Introduction of Bells Palsy and Ramsay Hunt Syndrome
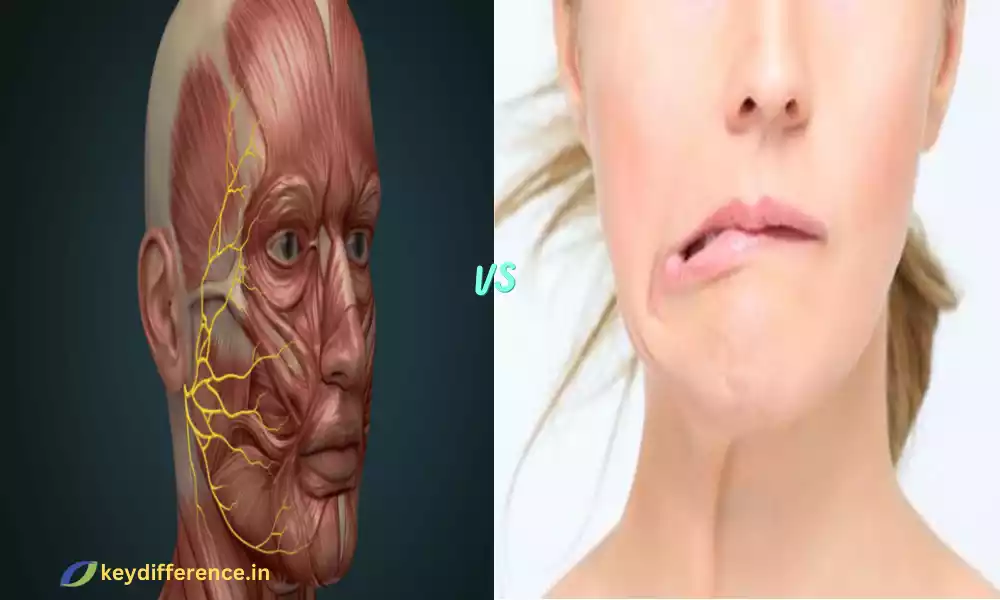
Bell’s Palsy and Ramsay Hunt Syndrome are two distinct disorders that affect facial nerves and can lead to facial paralysis or weakness. Although they have some commonalities including the involvement of facial nerves, they are distinct with regard to their sources, signs, and treatment strategies.
Knowing the differences is essential to ensure a correct diagnosis and proper treatment. we will go over the differences between Bell’s Palsy and Ramsay Hunt Syndrome to provide the most complete understanding of these disorders.
Definition of Bell’s Palsy
Bell’s Palsy is a neurological condition that is characterized by the unintentional and inexplicably weakening or paralysis of facial muscles, which are usually located on the opposite part of your face.
This disorder is caused by the inflammation or dysfunction in the facial nerve (cranial nerve VII) which regulates the muscles involved in facial expressions and tasting sensations in the front two-thirds portion of the tongue.
Bell’s Palsy tends to be temporary and generally resolves over time, though the exact cause isn’t known as viral infections and immune reactions as possible causes.
