Introduction
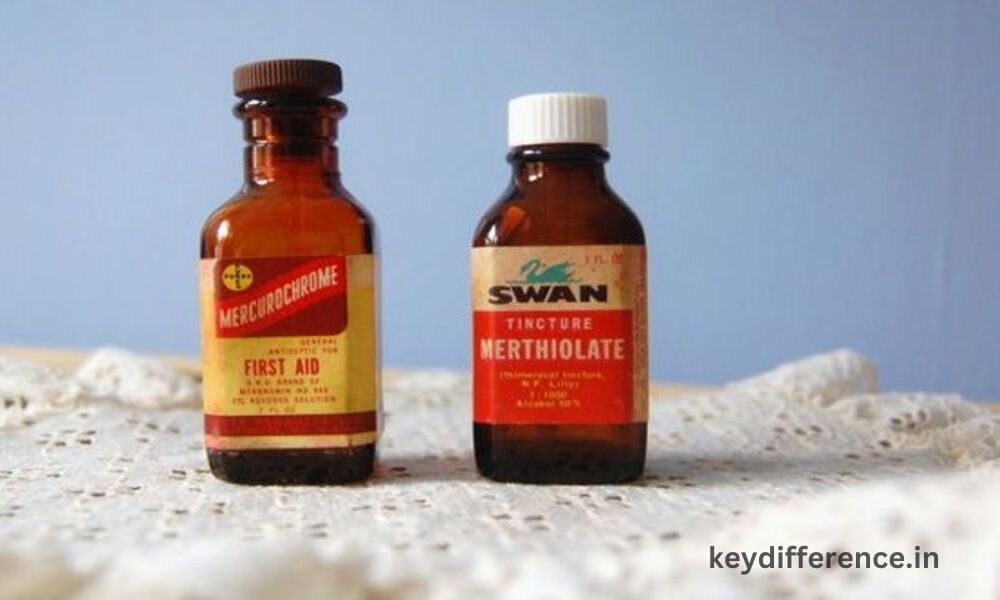
Merthiolate and Mercurochrome were once widely used topical antiseptic solutions that were popularly employed for wound disinfection and first aid purposes, due to their effectiveness at treating minor cuts, scrapes, and burns. Unfortunately, both products now face concerns regarding safety concerns as well as regulatory restrictions that have led to their usage decreasing significantly.
Understanding the differences between Merthiolate and Mercurochrome is critical for making informed antiseptic choices and safeguarding personal safety.
This content outline explores their characteristics, uses, safety concerns and regulatory changes; through an examination of these aspects people can gain a better understanding of these antiseptic solutions as well as explore safer options which more closely meet their individual needs.
What is Merthiolate?
Merthiolate was a Topical antiseptic solution Commonly used for wound Disinfection and first aid purposes, Containing the active ingredient Thimerosal, an amalgamation of Ethylmercury and Thiosalicylate that is well known for its antimicrobial properties and has even been utilized as an additive in vaccines and other medical products as a preservative.
Merthiolate first gained Widespread acceptance as a Household Antiseptic during the early to mid-20th century. This Antiseptic was often used for cleaning and Disinfecting minor cuts, scrapes and burns – it even gained recognition due to its distinctive reddish-brown hue and unique smell.
Due to concerns of mercury toxicity, Merthiolate as an antiseptic has experienced significant reduction in use since the U.S. Food and Drug Administration banned its use in over-the-counter products (OTC), while prescription medication use remains restricted; thus making this substance no longer widely accessible for consumer use in many countries.
Merthiolate used to be widely utilized, yet due to regulatory changes and safety issues its usage and availability have significantly declined over time.

How is this medicine (Merthiolate) best taken?
Merthiolate (commonly referred to as Thiomersal or Thimerosal) is used as an effective topical antiseptic solution.
Here’s how it should be administered:
Before applying Merthiolate, be sure that the affected area is clean and free from dirt, debris or other potential contaminants. Gently wash it using mild soap and water then pat dry using a clean towel.
Merthiolate comes in liquid form. Here are the steps for its application:
a. Open the Bottle: Carefully remove any caps on Merthiolate bottles that come equipped with applicators attachments before opening them up and carefully open.
b. Apply a Small Amount: Gently squeeze the bottle to release a small amount of Merthiolate onto the affected area, as doing so could slow down healing time or cause skin irritation. Excessive amounts could slow healing or even result in longer healing processes or increased skin sensitivity.
c. Apply evenly: When needed, if needed use a sterile cotton ball or swab to distribute the liquid evenly across the affected area and cover every wound or area with an even layer of Merthiolate.
