Introduction of Squamous and Ulcerative Blepharitis
Blepharitis is a very common and frequently misunderstood eye problem that affects the eyelids, creating discomfort and visual disturbances. There are various kinds of blepharitis, including ulcerative and squamous blepharitis two distinct, but commonly seen types.
Understanding the causes, symptoms, and symptoms, as well as the diagnosis and treatments for these conditions is crucial for medical professionals as well as those seeking to control and ease the pain they cause.
We look at the main aspects of squamous as well as ulcerative blepharitis. We provide important insights into their causes and the best way to treat the issues.
Definition of Squamous Blepharitis
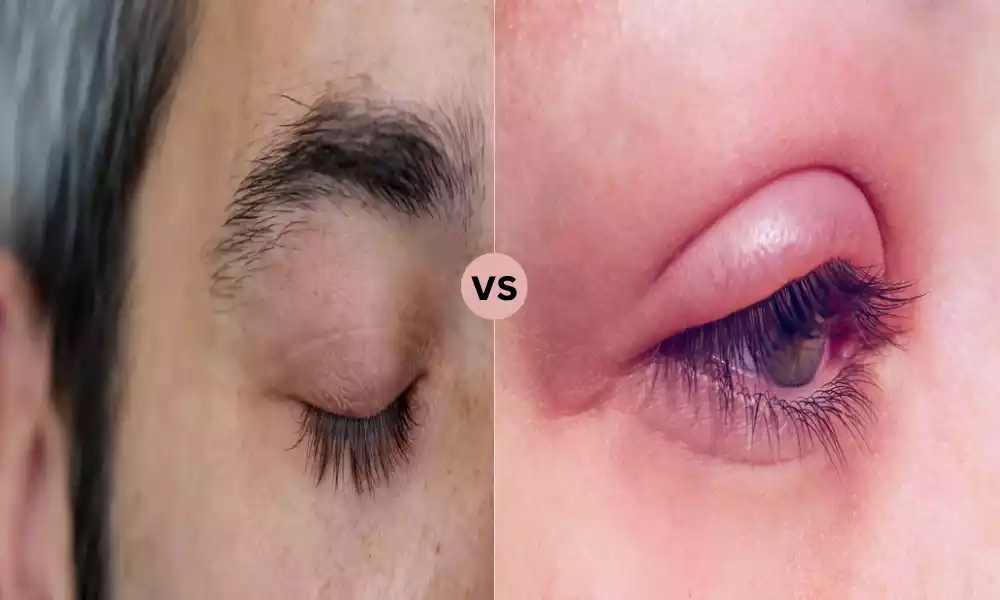
Squamous blepharitis, sometimes referred to as anterior blepharitis, is an eye disorder that manifests as irritation and inflammation in the front (front) part of the eyelids, specifically the follicles and skin. It is most commonly affecting the outermost layer of the eyelids, which includes the squamous epithelium which is the scale-like, flat tissue that protects the skin’s surface.
The condition is usually caused by a mixture of factors, which include an overgrowth of bacteria, like Staphylococcus species, and seborrheic skin dermatitis. Squamous blepharitis is often accompanied by symptoms that include burning, itching, red sensations, and crusty debris that forms on the bottom of eyelashes.
The proper treatment of squamous blepharitis requires maintaining a healthy eyelid hygiene applying warm compresses and occasionally using medicines like steroids or antibiotics to decrease inflammation and limit the growth of bacteria.
Knowing the signs of squamous blepharitis is essential for determining the best treatment and diagnosis because it has the potential to significantly affect the comfort and visual health of those who are affected by the condition.
