Introduction
When it comes to common kitchen herbs, cilantro and parsley often appear together. Though their appearance may resemble each other with vibrant green leaves, each herb possesses distinct characteristics and flavors which set it apart.
We will explore these differences between cilantro and parsley by investigating their appearance, taste, culinary uses, nutritional content, cultivation processes, potential substitutions and cultivation options. By understanding their distinctive qualities you’ll be better equipped to enhance culinary creations while appreciating their variety of flavors that they add.
Definition of Cilantro
Cilantro (Coriandrum sativum), also commonly referred to as coriander leaves or Chinese parsley, is an annual herb belonging to the Apiaceae family that grows yearly in warm regions like China. Cilantro is widely known for its vibrant green leaves, which are widely used as culinary herbs across cuisines worldwide.
The plant can reach 2 feet in height with delicate lacy leaves divided into smaller leaflets that produce fragrant oil-rich blooms. Citrus cilantro produces small white or light pink flowers that develop into seeds known as coriander seeds, each having their own distinctive flavor profile compared to its leaves.
Cilantro is renowned for its distinct, fresh, and citrusy taste which adds an interesting dimension to many dishes; commonly found in Mexican, Indian, Thai and other Asian cuisines as garnishes or ingredients in salsas, curries salads or soups.

Definition of Parsley
Parsley (Petroselinum crispum) is an annual herb from the Apiaceae family that is widely recognized for its vibrant green, curly or flat leaves, often used as both culinary garnishes and garnishes. Parsley is a versatile culinary ingredient used globally.
This plant typically reaches between 1-2 feet high and features multiple feathery leaflets arranged feather-like. There are two primary varieties of parsley; curly (Petroselinum crispum var. crispum) and flat leafed (Petroselinum crispum var. cruptum).
Curly (Petroselinum crispum) and flat-leaf (Petroselinum crispum var. neapolitanum) parsleys differ by having tightly curled leaves while flat-leaf parsley has wider, smoother ones; both types share similar tastes but with slight variations in flavor intensity.
Parsley boasts a refreshing herbaceous flavor with subtle bitter notes that is often described as mild peppery or earthy. It is often added as garnish to salads, soups, stews, sauces and various meat or vegetable dishes for additional flair and nutritional benefits such as vitamin A and K content, iron content and potassium content.

Comparison Table of Cilantro and Parsley
Sure! Here’s a comparison table highlighting the key differences between cilantro and parsley:
| Aspect | Cilantro | Parsley |
|---|---|---|
| Scientific Name | Coriandrum sativum | Petroselinum crispum |
| Appearance | Delicate, lacy leaves, deeply divided | Curly or flat leaves, arranged in a feather-like manner |
| Flavor | Fresh, citrusy, with a hint of soapiness | Fresh, herbaceous, slightly peppery |
| Culinary Uses | Mexican, Indian, Asian cuisines | Mediterranean, European, Middle Eastern cuisines |
| Common Dishes | Salsas, curries, salads, soups | Salads, sauces, stews, meat/vegetable dishes |
| Nutritional Value | Rich in vitamins A, C, K, and antioxidants | Rich in vitamins A, C, K, iron, and potassium |
| Availability | Commonly available | Commonly available |
| Substitutions | Culantro, parsley flakes, mint, basil | Cilantro, dill, tarragon, chervil |
| Growing Conditions | Thrives in cool weather, well-drained soil | Can tolerate a wide range of conditions, prefers moist soil |
| Key Feature | Distinct, fresh, citrusy flavor | Fresh, herbaceous flavor |
Please note that these are general characteristics, and individual preferences may vary.
