially severe health concerns.
Avoid Unnecessary Treatments: Proper identification of Milia can help avoid unnecessary treatments or interventions as many cases will resolve on their own without intervention from any practitioner. Inappropriate treatments could lead to scarring and other skin issues.
Psychological Impact: Both conditions may have an emotional or psychological effect if they appear on the face, particularly if visible. Understanding what caused it can assist with managing it more easily and taking appropriate measures if desired.
Healthcare Costs: Accurate diagnosis can save unnecessary healthcare costs by avoiding ineffective treatments and providing proper medical attention when necessary.
Educating Patients: Informed patients about Milia or Xanthelasma help make informed decisions regarding treatment and understand what to expect in terms of appearance, potential health implications, and prognosis.
Prevent Future Occurrences: Understanding what factors lead to Milia or Xanthelasma may help in taking preventive steps against its recurrence, such as skin care practices for Milia or lifestyle/dietary modifications for Xanthelasma.
Connection with Underlying Health Issues
Milia stands out from Xanthelasma due to its focus on underlying health concerns. this connection is key in distinguishing one from another.
Milia typically does not indicate any systemic health concerns. they are simply caused by trapped keratin and should primarily be seen as cosmetic issues. They might be related to skin trauma or particular types of skincare products, but should not necessarily signal serious medical conditions.
Xanthelasma
Unlike Milia, Xanthelasma often has deeper links to underlying health conditions:
High Cholesterol: Xanthelasma can be an indicator of high levels of cholesterol or other lipids in the blood, consisting of yellowish plaques with deposits made up of cholesterol which could signal an underlying disorder in lipid metabolism.
Liver Diseases: Lipid metabolism disorders that interfere with liver health could result in the formation of Xanthelasma.
Genetic Factors: Genetic disorders that alter cholesterol metabolism could also contribute to Xanthelasma.
Cardiovascular Risk: Because cholesterol levels play a part in its appearance, Xanthelasma could be seen as a visible indication of increased cardiovascular disease risk, including heart attacks and strokes.
Similarities Between Milia and Xanthelasma
Even though Milia and Xanthelasma are distinct conditions with distinct causes and implications, they do share some similarities:
Appearance on the Facial Structure: Both Milia and Xanthelasma typically appear around the eye area, Milia typically manifests in and around the eyes and cheeks while Xanthelasma tends to form on eyelids.
Cosmetic Concern: Both conditions can be considered cosmetic issues as they typically do not cause physical discomfort or interfere with eye function. Individuals often seek treatment solely for aesthetic purposes.
Non-Contagious: Milia and Xanthelasma are not contagious diseases, and neither are caused by infections, thus eliminating any risk to others through contact.
Treatment Options: While treatments for both conditions may differ depending on individual preference, both may be effectively addressed through medical procedures if removal for cosmetic reasons is desired. Common treatments could include topical creams, laser therapy, or minor surgical procedures.
General Safety: Both Milia and Xanthelasma tend to be harmless conditions that don’t typically cause long-term health concerns, aside from any possible Xanthelasma-related health implications. They’re predominantly skin conditions that usually don’t lead to additional medical issues.
Misdiagnosis Risk: Given their similar appearance and location on the face, misdiagnosis could occur without professional medical evaluation.
Chronic Aspect: Both Milia and Xanthelasma can be persistent and chronic conditions. While Milia may resolve on its own for infants, they often persist into adulthood similarly, Xanthelasma remains persistent and persistent unless treated.
Milia and Xanthelasma share many similarities, such as appearance, location, cosmetic nature, and overall harmlessness. However, their differences are significant when it comes to root causes and health implications – thus emphasizing the need for accurate identification and comprehension of each condition.
Recommendations for Care and Treatment
Absolutely! Below are my recommendations for the care and treatment of both Milia and Xanthelasma:
Avoid Picking or Squeezing Milia: Self-treatment may result in scarring or infection. Instead, allow them to resolve naturally or seek professional advice for removal.