Cover the Area (Optional): Depending on the nature and severity of your wound or recommendation from healthcare providers, covering it with a sterile dressing or bandage may help protect it from external contaminants while encouraging healing. This step protects from external contaminants while supporting fast recovery timeframes.
Follow instructions provided by healthcare professionals or product packaging. Merthiolate usage frequency will depend upon its severity in treating conditions as well as specific guidelines issued for its usage.
Important Considerations:
If in doubt about how best to use Merthiolate or your condition worsens or does not improve as anticipated, seek medical advice immediately from
A. health provider in order to receive professional evaluation and guidance.
B. Allergic Reactions and Sensitivities: Some individuals may experience allergies to Merthiolate or its ingredients. If any signs of an allergic reaction such as rash, itching, swelling, difficulty breathing occur while using Merthiolate or its ingredients, discontinue use immediately and seek medical advice immediately.
C. Merthiolate should only be used externally and should never be taken orally or applied topically without medical supervision or guidance. It should never be applied directly onto mucous membranes, deep open wounds, or large areas of skin without medical oversight.
D. Understand and adhere to product warnings: Always read and comply with instructions and warnings provided by the manufacturer of any product you purchase, especially those with age restrictions or usage limits. If there are specific precautions or contraindications associated with it – such as age restrictions or usage constraints – pay close attention.
Always consult a healthcare professional or pharmacist for personalized advice regarding how much Merthiolate to use and take for your specific condition.
What do I do if I miss a dose?
Merthiolate, as a topical antiseptic medication, should not be administered according to a fixed dosing schedule or dose regimen. Instead, it should be applied as needed for treating minor cuts, scrapes and skin irritations; should an application fail due to forgetfulness on your part, just simply resume its next scheduled application and continue treating accordingly.
Consistency is key when applying antiseptics like Merthiolate to promote healing and avoid infections, so it is advisable to adhere to a regular schedule for cleaning and applying the antiseptic to affected areas until healing has taken place or as directed by healthcare professionals.
If you have any concerns or inquiries about how and when to use Merthiolate, it’s advisable to seek professional guidance and advice based on your condition from healthcare professionals or pharmacists. They can offer tailored instructions and guidance as to how best manage wound or skin irritations.
What are some things I need to know or do while I take Merthiolate?
Merthiolate should be used with Caution; there are a few key points to keep in mind before Beginning use of this Medication:
Read and Follow Instructions Carefully: It is essential that you carefully read and heed any instructions provided by the manufacturer or healthcare professional for use of any medication, device or treatment regimen. Follow all recommended dosage, application frequency and duration.
Merthiolate should only be applied externally on the skin; it should not be consumed or applied to mucous membranes or internal body parts. Avoid contact with eyes, mouth and other sensitive areas.
Before applying Merthiolate, make sure that the affected area is clean and dry. Use mild soap and water to wash it gently, before patting dry with a clean towel – this helps increase effectiveness of antiseptic.
Avoid Excessive Usage: Merthiolate should only be applied at its recommended dose, as applying more may decrease its effectiveness or lead to skin irritation or delayed wound healing.
Allergies and sensitivities: Some individuals may be allergic or hypersensitive to Merthiolate or its ingredients. If signs of an allergic reaction appear such as rash, itching, swelling, difficulty breathing or other indications, discontinue use immediately and seek medical help immediately.
Contact a Healthcare Professional: If you have any concerns regarding the appropriate use or compatibility of Merthiolate with other medications or conditions, or if your wound or skin condition worsens or does not improve, seek advice from a healthcare provider or pharmacist immediately.
Storage and Disposal: Always follow the directions on the package when storing or disposing of Merthiolate. Keep it away from children and expired products should not be used; when disposing of either, follow local regulations and guidelines.
Seek medical advice if wounds or infections become severe: Merthiolate should generally suffice in treating minor cuts, scrapes and skin irritations. But for serious wounds like deep cuts, infected wounds or persistent infections it’s essential to seek prompt medical assistance as Merthiolate alone may not provide sufficient relief and professional medical treatment may be required instead.
Notably, Merthiolate was once used extensively as an antiseptic, but due to mercury contamination issues it is becoming less popular today. Therefore it’s essential that healthcare systems and individuals keep informed on current guidelines, recommendations and possible alternative products available within their region or healthcare system.
Always consult a healthcare provider or pharmacist for personalized advice regarding Merthiolate use based on your condition and personal circumstances.
What is Mercurochrome?
Mercurochrome, also referred to as merbromin or merbromin, is an antiseptic topical solution designed for treating minor wounds and skin infections. The active ingredient contained within it – mercury-derived red dye merbromin – possesses antibacterial and antifungal properties which make this formula effective against various skin infections.