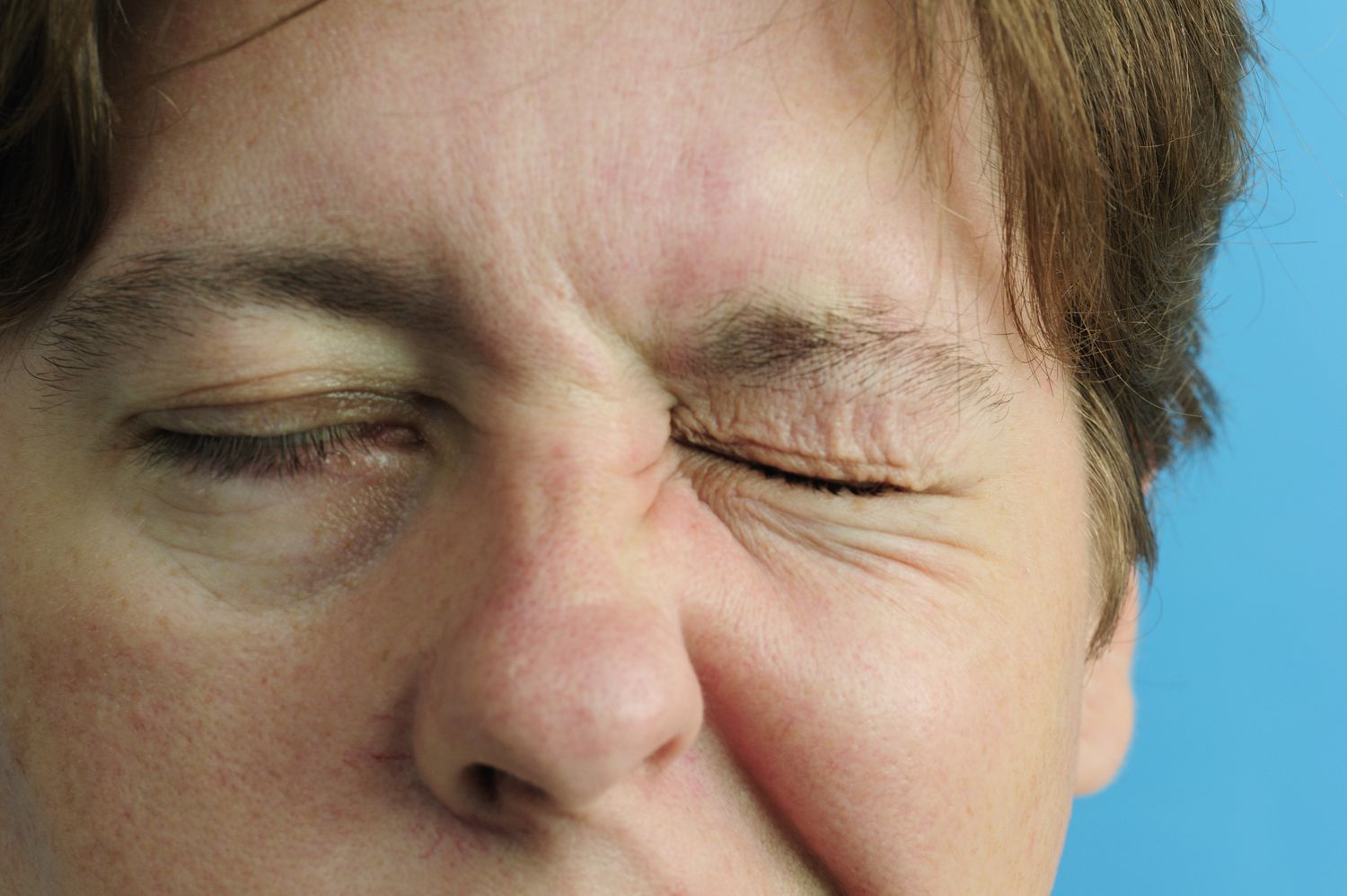
Definition of Ramsay Hunt Syndrome
Ramsay Hunt Syndrome, also called Herpes Zoster Oticus, is a neurologic disorder that is due to the reactivation of the Varicella-Zoster virus (Herpes Zoster) in the geniculate-geniculate ganglion, a nerve structure in the complex of facial nerves.
