“RS232 and RS485 are both serial communication standards widely used in various industries. While they share similarities in transmitting data serially, they significantly differ in their signaling methods, transmission distances, and noise immunity.
RS232, known for its simplicity, operates over short distances in point-to-point connections, whereas RS485, employing differential signaling, supports longer distances and multi-node networks. Understanding these key distinctions is crucial in choosing the appropriate standard for specific applications.”
Definition of RS232
RS232 (also known as Recommended Standard 232 is a well-established serial communication standard that is used to transmit information between devices. It specifies the mechanical, electrical, and functional specifications that allow serial communication between devices, usually using the serial port on computers or other electronic devices.
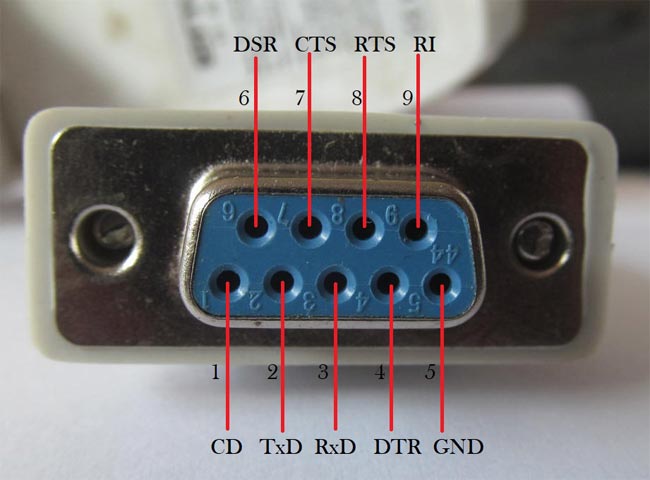
RS232 utilizes voltage levels to represent binary data, usually employing negative and positive voltage levels to signify ones and zeros in the respective sense.
It was extensively used to connect devices such as printers, modems, as well as computers, however, its popularity has decreased since the introduction of modern protocols due to the limitations on distance and the possibility of noise.
Definition of RS485
The RS485, also referred to as Recommended Standard 485, is a communication standard for sending information between multiple devices at quite large distances.
It uses differential signaling, that is, it sends data using the voltage difference between two wires instead of using voltage levels in absolute terms. RS485 permits multi-point communication which allows several devices to be connected via the same network or bus.
This standard is renowned for its durability even in a noisy environment and its ability to provide greater data rates over longer distances as opposed to RS232.
It is widely employed in building automation, industrial automation control systems, as well as other applications that require reliable communications across extended distances using several devices.
Comparison Table of RS232 and RS485
Certainly! Here’s a simplified comparison table highlighting the key differences between RS232 and RS485:
| Aspect | RS232 | RS485 |
|---|---|---|
| Signaling | Single-ended | Differential |
| Voltage Levels | Uses positive and negative levels | Uses voltage difference for data |
| Distance | Shorter distances (up to 50 feet) | Longer distances (up to 4000 feet) |
| Multi-point | Typically point-to-point | Supports multi-point |
| Data Rate | Lower data rates | Higher data rates |
| Noise Immunity | Less resistant to noise | More resistant to noise |
| Implementation Complexity | Simple | Moderate |
| Typical Applications | PC peripherals, short-range links | Industrial automation, long-range networks |
This comparison table encapsulates the fundamental differences between RS232 and RS485, focusing on signaling methods, distances supported, multi-point capabilities, data rates, noise immunity, implementation complexity, and typical application scenarios for each standard.
Similarities Between RS232 and RS485
Although they have their own differences, RS232 and RS485 do have a few things in common:
- Serial Communications: both RS232 as well as RS485 are both serial communication standards that allow data to be transferred between devices.
- Data Transmission: Both of them facilitate transmission of digital information however there are differences in techniques employed to handle and signal data.
