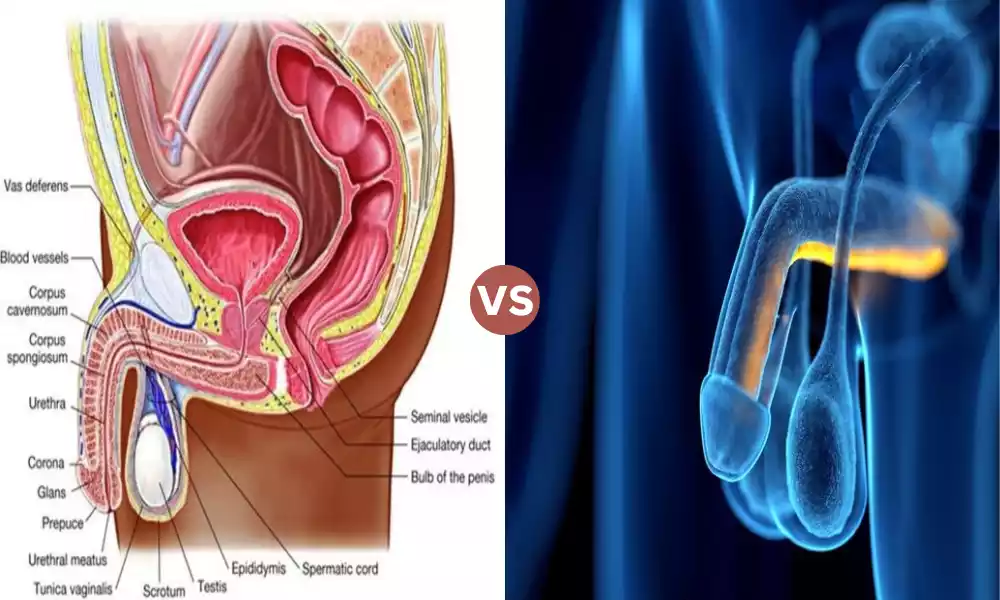
The main difference between corpus cavernosum and corpus spongiosum is that the corpus cavernosum is an erectile tissue of the penis located on either side of the ureter whereas the corpus spongiosum is an erectile tissue of the penis located below the penis and around the male urethra. inside the penis.
The Corpus cavernosum and corpus spongiosum are two different types of erectile tissue in male anatomy that help in erection. Normally, there are three erectile tissues (the two cavernosa and the spongiosum).
They are expandable, sponge-like structures that are involved in the process of penile erection. The corpus cavernosum fills with more blood to maintain a proper erection, while the function of the corpus spongiosum is to prevent the closure of the urethra.
Definition of corpus cavernosum
Corpus cavernosum refers to one of the paired structures in the male reproductive system that play an important role in penile erection. It is a spongy tissue with blood vessels that makes the penis hard when it fills with blood during an erection.
About 90% of the blood fills the corpus cavernosum during an erection. Therefore, in erection, this spongy tissue makes the penis hard enough to enter the vagina. In addition, muscle tissue helps in contraction which facilitates the movement of semen containing sperm from the tip of the penis.
The corpus cavernosum is made up of smooth muscles and structures called intracavernosal struts. Some common conditions affecting the corpus cavernosum are erectile dysfunction, penile cancer, thrombosis, penile fracture, Peyronie’s disease, priapism, ejaculation disorders, and cellulitis.
Common tests to check the health of the corpus cavernosum include a medical history, physical exam, ultrasound, X-ray, CT scan, and MRI. In addition, common treatments for conditions affecting the corpus cavernosum may include medications (antibiotics and pain relievers), surgery, and chemotherapy.
Definition of corpus spongiosum
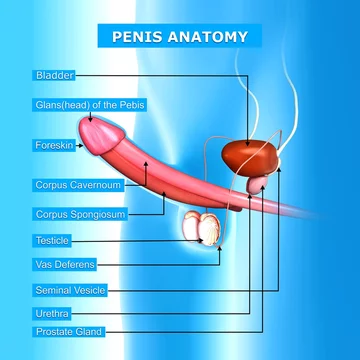
The corpus spongiosum is a spongy erectile tissue surrounding the male urethra within the penis. The corpus spongiosum plays an important role in erection by preventing the closure of the urethra.