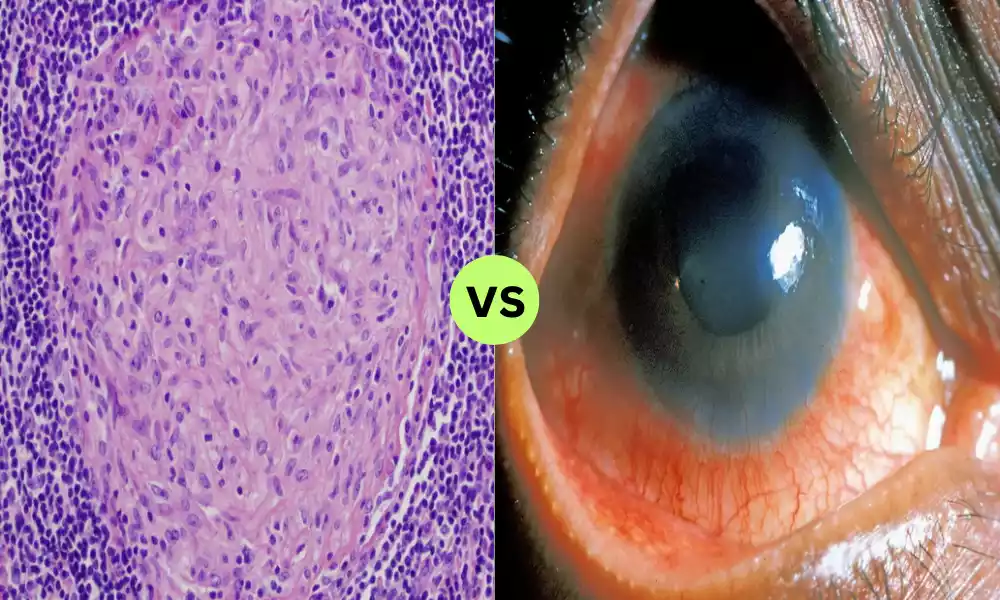
The condition is characterized by a variety of symptoms, such as the facial muscles becoming weak or paralyzed on one side as well as a vesicular eruption in the ear canal, or mouth as well as severe ear pain.
Furthermore, Ramsay Hunt Syndrome may result in other auditory or vestibular issues like the loss of hearing, as well as tinnitus and vertigo as a result of it being a problem for the vestibular and auditory nerves. It is crucial to identify and deal with Ramsay Hunt Syndrome promptly to reduce the risk of complications and increase the likelihood of healing.
Comparison Table of Bell’s Palsy and Ramsay Hunt Syndrome
Certainly! Here’s a comparison table summarizing the key differences between Bell’s Palsy and Ramsay Hunt Syndrome:
| Characteristic | Bell’s Palsy | Ramsay Hunt Syndrome |
|---|---|---|
| Etiology | Often triggered by viral infections, such as herpes simplex virus | Caused by reactivation of varicella-zoster virus (herpes zoster) |
| Vesicular Rash | Absence of vesicular rash | Presence of vesicular rash in the ear canal or mouth |
| Ear Pain | Typically lacks severe ear pain | Severe ear pain is a common symptom |
| Hearing Symptoms | Uncommon for hearing loss, tinnitus, or vertigo | This may lead to hearing loss, tinnitus, and vertigo |
| Treatment Approach | Focuses on corticosteroids and eye protection | Requires a combination of antiviral medications, corticosteroids, and pain management |
| Prognosis | Generally favorable, with gradual recovery | Better prognosis with early intervention, but recovery can be slower and incomplete |
This table highlights the crucial distinctions between Bell’s Palsy and Ramsay Hunt Syndrome, particularly in terms of their causes, clinical symptoms, and recommended treatments.
Importance of distinguishing between Bell’s Palsy and Ramsay Hunt Syndrome
Differentiating between Bell’s palsy as well as Ramsay Hunt Syndrome can be vital when working in a clinical environment due to various reasons:
- Treatment Approach:
- Bell’s Palsy: usually responds well to corticosteroid treatment as well as eye security measures. The administration of antiviral medication may not be required.
- Ramsay Hunt Syndrome: Requires a completely different treatment plan, involving corticosteroids as well as antiviral drugs to treat the herpes zoster virus. Management of pain may also be required.
- Prognosis:
- Bell’s Palsy: The majority of patients have a positive outlook, with the majority of patients experiencing gradual improvement in facial function.
- Ramsay Hunt Syndrome: Although early treatment may yield better results Recovery may be slow and insufficient, and issues such as hearing loss could persist.
- Prevention of Complications:
- The correct identification of Ramsay Hunt Syndrome is crucial due to the potential for serious complications, such as permanent hearing loss and facial weakness when not treated.
