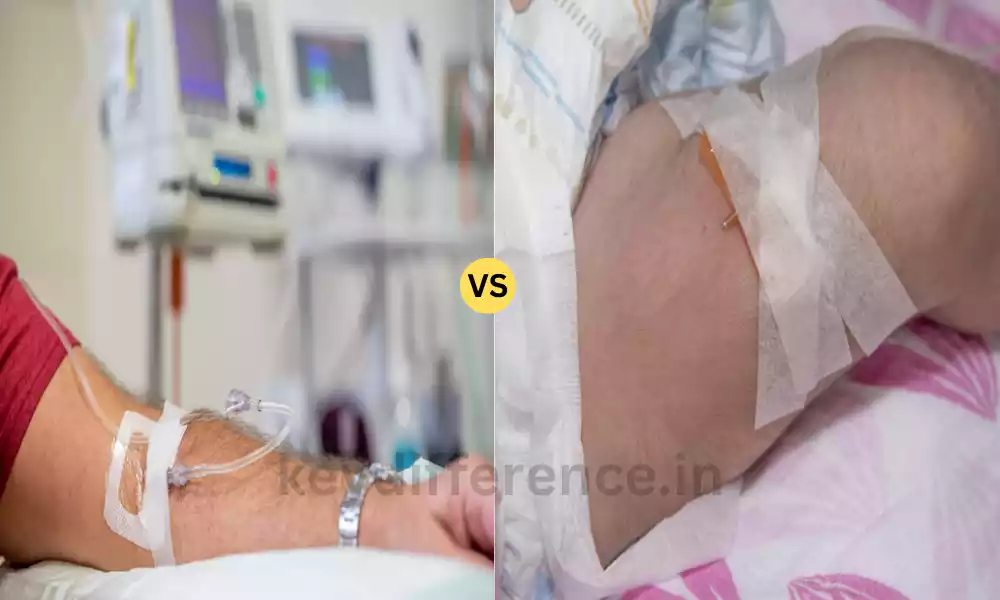
Immunoglobulin therapy, a vital treatment for many immune-related disorders can be administered using two main methods Intracavenous Immunoglobulin (IVIG) or Subcutaneous Immunoglobulin (SCIG).
These treatments are essential for patients suffering from immunodeficiency disorders or autoimmune conditions, as well as chronic inflammation illnesses. Understanding the difference between IVIG and SCIG is essential for healthcare professionals as well as patients as well since it affects the effectiveness of treatment in terms of convenience, efficiency, and wellbeing
We will explore the differences between these two methods of administration and highlight their distinct features, benefits, and disadvantages, assisting people in making informed decisions regarding their health care.
What is IVIG?
IVIG is an acronym is an acronym for Intravenous Immunoglobulin. It is a medical procedure where a concentrated concentration of the immunoglobulins (antibodies) that are derived from the blood of healthy donor donors are injected directly into the bloodstream of a person through an intravenous infusion.
IVIG can be used to improve the immune system and to treat autoimmune diseases such as immunodeficiency disease, and other diseases. It assists in providing patients with higher levels of antibodies that improve their capability to fight off infections and regulate the immune system’s activities.
What is SCIG?
SCIG is the abbreviation for Subcutaneous Immunoglobulin. It is a medical procedure that involves the use of immunoglobulins (antibodies) collected by healthy donor donors can be injected into the subcutaneous tissues of a patient usually via a subcutaneous injection.
SCIG is utilized to treat a variety of ailments, particularly immune deficiency illnesses, by providing the patient with a constant and constant amount of antibodies to boost their immune system.
In contrast to IVIG which is administered intravenously, SCIG can be administered by self-administration, or caregiver-assisted treatment and is generally administered regularly, usually weekly or biweekly, making it a suitable option for certain patients.
Importance of immunoglobulin therapy
Immunoglobulin therapy, also referred to as antibody replacement therapy plays an important role in healthcare and in the treatment of diverse medical conditions due to its many significant benefits:
- Enhancing Immune function: The treatment of immunoglobulin provides patients with an essential element of their immune system – antibodies. It boosts the immune system’s capacity to fight infections and is especially beneficial for people with immunodeficiency conditions.
- Treatment of Autoimmune disorders: The immune system targets the healthy tissues of the body. Immunoglobulin therapy may help manage and block this immune system’s abnormal response, which reduces inflammation and damage to tissue.