- Communication Protocols The HTML0 protocol is based on standards-based communication protocols, which define the way the data will be formatted sent, and received.
- Utilized in various Industries: RS232 and RS485 are used in various industries, such as industrial automation, telecommunications and even computing, though in different capacities because of their distinctive characteristics.
- Historical significance: Both standards have been widely utilized in the past and have been widely used in the past, with RS232 being more common in older systems, while RS485 becoming more prominent in applications that require long-distance or multi-point communication.
- Support for legacy devices: Even though newer communications standards have come out, RS232 and RS485 remain in use in the modern world as there are many devices and equipment that support these interfaces due to compatibility to meet compatibility.
Advantages of RS485 over RS232
Here are the advantages of the RS4885 over its counterpart the RS232:
- Long Distance Communications: RS485 can transmit data at much further distances than its RS232 equivalent; supporting cable lengths up to 4000 feet while its counterpart has only 50-foot maximum support. RS485 can transmit data at much faster rates than its RS232 predecessor, supporting data rates up to 10 Mbps while its limit lies at 115,200 bps.
- Multiple Devices: RS485 allows communication among multiple devices on one network while RS232 supports only two-way communications.
- Noise Immunity: RS485 offers higher immunity from noise and interference compared to RS232 due to its differential signaling system that minimizes common-mode noise levels.
- Reduced Cost: RS485 can be less costly in large networks due to supporting more devices at once reducing individual device costs per device.
RS4885 offers greater robustness in harsh environments due to the differential signaling system which resists electrical noise and interference more effectively than its RS232 equivalent. - Flexibility: RS485 can be utilized across numerous fields of application including industrial automation, transportation systems, and building automation. Due to its long-distance communications capability and fast data transfers between devices.
RS485 provides a more powerful, versatile, and flexible communication protocol than RS232 for applications requiring high-speed data transfers, long-distance communications, or communications among multiple devices.
When to Use RS232 or RS485
Here are some things to consider to help you decide when you should use the appropriate standard:
When to Use RS232:
- Short-distance Communication: RS232 is suitable for communications for relatively short distances usually between 50 and 50 feet (15 meters). It is typically utilized to connect devices in the same space or space.
- Point-to-Point Communication: RS232 is designed to support point-to-point communication, which means it only connects two devices at a time. If you’re looking for a straightforward one-to-one connectivity requirement, RS232 may be an easy option.
- Lower Data Rate: RS232 can be used for applications that don’t need high rates of data transfer. It’s suitable for applications that require speeds of up to 115.200 bits per second.
- Legacy Systems: RS232 is extensively supported and is compatible with many older systems and equipment from the past. If you’re working with older equipment, RS232 may be the best choice.
When to Use RS485:
- Long-distance Communication: The RS485 protocol is ideal for long-distance communications and can transmit data at distances up to 4,500 feet (1,200 meters) or greater. It is well-suited to applications that require communication between devices that span a vast space.
- Multi-Point communication: RS485 supports multi-point communication that allows the connection of multiple devices together on one bus. If you want to connect several devices at once then RS485 is the more effective choice.
- High Data Rate: The High Data Rate RS485 can handle greater speeds of data than RS232 and is therefore suitable for applications that require speedier data transfer, like Industrial automation systems and controls.
- Noise Immunity: RS485 provides greater noise resistance because of its differential signaling. This makes it more robust in noisy industrial settings. It is also less prone to electrical noise and interference.
- Full-Duplex or Half-Duplex: It can be used in both full-duplex as well as half-duplex modes, allowing the flexibility to communicate according to the requirements of your business.
Conclusion
RS232 is an affordable and straightforward protocol suitable for short-distance communication between devices, while RS485 provides robust long-distance and multiple-device communication with ease.
Both protocols can also communicate at high data transfer rates at long distances simultaneously – but when choosing between these options one must understand their differences carefully as doing so could have significant effects on performance, reliability, and cost-efficiency.