- Patient Management:
- A treatment plan that is tailored to the particular condition will ensure that patients get the best treatment which reduces their discomfort and enhances their living quality.
- Avoiding Unnecessary Medications:
- Inadvertently administering antiviral medication in the case of Bell’s Palsy can expose patients to potentially harmful negative side effects with no significant benefit.
- Patient Education:
- Accurate diagnosis allows healthcare professionals to inform patients on how to manage their problems and the expected course of treatment and possible complications. This can help manage the expectations of patients and anxieties.
- Research and Epidemiology:
- The accurate diagnosis and the reporting of cases aid in studies of epidemiology, allowing researchers to discover the extent and causes of these diseases.
In the end, recognizing Bell’s Palsy and Ramsay Hunt Syndrome is crucial to ensure that patients receive the most appropriate treatment, maximize their chances of healing, and avoid the possibility of complications. This also assists healthcare professionals in making informed choices and helps in the growth of medical research regarding facial nerve disorders.
Sudden onset of facial weakness or paralysis
“Sudden onset of facial weakness or paralysis” is an indication of a medical condition that may be seen in a variety of medical conditions, including those that affect the nerve that controls facial expressions (cranial nerve VII) or the structures around it.
The symptom is usually described as the sudden loss of control of the facial muscles and neck, usually in one direction.
There are several conditions that can cause “sudden onset of facial weakness or paralysis” could be noticed:
- Bell’s Palsy: It is among the most frequent causes of facial weakness that is sudden. It’s caused by irritation or compression in the facial nerve which causes paralysis on either side of your face. The cause of the condition is usually not known, however, viral infections are thought to be the trigger.
- Ramsay Hunt Syndrome: This disorder is marked by an abrupt facial weakness. However, it’s caused by a vesicular rash within the ear canal or mouth. It is caused by the activation of the varicella-zoster disease in the nerves of the face.
- Stroke: A facial weakness could be a sign of a stroke, especially when it is sudden and occurs along with other signs like leg or arm weakness or difficulty speaking and confusion.
- Lyme Disease: In certain cases, Lyme disease, caused by a tick-borne bacterium can cause facial paralysis, usually in one direction.
- Face Trauma: A trauma to the nerve of your face or the structures surrounding it may result in sudden facial weakness or paralysis.
- Tumors: Growths or tumors pressuring the facial nerve could cause facial weakness that is sudden and unexpected.
- Guillain Barre Syndrome: Although less prevalent, this autoimmune condition may affect the brain’s nerves, which include the facial nerve, which can lead to sudden weakness.
- Idiopathic Reasons: In certain instances, facial weakness could be present without a known reason, and may disappear on its own.
It’s crucial to keep in mind that any sudden facial weakness or paralysis must be examined by a physician immediately.
A precise diagnosis is crucial to determine the reason and to initiate the appropriate treatment which could include physical therapy, medications, or surgical interventions, based on the underlying condition.
Inability to close one eye or smile on one side
“The “inability to close one eye or smile on one side” is a specific symptom that is a sign of weakness in the facial muscles or paralysis. It is typically associated with conditions that affect facial nerves (cranial nerve VII).
Here are a few conditions that cause this symptom can be seen:
- Bell’s Palsy: It is a frequent cause of facial weakness. It is typically manifested by an inability to keep one eye closed or smiling on the opposite aspect of your face. It is usually sudden and is caused by irritation or compression on the nerves of the face.
- Stroke: For some strokes, especially those that affect the facial region in the brain people might suffer from an impairment in the facial muscles on one hand. This may result in an inability to shut the eye, or even smile correctly.
- Face Trauma: A facial injury, trauma, or physical damage may cause damage to the facial nerve or the structures that are associated with it, resulting in the face being weak on one side.
- Tumors: The growth of tumors near the facial nerve may cause damage or compression to the nerve, leading to facial weakness on one side.
- Diseases: A few infections which include those that affect the ear or the surrounding areas, can cause facial weakness, which makes the face difficult to shut one’s eyes or smile with symmetry.