- The prevention of infections: The method is commonly employed as a preventative treatment to avoid infections in people who are more at risk because of immunodeficiencies like primary immunodeficiency diseases or certain drugs.
- Managing chronic inflammationFor some inflammation and autoimmune disorders immunoglobulin therapy may assist in managing symptoms and reduce disease activity, thereby improving the quality of life for patients.
- Neurological disorders: In certain neurological disorders, such as Guillain-Barre syndrome and chronic inflammation demyelinating neuropathy (CIDP) the immunoglobulin treatment can help to regulate the immune system and enhance the functioning of nerves.
- Convenience and lifestyle improvement: Subcutaneous immunoglobulin (SCIG) therapy provides the convenience of treatment at home that allows patients to live an active life, without frequent clinic visits that are associated with intravenous treatment.
- Potentially Life-saving Treatment: In the case of severe immunodeficiency, or acute infections, like viral or bacterial infections immunoglobulin therapy may save lives.
- Prevention of serious complications: By maintaining the levels of antibodies immunoglobulin therapy may help to prevent the recurrence of infections as well as the serious complications they can create.
- Supporting patients suffering from chronic conditions: It is a powerful way to enhance the quality of life of people suffering from chronic illnesses by managing symptoms and decreasing the severity and frequency of flares.
- Controlling Allergic Reactions: For those who suffer from serious allergies, the treatment of immunoglobulin could aid in reducing their sensitization in time to the allergens, thus reducing the chance of having severe reactions.
The importance of immunoglobulin therapy for a variety of patients, ranging from patients suffering from immunodeficiency disorders to those suffering from autoimmune disorders or chronic infections, and much more.
It can help improve the immune system’s effectiveness manage chronic illnesses and improve the overall health and well-being of the people who are treated.
Comparison Table of VIG and SCIG
Here’s a comparison table of IVIG (Intravenous Immunoglobulin) and SCIG (Subcutaneous Immunoglobulin) based on various key factors:
| Factor | IVIG (Intravenous Immunoglobulin) | SCIG (Subcutaneous Immunoglobulin) |
|---|---|---|
| Method of Administration | Intravenous infusion | Subcutaneous injection |
| Rate of Administration | Infused over several hours | Typically self-administered or administered over a shorter time (e.g., 30 minutes) |
| Frequency of Administration | Typically every 3-4 weeks | Typically weekly or bi-weekly |
| Indications | Autoimmune disorders, immunodeficiency diseases, and more | Immunodeficiency diseases, chronic inflammatory diseases, and more |
| Advantages | Rapid onset of action, high serum IgG levels achieved | Convenient home-based treatment, lower risk of systemic side effects |
| Disadvantages | Requires hospital or clinic visit, potential for systemic side effects | Slower onset of action, lower serum IgG levels achieved |
| Convenience and Lifestyle | Requires healthcare facility visits | Allows for self-administration, reducing clinic visits |
| Patient Preferences and Considerations | May not be suitable for those who dislike needles or require frequent travel to healthcare facilities | Preferred by patients who want greater independence and convenience |
| Cost Considerations | Typically more expensive due to healthcare facility visits and longer administration times | Can be cost-effective due to reduced healthcare facility visits and shorter administration times |
| Suitability for Different Conditions | More commonly used in acute settings or for conditions requiring high and rapid antibody levels | More suitable for long-term management of chronic conditions or prophylaxis |
Please note that the suitability of IVIG or SCIG can vary depending on the individual patient’s medical condition, lifestyle, and preferences. The choice between IVIG and SCIG should be made in consultation with healthcare professionals, considering these factors and the patient’s specific needs.
Self-administered or administered by a caregiver
The decision of whether or not an immunoglobulin-based therapy (IVIG or SCIG) is administered by a patient on their own or by a healthcare professional is contingent upon the patient’s ability as well as their preferences and particular treatment plan.
Here’s a summary of this part:
- Self-Administration:
- SCIG: Subcutaneous Immunoglobulin therapy is typically intended to be administered by patients. This method provides patients with more control and independence in their treatments. It is particularly beneficial to patients who are comfortable with injections under the skin and prefer the convenience of administering treatment at home.