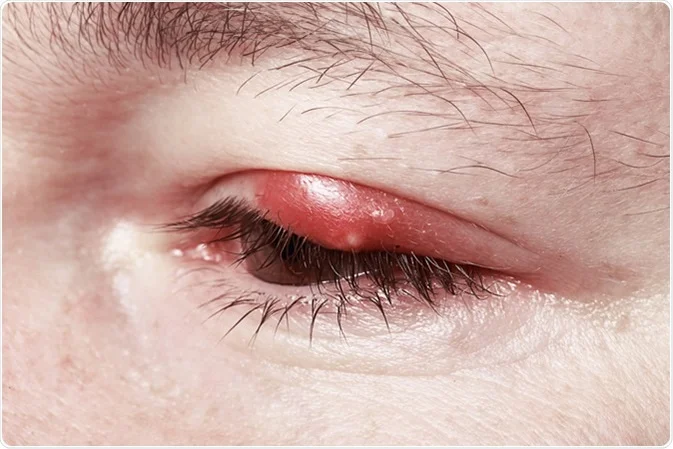
Definition of Ulcerative Blepharitis
Ulcerative Blepharitis is a form of chronic eye disorder that is characterized by inflammation and the appearance of small painful ulcers or sores around the margins of eyelids. These types of ulcers are typically found at the lower part of the eyelashes and may affect both the upper as well as lower eyelids.
The condition is usually related to bacterial infections like Staphylococcus aureus and often occurs in conjunction with other ailments like meibomian gland malfunction or Demodex infections.
Patients suffering from ulcerative blepharitis might be afflicted by symptoms like swelling, redness and burning sensations, itching, and a rough or foreign body feeling in the eyes. A presence of ulcers could cause blinking and eye movements to become uncomfortable, and could cause loss of eyelashes.
The proper diagnosis and treatment of ulcerative blepharitis generally require careful eyelid hygiene, such as gentle compresses, lid scrubs, and warm compresses in addition to the application of antibiotics or topical corticosteroids to stop inflammation and bacterial growth.
It is crucial to address the blepharitis ulcerative promptly to avoid complications and to improve the comfort of your eyes and overall health.
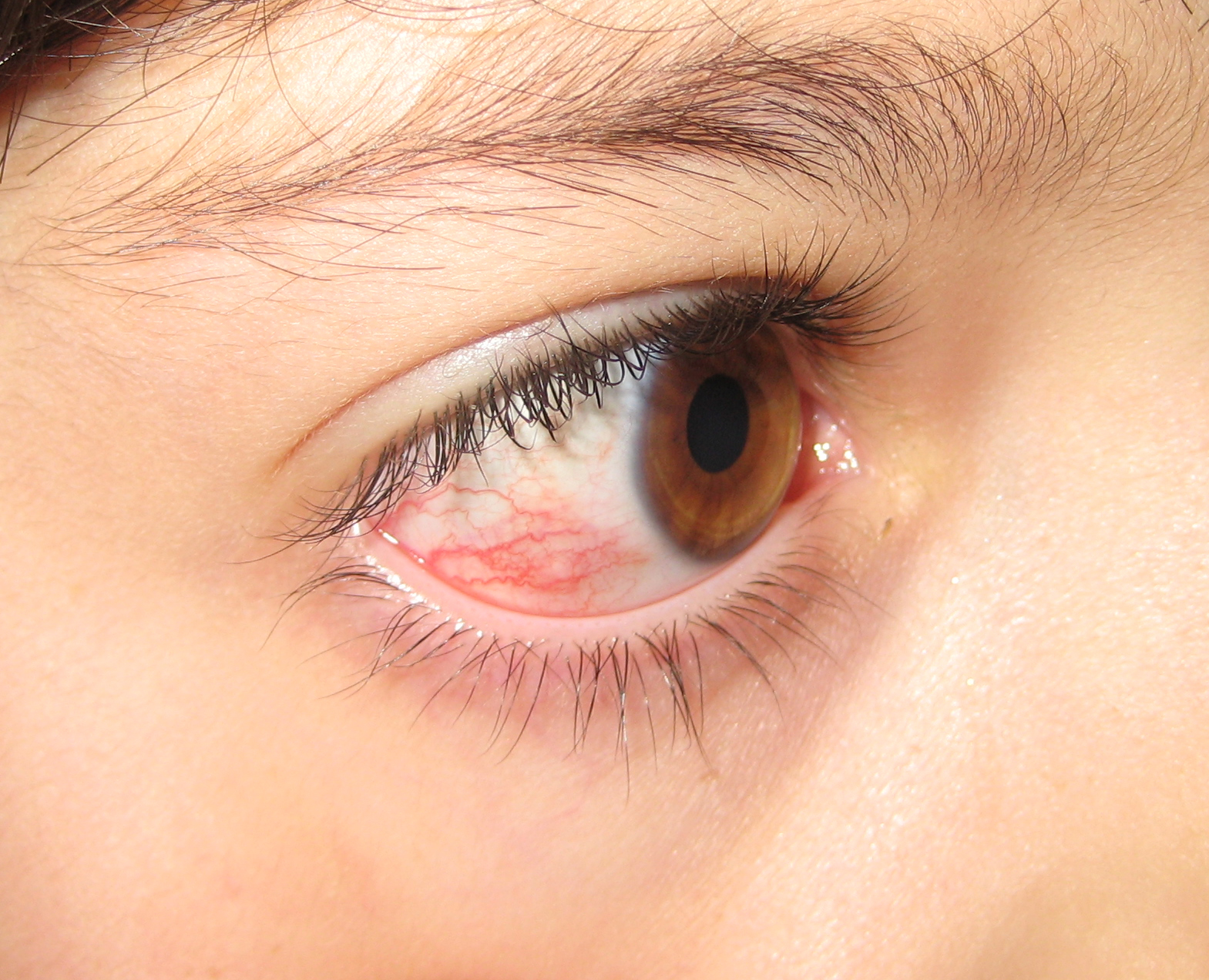
Comparison Table of Ulcerative Blepharitis
Certainly, here’s a comparison table highlighting the key characteristics of ulcerative blepharitis:
| Aspect | Ulcerative Blepharitis | Description |
|---|---|---|
| Location | Eyelid Margins | Typically affects the edges of the eyelids. |
| Ulcers | Presence of Ulcers | Characterized by small, painful ulcers or sores. |
| Symptoms | – Redness- Itching- Crusting- Eyelash Loss | – Swelling- Burning Sensations- Gritty or Foreign Body Sensation- Discomfort with Blinking |
| Causes | – Bacterial Infections- Allergic Reactions- Demodex Infestation | – Commonly associated with Staphylococcus aureus.- May involve allergies or sensitivities.- Presence of Demodex mites on eyelids. |
| Treatment | – Eyelid Hygiene- Antibiotics (Topical/Oral)- Anti-Demodex Medications | – Warm Compresses- Steroids (Topical)- Lubricating Eye Drops |
| Prognosis | Chronic Condition | Requires ongoing management to control symptoms. |