- Neurological Disorders: Multiple neurological diseases can lead to facial nerve dysfunction that can result in unilateral facial weakness.
- Idiopathic Causes: In certain cases, the root of the facial weakness might not be determined and might be classified as idiopathic.
If you notice that someone is experiencing difficulty closing their eyes or smiling only on the other side of the face it is crucial for them to get medical help immediately.
A medical professional can conduct an extensive examination to identify the cause behind the issue and recommend the appropriate treatment or procedures for the specific problem.
Early diagnosis and treatment are vital to maximize the outcome and avoid potential complications.
Similarities Between Bell’s Palsy and Ramsay Hunt Syndrome
Bell’s Palsy and Ramsay Hunt Syndrome are both conditions that result from problems with the facial nerve (cranial nerve VII) and have some commonalities that include:
- Face Nerve Involvement: Both disorders impact the facial nerve, causing different degrees of facial weakness, or paralysis on one side of the face.
- Rapid Onset: Both in Bell’s Palsy and Ramsay Hunt Syndrome, symptoms usually appear abruptly, within a time span of several hours or days, and are therefore acute conditions.
- Unilateral presentation: Symptoms in both cases typically only affect one face side which can cause asymmetric facial expressions.
- The loss of facial Muscle control: People suffering from both Bell’s Palsy and Ramsay Hunt Syndrome may experience difficulty closing their eyes, smiling, or expressing facial expressions on the affected side.
- Potential Eye Signs: Both conditions could cause eye-related problems that affect the affected eye, for example, excessive tear (epiphora) due to a lack of eye closure, as well as potential corneal exposure.
- Discomfort and Pain: Although it isn’t all-encompassing, people with Bell’s Palsy and Ramsay Hunt Syndrome may experience facial pain, discomfort, or a different sensation in the affected region.
- Potential Viral Association: While the precise causes of Bell’s Palsy viral causes such as herpes simplex have been proposed as possible triggers. Ramsay Hunt Syndrome is caused by the reactivation process of the Varicella-Zoster virus (herpes the zoster).
It is important to recognize that even though these conditions have some similarities, they have distinct differences, particularly in their causes, clinical appearance, symptoms, and treatment methods.
An accurate diagnosis is vital in order to differentiate between these two diseases and provide proper treatment since treatments can vary greatly.
Reference Books
Certainly! Here are some reference books across various genres and topics:
Fiction:
- “To Kill a Mockingbird” by Harper Lee – A classic novel addressing themes of racial injustice and morality.
- “1984” by George Orwell – A dystopian masterpiece exploring totalitarianism and surveillance.
- “The Great Gatsby” by F. Scott Fitzgerald – A classic American novel exploring themes of wealth, love, and the American Dream.
Science and Nature:
- “A Brief History of Time” by Stephen Hawking – A popular science book explaining complex concepts of cosmology and the universe.
- “Sapiens: A Brief History of Humankind” by Yuval Noah Harari – An exploration of the history and impact of Homo sapiens on the world.
- “The Immortal Life of Henrietta Lacks” by Rebecca Skloot – A non-fiction book about the life and legacy of Henrietta Lacks, whose cells were crucial in medical research.
Psychology:
- “Thinking, Fast and Slow” by Daniel Kahneman – An exploration of human decision-making and cognitive biases.
- “The Power of Habit” by Charles Duhigg – An examination of the science of habits and how they can be changed.
- “Man’s Search for Meaning” by Viktor E. Frankl – A memoir and psychological exploration of survival in Nazi concentration camps.
Conclusion
The world of books provides a vast and varied collection of information, stories, and personal growth. If you’re looking for a deeper understanding of the fields of psychology, science, or history or simply a break from a novel There’s a novel waiting to entertain your brain and broaden your horizons.
The classics of literature provide inspiration, education, and entertainment which makes them an indispensable source for learning throughout your life as well as enjoyment. So, take a dive into the pages to discover the wealth of treasures the literature world can offer. Enjoy reading!