“Rabbit and Jackrabbit often spark curiosity due to their similar names, yet they belong to different genera with distinctive characteristics. Despite some shared traits, these creatures exhibit notable differences in their habitats, physical attributes, behaviors, and ecological roles.
Exploring these variations sheds light on their unique adaptations and significance within their respective ecosystems.”
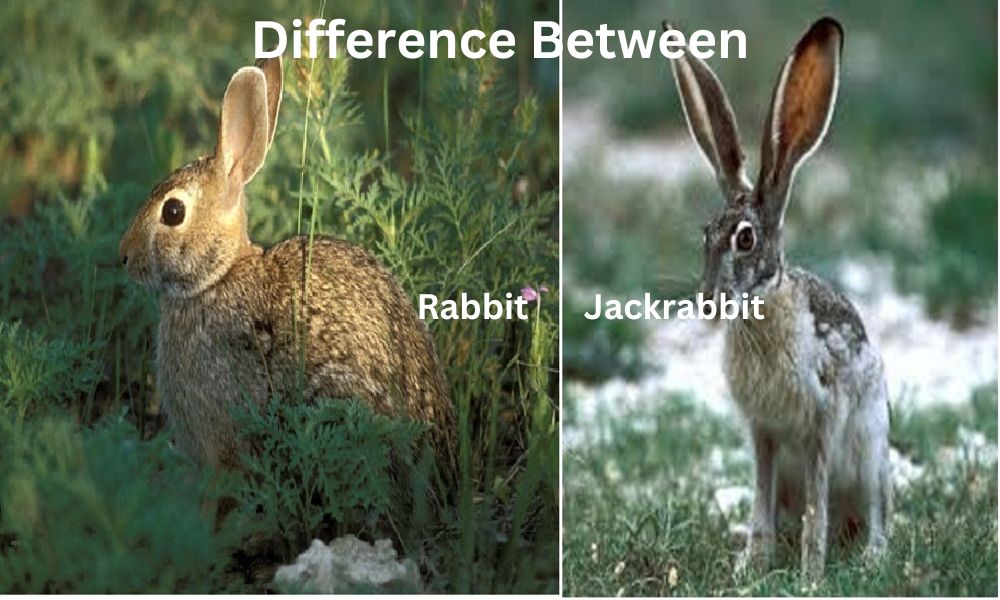
What is a Rabbit?
Rabbits are tiny, herbivorous mammals that belong to the family of Leporidae and are most commonly well-known for their fluffy fur, and large ears with short and long tails. They are distinguished by their propensity to burrow, their prolific breeding, and their herbivorous diet.
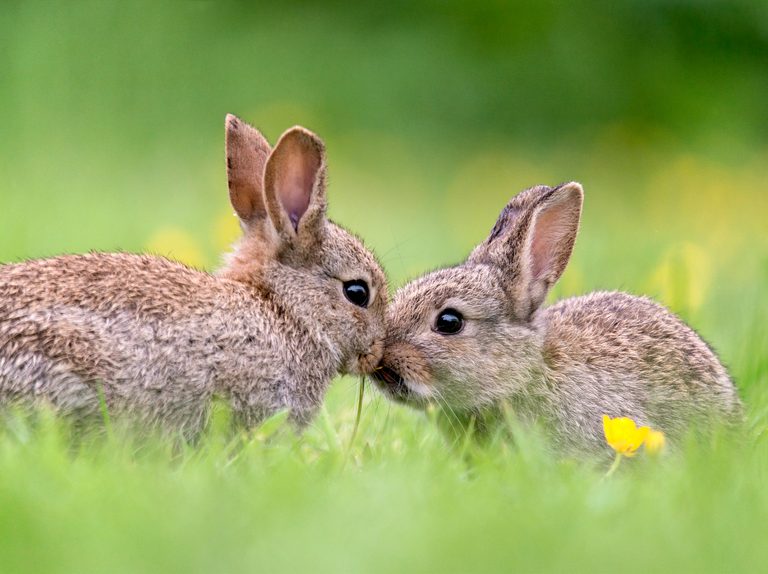

They can be found in different habitats across the globe which range from forests to the grasslands, to deserts. Rabbits are renowned for their social behavior and are often kept as pets due to their gentle behavior.
What is a Jackrabbit?
Jackrabbits are big-sized members of the genus of hares that is which are found across North as well as Central America. They are part of the Genus Lepus which is distinct from rabbits by their large ears, powerful hind legs, and long bodies.