This helps maintain the urethra as a viable open channel for ejaculation. In addition, the corpus spongiosum also contributes to the overall hardness and size of the penis during erection. The corpus spongiosum is made up of smooth muscle, collagen, and elastic fibers.
Some common conditions affecting the corpus spongiosum are erectile dysfunction and urethral stricture. Common tests to check the health of the corpus spongiosum include a sexual history, a mental health or physical exam, and imaging tests such as X-rays and MRIs.
Common treatments for conditions affecting the corpus spongiosum may include medications (sildenafil), dilation, urethrotomy, and open surgery.
Similarities Between Corpus Cavernosum and Corpus Spongiosum
Corpus cavernosum and corpus Spongiosum are two distinct types of male anatomy erectile tissue.
Both are spongy erectile tissue.
They are found within the penis.
Both erectile tissues are composed of smooth muscle cells.
They help in building and reproduction.
Both erectile tissues are affected by different conditions.
Conditions affecting these erectile tissues can be diagnosed through a physical exam and imaging tests.
Conditions affecting these erectile tissues can be treated through medications and surgery.
Difference between corpus cavernosum and corpus spongiosum
Certainly, here’s a simplified comparison table highlighting the key differences between Corpus Cavernosum and Corpus Spongiosum:
| Aspect | Corpus Cavernosum | Corpus Spongiosum |
|---|---|---|
| Location | Paired structures on the dorsal side of the penis | The single structure surrounding the urethra |
| Microscopic Structure | Cavernous spaces, smooth muscle, blood vessels | Spongy tissue with fewer cavernous spaces |
| Role in Erection | A major contributor to penile rigidity during arousal | Helps maintain urethral patency during erection |
| Erectile Function | Fills with blood, causing expansion and engorgement for erection | Limited expansion, contributes less to the erection |
| Protection During Intercourse | Less involved in protecting the urethra during intercourse | Surrounds urethra, providing cushioning |
| Role in Ejaculation | Not directly involved in ejaculation | Surrounds urethra and contributes to seminal fluid propulsion |
| Microscopic Composition | High concentration of blood sinuses | Less cavernous spaces, more fibrous tissue |
| Clinical Implications | Erectile dysfunction and treatments | Urethral disorders, hypospadias, and related issues |
Please note that this table provides a simplified overview of the main differences between Corpus Cavernosum and Corpus Spongiosum. The actual structures and functions are more complex, but this table should help provide a quick comparison.
Conclusion
The Corpus cavernosum and corpus spongiosum are two kinds of erectile tissue found in male anatomy. Males have two corpus cavernosum and only one corpus spongiosum in the penis. Both these tissues help in erection and reproduction.
The corpus cavernosum helps with proper erection by filling with blood, while the corpus spongiosum helps to maintain the urethra as a viable open channel for ejaculation.
Frequently Asked Question
Certainly, here are some frequently asked questions (FAQs) regarding Corpus Cavernosum and Corpus Spongiosum:
What are Corpus Cavernosum and Corpus Spongiosum?
- Corpus Cavernosum refers to two long erectile tissue structures located in the penis which offer rigidity during erections.
- Corpus Spongiosum, on the contrary, helps protect the urethra from damage by preventing the closure of the urethra during erection and assists in the ejaculatory process.
What is the role of Corpus Cavernosum and Corpus Spongiosum in sexual function?
- Corpus Cavernosum plays an essential part in the production and maintenance of a sexual erection. When stimulated the blood flow will increase in its chambers, which causes the penis to stiffen in tension as the erection develops.
- Corpus Spongiosum (CSS) is an anatomical structure made up of urethra and super vascular rings which protect and surround the body during sexual erection. They also help with propulsion during the ejaculatory process.
How do Corpus Cavernosum and Corpus Spongiosum differ in structure?
- Corpus Cavernosum contains numerous cavernous spaces, smooth muscle layers, and blood vessels which enable it to expand and fill with blood during an erection.
- Corpus Spongiosum features smaller cavernous spaces and increased fibrous tissue density, providing support and preventing urethral closure.