Mercurochrome emerged during the mid-20th century as an effective and easily available antiseptic solution, thanks to its deep red hue that helped patients easily identify areas that have been treated. Mercurochrome became commonly used to disinfect cuts, abrasions, and minor burns.
As with Merthiolate, concerns regarding mercury toxicity have led to regulatory restrictions and decreased usage of Mercurochrome. Many countries have banned or restricted its use due to potential health risks from prolonged mercury exposure.
Mercurochrome as an antiseptic may differ depending on your country and local regulations; more recently, alternative products with safer yet more effective ingredients have become more widely used as antiseptic solutions.

Why was mercurochrome taken off the market?
Mercurochrome (commonly referred to as merbromin) has been removed from many markets over safety concerns and potential health risks associated with its main active ingredient merbromin (a mercury compound).
Here are the primary reasons for discontinuing mercurochrome:
Mercury Content: Mercurochrome contains merbromin, which is a compound made up of mercury. Mercury is known for being toxic and Potentially Hazardous to human health; prolonged Exposure may have adverse Consequences when taken orally or Absorbed through the skin. Over time, concerns over mercury exposure led to restrictions or bans being placed upon products containing mercury such as mercurochrome.
Lack of Effectiveness: Studies have indicated that, despite safety concerns, mercurochrome may not offer significant advantages over other antiseptics or wound healing agents on the market. As alternative products with safer ingredients became more widely available, its demand has decreased accordingly.
Restrictive Measures: Regulator agencies such as the Food and Drug Administration (FDA), as well as similar organizations in other countries, have instituted restrictions and limitations on mercury-containing products to limit exposure and protect public health. These efforts seek to minimize exposure while at the same time limit the exposure.
Mercurochrome is a mercury-containing: As medical research and antiseptic product innovations advance, safer alternatives to mercury exposure have become available through products like iodine- or chlorhexidine-based antiseptics that provide similar or better results without the associated risks.
Notably, regulations and decisions regarding the availability of specific medications and products vary greatly across nations. While mercurochrome has been discontinued or restricted in many regions, it may still be available under certain circumstances or regulation.
Always consult local regulations or guidelines as well as healthcare professionals or pharmacists for up-to-date information regarding its availability in your region and use.
Overdosage of Mercurochrome Solution
Mercurochrome contains merbromin, and due to safety and potential toxicity concerns it is no longer widely available in many countries. If an accidental overdose of mercurochrome solution occurs it is imperative that medical help is sought immediately; the following information provided for general knowledge purposes only and should not replace immediate medical advice:
Contact Emergency Services: In the event of a suspected overdose of mercurochrome, immediately reach out for medical help by contacting either your local emergency helpline or going straight to an emergency room in order to receive proper medical assistance for potential toxicity issues.
Do not induce vomiting: Without specific instruction from a healthcare provider, do not induce vomiting after an overdose. Doing so could increase complications or risks to health if solution has already been absorbed into the body.
Provide Information: When seeking medical help, provide as much detail as possible about what has been consumed, including its name (mercurochrome) and any quantity or concentration involved. This will allow healthcare professionals to provide appropriate treatment.
Medical Treatment: Depending on the severity and symptoms presented, treatment for an overdose of mercurochrome may differ according to its severity and symptoms.Medical professionals may treat any immediate symptoms while providing supportive care; activated charcoal may be administered in order to absorb any residual amounts within the gastrointestinal tract while other measures may be implemented in order to decrease absorption further and ensure its eventual elimination.
Adhere to medical advice: It is imperative that you heed the advice and instructions of healthcare providers, who will monitor your condition, assess any possible complications and recommend the most suitable course of treatment based on individual circumstances.
Always keep in mind that mercurochrome is no longer widely available and this information provided here should only be used as general references. If you suspect an accidental overdose or ingestion of any substance, seek medical assistance immediately or contact a poison control center for advice tailored specifically to your circumstances and location.
Expired Mercurochrome Solution
It is not recommended to use expired mercurochrome solutions. It is impossible to guarantee the safety and effectiveness of any medication after its expiration. The chemical composition of expired mercurochrome could have changed, reducing the efficacy or increasing the risk for adverse effects.
Consider these important factors when dealing with expired mercurochrome solutions:
- Reduced effectiveness: Over time, the active ingredients of mercurochrome solutions may degrade. This can reduce their effectiveness as antiseptics or wound treatments. Expired solutions may not offer the protection from infection or healing of wounds that you desire.
- Potential adverse effects: An expired mercurochrome may contain components that are degraded or altered. These could cause irritation of the skin, allergic reactions or other negative effects. The risk of these undesirable effects increases when using an expired product.
- Follow the disposal instructions: Dispose of expired mercurochrome according to local regulations. Don’t pour it down drains or flush it. For safe disposal, contact your local waste management authority and follow their guidelines.