| Complications | – Corneal Inflammation- Conjunctivitis- Vision Disturbances | – Eyelash Misalignment- Corneal Damage – Scarring of Eyelids- Recurrent Infections |
Please note that the severity of ulcerative blepharitis and the effectiveness of treatment can vary among individuals. It’s crucial for individuals experiencing symptoms to consult with an eye care professional for proper evaluation and personalized management.
Significance of Understanding Different Blepharitis Types
Knowing the different forms of blepharitis, such as ulcerative and squamous blepharitis is crucial due to a variety of reasons:
- Accurate Diagnosis: Identifying different types of blepharitis is essential for health professionals to come up with a precise diagnosis. Blepharitis type may determine the best treatment strategy. Incorrect diagnosis can result in unproductive treatments and in the long run, pain for sufferers.
- Customized treatment plans: Different kinds of blepharitis require different treatments. For instance, squamous blepharitis generally is well-responded to by antibiotics and hygiene of the lids, however ulcerative blepharitis might require more aggressive treatment with topical corticosteroids and anti-demodex medicines. Knowing the type of blepharitis is a way for medical professionals to design treatment plans to address the underlying cause and symptoms efficiently.
- Management of Complications: Untreated or poorly managed the condition can cause complications like cornea inflammation, conjunctivitis dry eye syndrome, and visual problems. Knowing the kind of blepharitis is helpful in early intervention and the elimination of possible complications.
- Patient Education: Ensuring that patients are informed about the kind of blepharitis they suffer from allows them to be actively involved in their treatment. Patients who are aware of their condition will be more inclined to follow treatments and follow proper eyelid hygiene, which leads to improved outcomes.
- Preventive and lifestyle changes: Recognizing the root causes of blepharitis and whether they are due to bacterial infections allergies, or another cause will aid patients in making the necessary changes in their lifestyle to lower the likelihood of the recurrence. For example, better hygiene of contact lenses or the treatment of skin disorders such as seborrheic skin dermatitis might be suggested.