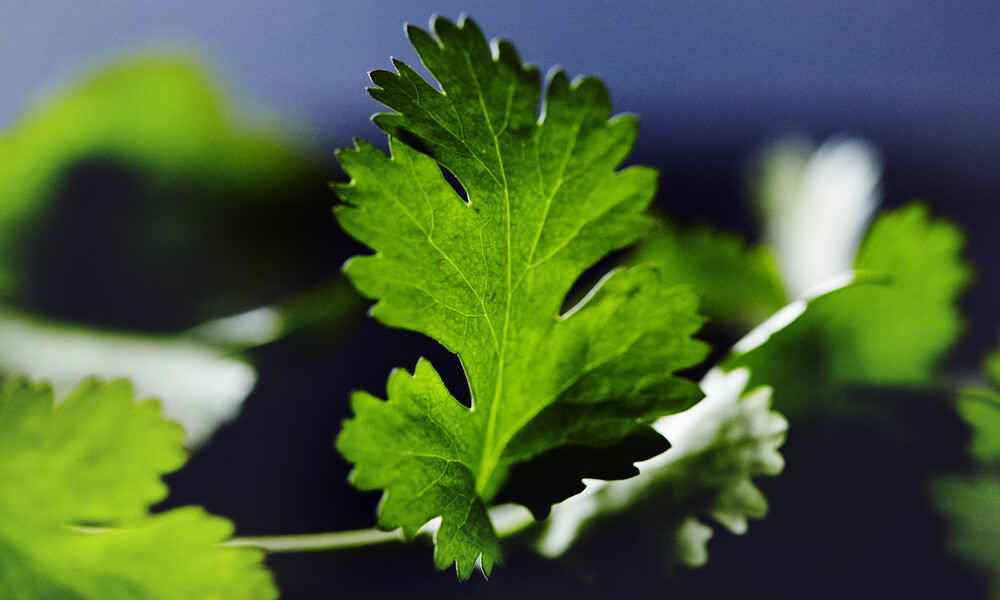
Description of cilantro’s appearance and leaf structure
Cilantro stands out with its delicate and feathery leaves, often bright green in hue and divided deeply into multiple leaflets that give a lacy or fern-like appearance. Each leaflet often has serrated edges for added distinction.
Cilantro leaves can vary in shape, from being more elongated or more rounded, with thin stems usually in green or light green colors and often bearing white or light pink flowers that bloom into coriander seeds with their own distinctive taste.
While cilantro plants can reach two feet in height and produce clusters of small white or light pink blooms which eventually bear coriander seeds that possess different flavor profiles than their leaves, culinary applications primarily utilize its leaves, adding vibrant freshness to many dishes.
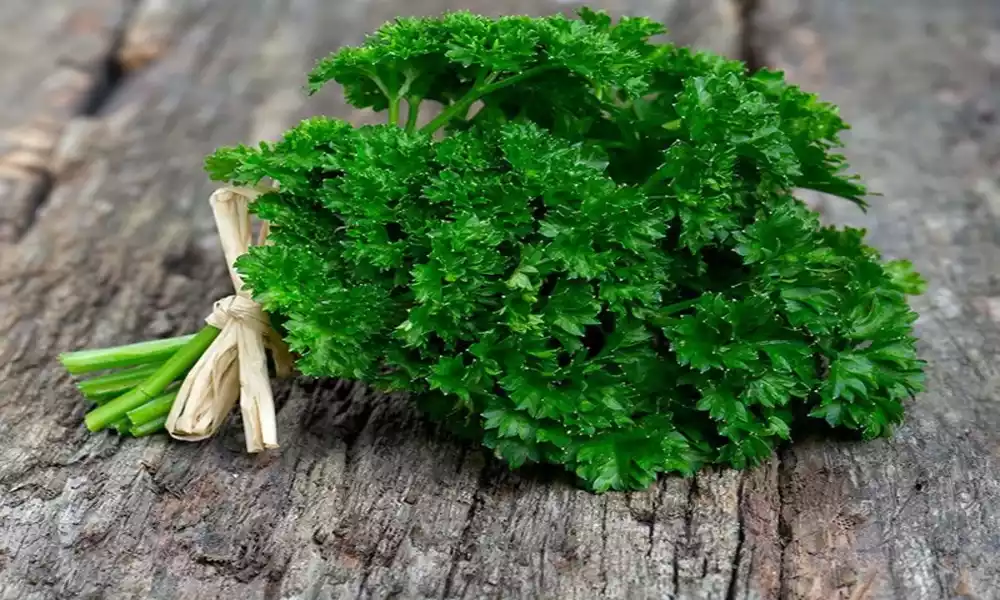
Description of parsley’s appearance and leaf structure
Parsley exhibits a distinct appearance with its vibrant green leaves and unique leaf structure. There are two main types of parsley: curly parsley (Petroselinum crispum var. crispum) and flat-leaf or Italian parsley (Petroselinum crispum var. neapolitanum).