- Administered by a Caregiver:
- IVIG: Intravenous Immunoglobulin therapy is usually administered by healthcare professionals within the hospital or clinical setting. This is due to the fact that IVIG is an intravenous injection, which requires specialized equipment and training to ensure safe and efficient administration. Such as family members or home health professionals, can be able to give IVIG from home however it is more typical for patients to be given IVIG in a medical environment due to the difficulty and risks that could be associated with intravenous administration.
The decision to choose between self-administration or caregiver administration is determined by factors like the patient’s ability and comfort to take care of this treatment. It also depends on the kind that is administered (IVIG and SCIG) and the advice of a healthcare professional.
The aim is to ensure a safe and efficient delivery of immunoglobulin therapy while ensuring that it is in line with the patient’s needs and lifestyle. Patients must discuss their choices and preferences with their medical team to determine the most appropriate strategy.
Convenient home-based treatment
Convenient home-based therapy is a term used to describe medical treatments that are administered from the comfort of the patient’s residence instead of requiring patients to go to a medical facility.
This method has several benefits:
- Comfort and familiarity: Patients are able to receive treatments in a familiar and relaxing environment, decreasing the anxiety and stress that come when visiting a healthcare facility.
- Flexibility: Treatment at home permits flexibility in treatment schedules, making it easier to incorporate treatment into your daily routine.
- Lower wait time and travel: Patients are spared the hassle and time of making trips to hospitals or clinics and waiting in line resulting in significant time savings.
- Independence: Patients who administer their medications, like Subcutaneous Immunoglobulin (SCIG) are able to gain the feeling of autonomy in their treatment and have control over their overall health.
- Privacy: Treatment at home offers greater privacy. This is especially crucial for patients receiving treatment that is sensitive or private.
- Reduced Risk of Infection: Avoiding crowded health facilities reduces the risk of being exposed to infections, particularly for those with weak immune systems.
- Cost-Efficiency: Treatments at home can be affordable since it eliminate the requirement for frequent visits to the clinic as well as the associated costs.
- Caregiver Participation: For patients who require assistance in treatments, caregivers can be educated to manage the therapy which reduces the burden on patients and allows caregivers or family members to be involved in the care of the patient.
Subcutaneous Immunoglobulin (SCIG) is a prime example of a treatment that could frequently be applied in the comfort of your home.
The effectiveness of treatment at home is contingent upon the particular therapy and the patient’s medical condition, as well as their capacity to administer themselves or allow a medical professional to assist in the treatment.
Healthcare professionals collaborate with patients to decide the most suitable treatment plan in light of these aspects.
Patient preferences and lifestyle considerations
The preferences of the patient and their lifestyle are crucial in choosing the most appropriate treatment with immunoglobulin (IVIG and SCIG) and the best method for administering it.
Here are a few key aspects that influence the preferences of patients and lifestyle choices:
- Independence and. Help:
- Patients who are independent and desire greater influence over the treatment they receive might opt for self-administration of therapies such as SCIG that can be administered at home. However, patients who require help or prefer having an individual caregiver may prefer therapies that are delivered with the help of a caregiver.
- Home-Based vs. Clinic-Based Treatment:
- Patients who have busy schedules and limited mobility might prefer treatment at home due to the convenience and flexibility they provide. However, some patients might prefer treatment in a clinic, especially in the event that they value the expertise of healthcare professionals or they have concerns about safety related to self-administration.
- Need for Frequent Clinic Visits:
- IVIG generally requires regular sessions with a physician for intravenous injections and may not fit with the routine of patients who want to avoid visits to healthcare facilities. SCIG due to its lower frequency of administration is a suitable choice for these patients.
- Travel and Mobility:
- Patients who travel often or live an active lifestyle might prefer self-administered treatments like SCIG that allow patients to keep their treatment going while away from their homes. IVIG is a requirement for visits to the clinic, may be more difficult for those who are constantly in motion.
- Experience with Needles or Injections:
- The patient’s comfort level with injections and needles is an important aspect. Patients who aren’t comfortable with needles might feel that IVIG as well as SCIG more attractive. However, some might prefer SCIG because injections are generally less invasive, and are less frightening.
- Privacy and Personal Space:
- Certain patients might appreciate the privacy and security offered by home-based treatments and are therefore more likely to choose SCIG, which allows treatment to be carried out discretely.
- Cost Considerations:
- Patients who have financial constraints might think about the cost-effectiveness of alternative treatments. SCIG due to its potential for reducing visits to clinics is a cost-effective option for certain patients.