- Research and advancements: Understanding the different forms of blepharitis is vital to continue research and the creation of new therapies and treatments. The latest developments in Ophthalmology are dependent on the correct identification and understanding of particular eye conditions such as blepharitis.
knowing the distinction between various types of blepharitis is not just essential for an accurate diagnosis and customized treatment, but also for preventing complications and enhancing the health of people suffering from the common eye condition.
Researchers, healthcare professionals, as well as patients gain a thorough knowledge of the different types of blepharitis, as well as their distinctive characteristics.
Distinguishing Squamous and Ulcerative Blepharitis from Other Eye Conditions
Differentiating squamous blepharitis from ulcerative from other eye disorders is vital for a correct diagnosis and treatment.
Here are some important tips to distinguish the kinds of blepharitis. other eye disorders:
Squamous Blepharitis:
- Location: Squamous blepharitis is a problem for the posterior (front) part of the eyelids. It is particularly affecting the lashes follicles and skin.
- Signs and symptoms: Common symptoms are burning, itching, redness sensations, and crusty debris that is located at the bottom of the eyelashes. The symptoms are usually restricted to the margins of the eyelids.
- Physical Exam: Health professionals can be able to detect flakes, scales, or dandruff-like particles on the skin of the eyelid and the eyelashes in a physical examination.
- Diagnosis: The diagnosis of squamous blepharitis requires an examination of the eyelid’s margins as well as in certain cases microscopical examination of samples.
- Treatment: Treatment typically involves eyelid hygiene cold compresses, warm compresses, and occasionally steroids or antibiotics to reduce inflammation and bacterial growth.
Ulcerative Blepharitis:
- Location: Ulcerative blepharitis can affect the eyelid’s margins and is identified by the appearance of small painful ulcers or sores on the edge of the eyelids.
- Signs and symptoms: Patients suffering from ulcerative blepharitis might be afflicted by swelling and redness that causes itching, burning sensations, and a smudge and foreign-body sensation around the eyes. It can also cause irritation when blinking.
- Physical Exam: Healthcare providers can detect the presence of crusts, ulcers, and possible loss of eyelashes in a physical examination.
- Diagnosis: The diagnosis is based on a clinical evaluation often with microscopic assessment and identifying the characteristic ulcers.
- Treatment: Treatment for ulcerative blepharitis is usually based on strict eyelid hygiene as well as antibiotics (topical or oral) as well as topical corticosteroids and, occasionally, anti-demodex medication.
Distinguishing From Other Eye Conditions:
- Conjunctivitis: Squamous and ulcerative blepharitis are most commonly seen in the eyelids as well as the eyelash margins Conjunctivitis is mainly affecting the conjunctiva (the transparent membrane that covers the white area that covers the eyes).
- Dry Eye Syndrome: Dry eye syndrome may cause discomfort in the eyes and redness, It’s not usually caused by ulcers or a crust around the eyelids’ margins, like in the case of blepharitis.
- Allergy Reactions: Allergic reactions can cause itching and redness in the eyes, but are typically caused by a previous history or exposure to allergens, or triggers.
- Styes (Hordeolum): Styes are localized infections that affect the eyelid glands. They may be similar to certain aspects of blepharitis. But, they tend to be painful and localized, whereas Blepharitis is more widespread and affects the eyelid’s margins.
- Corneal conditions: Conditions that affect the cornea, for example, corneal ulcers or keratitis can cause visual changes and pain, but they do not usually affect the margins of the eyelids.
If you are unsure or if symptoms continue to persist and persist, it is important to speak with an eye specialist to get a thorough assessment and a precise diagnosis and also to rule out any other conditions of the eye that might cause similar symptoms to blepharitis.
Management of Underlying Conditions
Controlling the underlying conditions that cause or worsen the symptoms of blepharitis is a crucial aspect of the treatment process. The treatment of these causes will reduce the intensity and frequency of flare-ups with blepharitis.
Here are some of the most common causes and treatment options:
- Meibomian Gland Dysfunction (MGD):
- MGD is often associated with Blepharitis is a common complication. It is caused by dysfunction of meibomian glands which create tears’ oily layer.
- Treatment includes warm compresses to help liquefy oil blockages, massages of the lid to stimulate glands, and occasionally meibomian gland probes or more specialized treatments like LipiFlow(r) as well as intense pulsed lighting (IPL) treatment.