Curly parsley is known for its tightly curled leaves, which give it a decorative and ornamental quality. The leaves are deeply divided and have a ruffled or fringed appearance, resembling miniature green curls. The leaflets are relatively small and narrow, with serrated edges. The stems of curly parsley are slender and often green or light green.
Flat-leaf parsley, also known as Italian parsley, features broader and smoother leaves compared to curly parsley. The leaves are flat, elongated, and have a more pronounced lobed or serrated structure. The leaflets are larger and wider, giving the plant a fuller and more robust appearance. The stems of flat-leaf parsley are relatively sturdy and can be green or reddish in color.
Both types of parsley have a vibrant green color and add a fresh burst of greenery to culinary preparations. While curly parsley is often used as a garnish due to its decorative nature, flat-leaf parsley is favored by many chefs for its strong flavor and versatility in various dishes.
Common culinary applications of cilantro’s taste
Cilantro’s unique flavor profile adds an unforgettable dimension to a variety of culinary creations, making its inclusion an essential ingredient. Below are a few common uses for its zest:
Salsas and Dips: Cilantro is often utilized in Mexican cooking when creating salsas, as its vibrant, citrusy taste complements tomato-based salsas beautifully. Furthermore, cilantro plays an integral part in creating refreshing guacamole dips as it adds an aromatic element.
Curries and Stir-fries: Cilantro is frequently featured in curries and stir fries from Indian and Asian cuisines, providing its distinctive zingy-herbal notes to complement the robust spices found within these dishes. It adds depth while simultaneously offering balance.
Soups and Broths: Cilantro can add an aromatic boost to any soup or broth dish, refreshing its palate while infusing its fresh aroma into its fluid form. Use as garnish on top or incorporate during the cooking process for maximum impact!
Salads and Dressings: Cilantro leaves are often added to salads to provide a refreshing burst of freshness and herbal notes, pairing well with citrus-based dressings that bring brightness to their overall flavor profile.
Tacos and Burritos: Cilantro is an essential element in many Mexican street food dishes such as tacos and burritos. Its distinct taste pairs beautifully with the flavors of grilled meats, beans, and spicy sauces for a delicious combination that brings out its vibrant herbaceous qualities.
Chutneys and Relishes: Cilantro is often included as an ingredient in Indian-style chutneys and relishes, balancing out both spicy heat and acidity for an overall enjoyable taste experience as well as adding vibrant green color.
Here are just a few ways that cilantro’s taste can be applied in various culinary applications. Thanks to its versatility, cilantro can easily be integrated into many different dishes, providing refreshing and flavorful accents to their overall composition.
Common culinary applications of parsley’s taste
Parsley offers an irresistibly fresh, herbaceous, and slightly peppery flavor profile. As such, its versatility makes it an invaluable herb that complements many dishes – some common culinary uses of parsley’s flavor include.
Salads: Parsley can add an aromatic and zesty taste to salads. Chopped and combined with other greens or used as ornamentation to further improve both its appearance and overall flavor.
Sauces and Dressings: Parsley can add an exquisite herbal note to sauces and dressings, giving them more depth of flavor while simultaneously increasing complexity and freshness. Vinaigrettes, creamy dressings, and herb-based sauces are just a few ways this bright herbaceous can add life and complexity.
Soups and Stews: Parsley is often added as an aromatic addition to soups and stews, adding both brightness and aroma. You can either add it during cooking or garnish it before serving to enhance the overall flavor profile of the dish.
Herb and Compound Butters: Parsley is an ideal herb to use when it comes to creating herb butter or compound butter, which can then be finely chopped and mixed with softened butter to form an irresistibly delicious spread that can be spread over bread, grilled meats or roasted vegetables.
Garnish: Parsley can add vibrant green hues and fresh flavors to dishes, adding both vibrancy and zest. Finely chopped leaves may be added or whole leaves used as decoration on meat, fish, pasta or vegetable dishes.
Mediterranean and Middle Eastern Cuisine: Parsley is an indispensable herb in Mediterranean and Middle Eastern cuisines, providing distinct regional flavor accents to dishes such as tabbouleh (a parsley and bulgur wheat salad), falafel, tzatziki sauce and hummus.