Opt for Gentle Skincare Products: When selecting cleansers and moisturizers for skincare needs, try opting for mild formulas to minimize any irritation to your skin.
Consider Professional Removal: If Milia persists or is bothersome, consulting with a dermatologist or skincare professional for removal can help via extraction, chemical peels, or laser therapy.
Sun Protection: Wear sunscreen daily in order to reduce the likelihood of Milia formation.
Consult Your Healthcare Provider: As xanthelasma can be indicative of serious underlying conditions, consulting with a healthcare provider for proper assessment is vitally important.
Cholesterol Management: If high cholesterol is the source, lifestyle modifications such as eating healthily and engaging in regular physical activity could be suggested as ways of combatting its symptoms.
Consider Professional Removal: Cryotherapy, laser therapy or surgical excision may all be options to address Xanthelasma.
Maintain and Manage Underlying Health Conditions: Scheduling regular check-ups with medical providers to monitor any underlying health conditions is of utmost importance, as is seeking appropriate medical treatment if any arise.
Common Recommendations for Both Seek Professional Diagnosis: As both Milia and Xanthelasma can have different causes and treatments, it is vital to seek medical advice to determine the most suitable course of action. A proper diagnosis by healthcare providers will enable patients to make an informed decision.
Maintain Good Skincare Habits: Establishing proper cleansing, moisturizing, and sun protection habits can significantly benefit overall skin health.
Avoid Self-Diagnosis and Treatment: Consult a healthcare provider rather than trying to diagnose and treat these conditions on your own, as incorrect treatments could have serious repercussions.
Follow Treatment Guidelines: For optimal results from the treatment prescribed, always comply with and heed the guidelines of healthcare providers precisely.
Although general skincare practices can be helpful for both Milia and Xanthelasma, specific care and treatment recommendations vary greatly based on each person’s particular case of Milia or Xanthelasma.
Understanding its nature is crucial in developing an appropriate plan, thus professional medical evaluation and guidance should always be sought before proceeding with treatments on your own.
Reference Book
Certainly! If you’re looking to delve deeper into the study of Milia, Xanthelasma, and other skin conditions, you might find the following reference books helpful:
- “Dermatology: 2-Volume Set” by Jean L. Bolognia, Joseph L. Jorizzo, and Julie V. Schaffer: This comprehensive work covers a wide range of skin conditions, including detailed information about Milia and Xanthelasma.
- “Andrews’ Diseases of the Skin: Clinical Dermatology” by William D. James, Dirk Elston, et al.: A well-respected reference that provides clinical information on a wide array of skin conditions.
- “Clinical Dermatology: A Color Guide to Diagnosis and Therapy” by Thomas P. Habif: Known for its practical guidance and visual aids, this book can be particularly helpful in recognizing and treating various skin disorders.
- “Fitzpatrick’s Color Atlas and Synopsis of Clinical Dermatology” by Klaus Wolff, Richard Johnson, et al.: A popular choice for visual comparison, this atlas includes high-quality images of skin conditions, including Milia and Xanthelasma.
- “Cosmetic Dermatology: Principles and Practice” by Leslie Baumann: For those interested in the cosmetic aspects and treatments of skin conditions, this book offers insights into aesthetic procedures.
Conclusion
Milia and Xanthelasma are two skin conditions that often appear around the eyes on faces. While both share some superficial similarities in terms of location and cosmetic concern, their differences are significant Milia.
Small cyst-like bumps without health repercussions that often resolve on their own On the other hand, Xanthelasma are yellowish plaques that could indicate high cholesterol or liver diseases that require further investigation.
Correct identification and understanding of these conditions are crucial to proper care, treatment, and management. Although Milia tends to require minimal interventions, Xanthelasma may necessitate medical evaluation and treatment.
Due to potential links with underlying health conditions associated with Xanthelasma, professional medical assessment becomes even more necessary in these instances.