- Seborrheic Dermatitis:
- Seborrheic dermatology can affect the facial skin and scalp including the eyelids’ margins.
- Treatment is a gentle cleanse using a gentle non-irritating cleanser and the application of creams for antifungal use on the skin or steroids as prescribed by dermatologists.
- Demodex Infestation:
- Demodex mites may aggravate symptoms of blepharitis. Treatment options include:
- Lid scrubs using tea tree oil-based cleanser.
- Prescription medicines, like Ivermectin, are sometimes required in the most severe of situations.
- Eyelid hygiene is important to avoid re-infestation.
- Demodex mites may aggravate symptoms of blepharitis. Treatment options include:
- Bacterial Infections:
- Bacterial infections, especially Staphylococcus species, may contribute to blepharitis.
- Treatment can include antibiotic ointments and oral antibiotics prescribed by your medical professional.
- Allergies:
- Allergies, which include seasonal allergies, or contact allergies, can worsen the symptoms of blepharitis.
- It could involve the elimination of allergens, taking antihistamines, or even prescription eye drops for allergies.
- Contact Lens Wear:
- Contact lens-related causes can lead to blepharitis. The proper hygiene of your contact lenses is vital.
- Try switching to disposable contact lenses, or reduce the time for wearing lenses if recommended by an eye doctor.
- Systemic Health Conditions:
- Health conditions that are systemic in nature like rosacea can cause blepharitis.
- Treatment involves treating the underlying condition using the guidance of a medical professional or dermatologist.
- Dry Eye Syndrome:
- Dry eye syndrome is often associated with blepharitis. Treatment for dry eye involves using lubricating drops, and in extreme instances, prescription medicines or techniques such as punctal plugs.
- Stress and Lifestyle Factors:
- Stress and poor routines can cause blepharitis to worsen.
- Strategies for managing stress and a balanced diet, enough sleep, and quitting smoking can improve the overall health of your eyes.
It is essential to speak with an eye doctor like an optometrist or ophthalmologist, to determine and treat any other underlying issues that contribute to the condition known as blepharitis.
They can design a custom treatment plan, and also provide advice regarding long-term care and preventative measures. In addition, regular cleaning of the eyelids must be followed to avoid flare-ups with blepharitis.
Reference Books
Certainly, here are some reference books that provide valuable information on ophthalmology, eye conditions, and related topics, including blepharitis:
- “Kanski’s Clinical Ophthalmology: A Systematic Approach” by Jack J. Kanski and Brad Bowling – This comprehensive textbook covers various eye conditions, including blepharitis, and provides in-depth information on their diagnosis and management.
- “Ocular Surface Disease: Cornea, Conjunctiva and Tear Film” by Edward J. Holland and Mark J. Mannis – This book focuses on diseases of the ocular surface, which includes conditions like blepharitis. It provides insights into the latest research and treatment options.
- “Blepharitis: Current Strategies for Diagnosis and Management” by Sihem Lazreg, Mohamed Yahiaoui, and Ahmed Chraibi – This book specifically delves into the topic of blepharitis, offering a comprehensive overview of its diagnosis and management strategies.
- “Basic and Clinical Science Course (BCSC): External Disease and Cornea Section” by American Academy of Ophthalmology – Part of the BCSC series, this book covers a wide range of external eye conditions, including blepharitis, and is a trusted resource for ophthalmology professionals.
- “Clinical Manual of Contact Lenses” by Edward S. Bennett and Vinita Allee Henry – If contact lens wear is related to your interest in blepharitis, this book provides valuable information on the fitting, care, and management of contact lenses, which can impact blepharitis management.
Conclusion
Understanding the difference between ulcerative and squamous blepharitis their distinctive characteristics and the best strategies for managing them is vital for both medical professionals as well as those who are affected by these conditions.
It is important to distinguish between these kinds of blepharitis, and excluding other eye disorders is vital to ensure a precise diagnosis and individualized treatment strategies.
In addition, addressing the underlying causes like meibomian gland dysfunction, seborrheic dermatologic dermatitis, or infections caused by bacteria, play crucial roles in managing and preventing flare-ups in blepharitis.
Through staying up-to-date and seeking out advice from eye specialists people can improve their overall eye health and well-being.