Marinades and Rubs: Parsley can add an herbaceous and slightly peppery note to marinades and spice rubs for meats, adding both texture and aroma. Pairing well with other herbs and spices enhances its overall taste and aroma further.
These are only some examples of how parsley’s distinctive taste can be utilized in culinary applications. With its refreshing taste and adaptability, parsley is an excellent addition to many dishes for adding depth and vibrancy.
Health benefits associated with consuming cilantro
Consuming cilantro may provide several health advantages due to its rich nutrient profile and potential medicinal uses.
Here are a few advantages associated with eating cilantro:
Cilantro Is Packed With Nutrients: Cilantro boasts essential vitamins A, C, and K as well as minerals such as potassium, calcium, and manganese that contribute significantly to supporting overall health and wellbeing. These essential nutrients play an invaluable role in contributing to overall wellness.
Antioxidant Properties: Cilantro boasts numerous antioxidants such as flavonoids and phenolic compounds which help combat free radical damage caused by free radicals in our bodies. Antioxidants have anti-inflammatory effects as well as potential anticancer properties.
Digestive Health: Cilantro has long been used to aid digestion. It may stimulate the production of digestive enzymes and aid in breaking down food while alleviating symptoms such as bloating or indigestion.
Detoxification Support: Cilantro may contain chelating properties that help flush heavy metals such as lead, mercury, and aluminum from your body – this potential detox effect could improve overall health and reduce any heavy metal toxicity concerns. Studies indicate that cilantro may possess anti-inflammatory effects, which could help reduce chronic inflammation in the body and its related conditions such as heart disease, arthritis, and certain cancers. Chronic inflammation has been linked to numerous medical problems including cardiovascular disease, arthritis, and certain cancers.
Heart Health: Cilantro contains compounds that may help lower blood pressure and support heart health, while also potentially helping reduce LDL cholesterol levels and contributing to a healthier cardiovascular system.
Immune System Support: Coriander’s high concentration of Vitamin C may provide immune support and protection from common illnesses. Vitamin C has long been recognized for bolstering its antioxidant benefits and stimulating collagen production for healthy skin and wound healing, making cilantro an ideal addition to our daily diets.
Notably, although cilantro may offer potential health benefits, individual results may vary and it should not be seen as a replacement for medical advice or treatment. Furthermore, some individuals may be allergic to cilantro and experience adverse reactions; therefore if any concerns or specific health conditions arise it would be prudent to speak to your healthcare provider first.
Health benefits associated with consuming parsley
Consuming parsley may provide numerous health advantages due to its nutritional content and potential medicinal uses.
Here are a few potential health advantages associated with eating parsley:
Nutritious Herb: Parsley is an abundant source of nutrition, packed with essential vitamins A, C and K as well as iron, calcium and potassium minerals that play vital roles in supporting immunity, bone health and blood clotting processes in our bodies. These nutrients also play a part in supporting other bodily processes including immune support and blood clotting mechanisms.
Anti-Inflammatory Properties of Parsley: Parsley contains flavonoids and other anti-inflammatory compounds, making regular consumption beneficial in combatting inflammation in the body, linked to chronic conditions like heart disease, arthritis and certain forms of cancer.
Antioxidant Effects of Parsley: Parsley is a great source of antioxidants such as vitamins C, beta-carotene, and flavonoids which help neutralize harmful free radicals in your body to reduce oxidative stress and protect cells against damage.
Digestive Health: Parsley has long been used as an aid in digestion and alleviation of digestive issues. It contains compounds which may stimulate production of digestive enzymes and aid healthy digestion while relieving symptoms like bloating and gas.
Kidney Health: Parsley may help promote kidney health through diuretic properties, increasing urine production and supporting elimination of waste products from the body. By flushing out toxins and flushing them out naturally from our systems.
Fresh Breath and Oral Health: Parsley’s high chlorophyll content contributes to its freshening effect on breath. Chewing on parsley leaves or using it in natural mouthwashes may help combat bad breath while its antimicrobial properties help inhibit bacteria growth within the mouth.
Eye Health: Parsley contains two antioxidants known to support eye health: lutein and zeaxanthin, known to protect against age-related macular degeneration (AMD) as well as lower cataract risks. These compounds may provide protection from AMD as well as decreasing their risks.