- Psychological Well-Being:
- The psychological health of patients must not be overlooked. For certain patients people, the convenience and ease of treatment at home could have an effect on their general quality of life and mental wellbeing.
- Treatment Duration and Frequency:
- The treatment plan and duration may affect patient preferences. Certain patients might prefer a longer time frame with less frequent treatments while others might prefer regular, but shorter treatment.
The patient’s lifestyle personal preferences, as well as a medical condition, are all factors in the decision between IVIG and SCIG in addition to whether the treatment is given at home or in a clinical setting.
A patient-centric approach, which includes an open dialogue with health professionals, is vital in order to ensure that the chosen treatment is in accordance with the patient’s wishes and desires.
Healthcare infrastructure and resources
The infrastructure and resources of healthcare are crucial considerations when deciding the best immunoglobulin therapy (IVIG or SCIG) and the method of administration. These aspects can greatly impact the effectiveness and feasibility of the treatment.
Here are some important aspects in relation to the infrastructure of healthcare and resources:
- Clinical Expertise:
- The availability of healthcare professionals who have knowledge of the administration of IVIG or SCIG is crucial. IVIG is administered intravenously and requires skilled staff for secure and efficient infusion. SCIG administration can include training for healthcare professionals as well as caregivers or patients.
- Facility Accessibility:
- The geographical location and accessibility to healthcare facilities could be an important aspect. Patients who live in areas that are remote could have difficulties getting into hospitals or clinics to receive IVIG treatment, which makes SCIG the best option for patients living in remote areas.
- Availability of Equipment:
- IVIG administration requires specialized equipment for intravenous infusions including pump infusions as well as monitoring equipment. Making sure that there is a reliable and effective operation for this equipment is essential. SCIG typically requires fewer special devices.
- Infrastructure for Storage and Handling:
- Proper storage and handling of immunoglobulins is crucial to ensure their effectiveness and integrity. Healthcare facilities require infrastructure to ensure secure stock, controlled temperature, and management of inventory.
- Infection Control Protocols:
- The two procedures IVIG and SCIG must adhere to strict protocols for infection control. Healthcare facilities should be equipped with these protocols to limit the risk of contracting infection when treating.
- Training and Education:
- Healthcare professionals require training for administering IVIG and SCIG efficiently and safely. Patients and caregivers need instruction on self-administration, when appropriate.
- Patient Load and Scheduling:
- The capacity of hospitals and the load of patients they manage can affect their availability for treatment slots as well as the appointment schedule for IVIG. SCIG which is usually located at home, may be more flexible in this regard.
- Cost Implications:
- The price of IVIG can be affected by factors like costs for clinics, hospital stays, and the use of equipment. Healthcare facilities should be open regarding these costs and allow patients to make informed choices.
- Regulatory Compliance:
- Compliance with regulations as well as quality-assurance standards are essential for the safe and efficient administration of immunoglobulin therapy. Healthcare facilities must comply with these guidelines.
- Emergency Response and Support:
- Healthcare facilities should have emergency response procedures in place to handle any adverse reactions or problems related to IVIG and SCIG.
The health infrastructure and the resources accessible in a specific area or health facility play a crucial impact in determining the best treatment method and dosage.
An in-depth analysis of these aspects along with specific patient preferences and needs is essential to make informed decisions about the treatment.
Patients must work together with their health provider to ensure that their chosen treatment is in line with the available resources for healthcare.
Ongoing advancements in immunoglobulin therapy
Continuous advances in immunoglobulin therapy are due to research in the field of science, technological advances, and an increasing knowledge that the immune system is a complex one. These developments aim to increase the effectiveness as well as the safety and accessibility of treatments using immunoglobulin.
Here are a few key areas of research:
- Subcutaneous Immunoglobulin (SCIG) Formulations: Research keeps improving the composition of SCIG which makes the drug more potent and efficient. These developments aim to reduce the volume of every infusion as well as the frequency of administration while maintaining the effectiveness of therapy.
- Personalized Immunoglobulin Therapy: Advancements in immunology and genetics permit for more customized treatments. Making the treatment tailored to a person’s unique requirements and immune profile will improve the outcome.
- Enhanced safety profiles: The efforts are continuing to minimize negative reactions and increase the effectiveness of immunoglobulin therapy. This involves the creation of formulations that are less allergenic and better monitoring during the administration.