Before using any medication, it’s a good idea to check its expiration date. It is best to throw away any expired mercurochrome solutions and replace them with a new, unopened product. Consult a pharmacist or healthcare professional if you have any questions or concerns about the use of Mercurochrome Solution or other medications.
What stings more Merthiolate or mercurochrome?
Both Merthiolate and Mercurochrome may cause a stinging sensation upon application; the degree may vary from person to person due to differences in sensitivity and perception of pain; therefore the experience may differ greatly between users.
Merthiolate has a stronger stinging sensation compared to Mercurochrome due to the active ingredients present such as thimerosal that may produce a burning or stinging sensation when applied directly onto skin.
Mercurochrome has a milder stinging sensation compared to Merthiolate. Unfortunately, it has fallen out of favour as safety concerns and alternative antiseptic solutions become available; thus limiting access.
If you are Experiencing any sort of Stinging sensation or have specific Inquiries about using antiseptic products, it is Recommended that you speak to a Healthcare provider or pharmacist for tailored advice specific to your Circumstances and needs.
Comparison Table of Merthiolate and Mercurochrome
Here’s a comparison table highlighting the key differences between Merthiolate and Mercurochrome:
| Aspect | Merthiolate | Mercurochrome |
|---|---|---|
| Composition | Contains thimerosal, a compound of ethyl mercury and trisilicate. | Contains merbromin, a red dye derived from mercury. |
| Color | Clear, colorless solution. | Deep red solution. |
| Odor | Characteristic odor. | No distinctive odor. |
| Antiseptic Properties | Broad-spectrum antimicrobial properties. | Effective against bacteria and fungi. |
| Common Uses | Wound disinfection, first aid purposes. | Treatment of minor cuts, scrapes, and burns. |
| Safety Concerns | Concerns regarding potential mercury toxicity. | Concerns regarding potential mercury toxicity. |
| Regulatory Status | Banned or restricted in many countries. No longer widely available. | Banned or restricted in many countries. Availability varies. |
| Alternatives | Safer alternatives available for wound disinfection. | Safer alternatives available for wound disinfection. |
It’s important to note that both Merthiolate and Mercurochrome have faced regulatory restrictions and concerns about potential mercury toxicity.
As a result, safer alternatives for wound disinfection are now widely available. It is recommended to consult healthcare professionals or refer to local regulations for guidance on suitable antiseptic options.
Importance of understanding the differences between the Merthiolate and Mercurochrome
Understanding the differences between Merthiolate and Mercurochrome are crucial for several reasons, including:
Safety: Both Merthiolate and Mercurochrome contain mercury-derived compounds, raising concerns of potential toxicity. Excessive mercury exposure can have adverse health consequences over time. By understanding the differences between them and choosing safer options that reduce mercury exposure risks more efficiently.
Compliance: Due to their mercury content, regulatory agencies have implemented restrictions and bans on Merthiolate and Mercurochrome usage. Being informed of such changes allows individuals to comply with local guidelines while avoiding products no longer approved or widely available.
Effectiveness: Merthiolate and Mercurochrome have both long been used as antiseptics, but individuals should understand there may now be safer and more effective options available to them. By understanding their differences, individuals can discover and select options with comparable or greater efficacy without as many safety issues associated with either product.
Knowledge Is Power: Becoming knowledgeable of the differences between Merthiolate and Mercurochrome gives individuals power to make informed healthcare decisions. They can consult healthcare professionals about their antiseptic needs, consider alternative products available on the market and choose what would best serve wound care or first aid needs.
Personal and Public Health: By opting for less toxic alternatives and limiting exposure to products with potential hazards, individuals can boost both personal wellbeing and public health. Acknowledging the differences between Merthiolate and Mercurochrome helps make informed choices that prioritize safety while decreasing risks to self and others.
Understanding the differences between Merthiolate and Mercurochrome is crucial for personal safety, regulatory compliance, and informed antiseptic choices. By prioritizing safer options and prioritizing health over cost, individuals can have a positive effect both on themselves and public health.
Conclusion
Merthiolate and Mercurochrome are both topical antiseptics with distinct differences. Merthiolate (also known as Thiomersal or Thimerosal) contains thimerosal as its active ingredient and is well known for its broad spectrum antimicrobial action, disrupting cell membranes of microorganisms in order to prevent infection in minor cuts and wounds. Mercurochrome works similarly by decontaminating wounds using certain components found within it such as chlorine dioxide.
Mercurochrome or Merbromin acts as a topical antiseptic and is typically prescribed to treat minor wounds or skin irritations. Although its exact mechanism of action remains undetermined, its mechanism may include denatured proteins scavenged from microbe cells that inhibit their growth.