Note that while parsley may provide potential health benefits, individual results may vary and should not be used as a replacement for professional medical advice or treatment. Furthermore, some individuals may have allergies or sensitivities to parsley which is why if you have specific health concerns or conditions it’s advisable to speak to a healthcare provider immediately.
Vitamins, minerals, and antioxidants found in cilantro
Cilantro is an herb packed with Essential vitamins, minerals, and Antioxidants.
Here are some key nutrient Highlights found in cilantro:
Vitamin A: Cilantro is an excellent source of Vitamin A, an Essential nutrient for Maintaining eye health, supporting Immunity and Supporting skin Wellbeing.
Vitamin C: Cilantro contains vitamin C, an antioxidative that protects cells from damage while simultaneously strengthening immunity and aiding collagen synthesis.
Vitamin K: Cilantro is an Excellent source of vitamin K, an Essential nutrient needed for blood clotting, bone health and calcium Metabolism.
Minerals:
Potassium: Cilantro contains potassium, an essential mineral which plays a crucial role in maintaining proper fluid balance, supporting heart function, and aiding muscle contraction.
Calcium: Cilantro contains small amounts of calcium, an essential nutrient for strong bones and teeth as well as supporting nerve function and muscle health.
Iron: Cilantro contains iron, an essential mineral required for producing hemoglobin (which transports oxygen around your body). Iron also plays an integral role in energy production and maintaining healthy red blood cells.
Antioxidants: Flavonoids:cit Cilantro contains various flavonoids, including quercetin and kaempferol, that have been associated with anti-inflammatory and potential anticancer properties.
Beta-carotene: Cilantro contains beta-carotene, an Essential precursor of vitamin A that acts as an Effective Antioxidant to protect against oxidative stress and cell Damage.
Lutein and Zeaxanthin: Cilantro contains Antioxidants such as lutein and Zeaxanthin which may provide Protection from age-related macular Degeneration (AMD).
Noting the variance of cilantro’s nutritional composition depends on various factors including soil conditions, cultivation methods and plant maturity.
Vitamins, minerals, and antioxidants found in parsley
Parsley is an Abundance of vitamins, minerals, and Antioxidants – here are just a few!
Here is a Breakdown of its key nutrient sources:
Vitamin A: Parsley contains high concentrations of Vitamin A, an essential nutrient for vision health and immunity function as well as supporting healthy skin and mucous membranes.
Vitamin C: Parsley is an Excellent source of vitamin C, an anti-oxidant known to enhance Immune function, Collagen Synthesis and iron Absorption. And parsley also contains vitamin K for blood clotting, bone health and healthy blood vessels – important factors in overall cardiovascular wellness. Additionally, parsley provides essential minerals.
Iron: Parsley is an excellent source of iron, an essential mineral required for oxygen transport, energy production and maintaining healthy red blood cells. Calcium: Calcium is necessary for maintaining strong bones and teeth as well as supporting nerve function and muscle health – two critical aspects that parsley supplies abundantly.
Potassium: Parsley provides potassium, an electrolyte mineral essential for maintaining proper fluid balance, supporting heart function and supporting nerve and muscle functioning.
Antioxidants: Parsley also provides powerful antioxidant protection.
Flavonoids: Parsley contains Flavonoids such as apigenin, which has been associated with both anti-Inflammatory and Antioxidant effects.
Beta-Carotene: Parsley provides an abundant source of beta-carotene, an essential precursor for vitamin A as well as an antioxidant to protect cells against oxidative damage.
Lutein and Zeaxanthin: Parsley contains antioxidants that may provide benefits to eye health and even help protect against age-related macular degeneration (AMD).
Noting the variability of parsley’s nutritional profile depends on factors like its growing conditions, plant variety, and freshness; including parsley in your diet can provide an ample source of essential vitamins and minerals, offering various health benefits.
Conclusion
Coriander and parsley are two distinctive herbs with individual properties and flavors, although their appearance may be similar. Each has its own culinary uses and specific culinary applications. Citrusy cilantro leaves are prized for their crisp citrusy taste and delicately feathery leaves, making this herb an integral component of Mexican dishes like salsas, curries, soups, and Mexican food. Cilantro may also provide several health benefits including antioxidant properties, digestive support, and potential detoxification effects.