- Extended Half-Life products: Long-acting immunoglobulins have been developed in order to decrease the frequency of injections while improving the patient’s convenience and compliance.
- Improvements in Delivery Systems: The latest developments in delivery methods, including needle-free, painless injection techniques are being investigated to make treatment more pleasant for patients.
- Oral Immunoglobulins: research into the creation of oral immunoglobulins seeks to offer an alternative to injectable treatments, possibly improving the adherence of patients.
- Expanding indications: Clinical trials are ongoing and research is examining the possibility of using immunoglobulin therapy to treat a variety of medical conditions, as well as broadening the scope of treatment for illnesses.
- Home-Based Therapy: The advancements in remote medicine, patient education, and monitoring systems aid in the growth of treatment at home using immunoglobulin increasing patient comfort and reducing hospital visits.
- Biosimilar Products: Biosimilar Products: The creation of biosimilar immunoglobulins will provide cost-effective alternatives while preserving safety and effectiveness.
- Better Manufacturing Research and development in the manufacture of immunoglobulins helps ensure consistency of quality, lower production costs and address issues in the supply chain.
- Study of Mechanisms for Action: A deeper comprehension of how immunoglobulin treatment operates at the molecular scale is the driving force behind research that aims to increase its effectiveness in various conditions.
- Accessibility and accessibility improved: There are ongoing efforts to increase the accessibility of immunoglobulin therapy and affordable to patients and address pricing issues and shortages of supply.
- Therapeutic Immunomodulation: The research team is investigating the possibility of developing immunomodulatory therapies that utilize immunoglobulins to treat a broad range of immune-related inflammation-related disorders.
The advancements in immunoglobulin therapy are always evolving, providing the possibility of more efficient treatments, improved patient experiences, and improved outcomes for those suffering from illnesses that affect the immune system.
Healthcare professionals and patients should be aware of these advancements so that they can make informed choices regarding treatment and give the best treatment.
Similarities Between IVIG and SCIG
IVIG (Intravenous Immunoglobulin) and SCIG (Subcutaneous Immunoglobulin) are both types of immunoglobulin therapy.
They have many similarities:
- Immunoglobulin source: SCIG and IVIG make use of immunoglobulins (antibodies) that are derived from the plasma from healthy donors to enhance the patient’s own antibody. This boosts the immune system and can provide passive immune protection.
- Primarily Indications: SCIG and IVIG are used to treat a variety of medical conditions, such as primary immunodeficiency disorders as well as autoimmune disorders, and various chronic inflammatory conditions.
- Efficiency: Both IVIG as well as SCIG are effective in raising the serum IgG levels in patients, assisting in fighting off infections, and managing immune-related diseases.
- Safety: While both therapies might have potential adverse effects, they are generally regarded as safe and well-tolerated if administered in accordance with the directions of medical professionals.
- Monitors Regularly: Patients who are receiving IVIG or SCIG generally require regular monitoring to evaluate the effectiveness of the treatment and to adjust dosages if necessary.
- Treatment adaptation: Treatment intervals can be modified for both IVIG and SCIG, based according to the patient’s response as well as particular medical conditions.
- For Infection Prevention: The two therapies can be effective in reducing the chance of developing serious infections, so they are beneficial to those who suffer from immunodeficiency diseases.
- Method of Action: IVIG and SCIG function by providing patients with a variety of antibodies that can aid in regulating the immune response to reduce inflammation and increase the body’s capacity to fight off infections.
- Lang-Term Administration: IVIG and SCIG can be utilized to treat long-term illnesses aiding patients to maintain an improved quality of life as well as reduce the severity and frequency of symptoms.
- Prescription Medicines: IVIG and SCIG are prescribed medicines and their use must be monitored by health experts.
It is important to remember that although IVIG and SCIG have many similarities they also differ in terms of the method used to administer as well as patient preferences and the importance of lifestyle, as described in the previous responses.
The decision to choose between IVIG and SCIG must be based on the individual patient’s requirements and the advice of healthcare professionals.
Conclusion
The choice between Intravenous Immunoglobulin (IVIG) or subcutaneous Immunoglobulin (SCIG) is based on the careful assessment of the person’s medical conditions and preferences, as well as available health resources.
Both treatments offer efficient immunoglobulin treatments to boost the immune system and treat different ailments. Care that is individualized to the patient’s specific needs and conditions is essential in making the best decision between SCIG and IVIG for the best outcomes for patients.