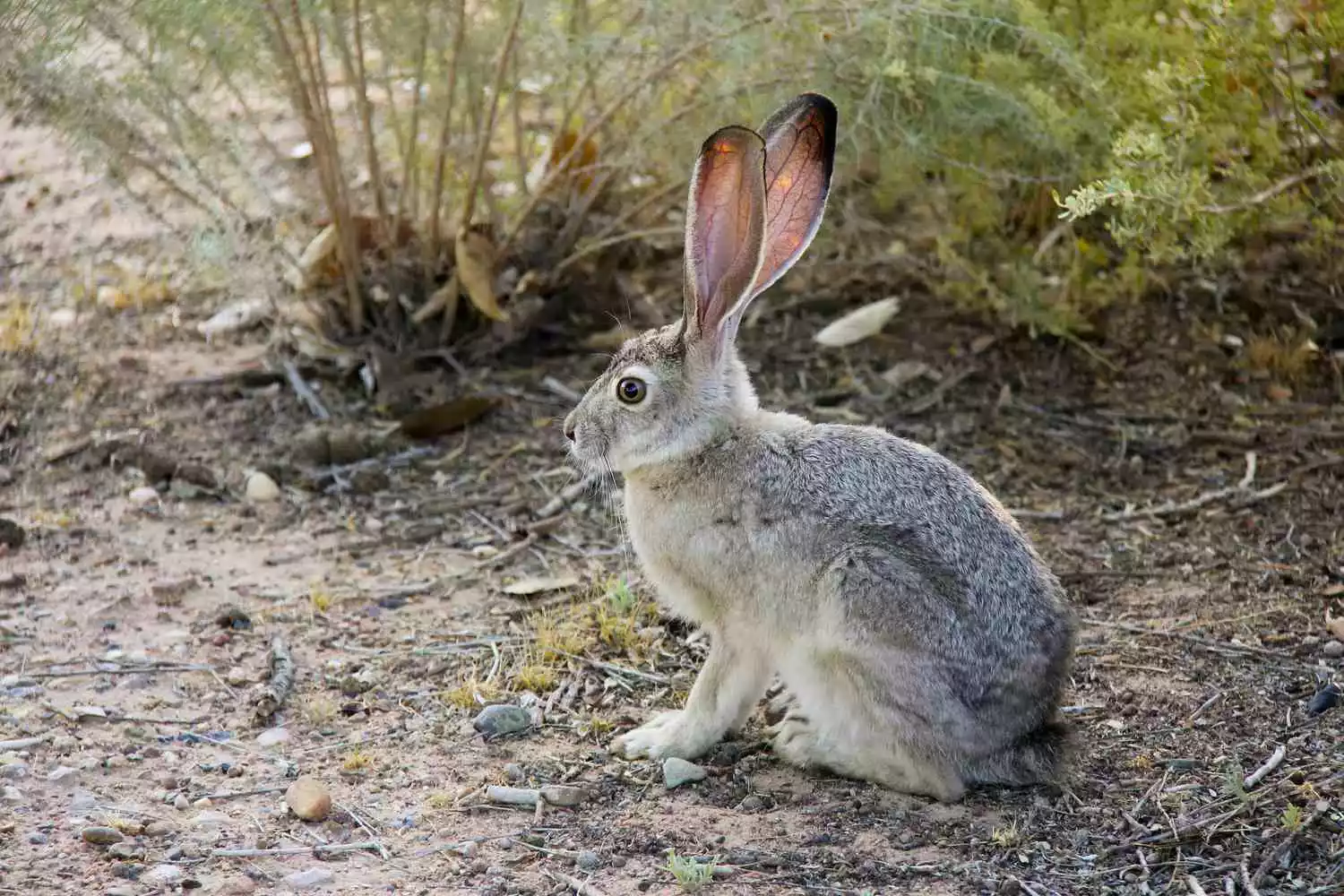

Like rabbits, jackrabbits are larger in size, have larger legs, and designed to run fast, and are designed to open environments like grasslands, deserts, and scrublands. They are well-known for their agility and speed and rely on their ability to beat predators.
Importance of understanding their differences
Understanding the difference between jackrabbits and rabbits has some important aspects:
- Ecological Understanding: Knowing their distinctions assists in understanding their distinctive ecological functions. Rabbits and jackrabbits are both characterized by different behaviors as well as diets and adaptations, which impact their interactions with their ecosystems in different ways. Understanding these distinctions helps in understanding the balance and function of these ecosystems.
- Conservation Strategies: Knowing the specific characteristics and habitats of rabbits as well as Jackrabbits is essential for efficient conservation strategies. Recognizing their specific requirements enables them to be targeted in conservation efforts that help ensure their habitats and populations more effectively.
- Impact on Agriculture: Understanding the differences between these species aids in the management of potential conflicts with agriculture. Rabbits, which are known because of their widespread breeding may pose different problems compared to jackrabbits. Both species might have different feeding patterns or affect crops in different ways. This knowledge helps to develop the right measures to minimize the damage to crops.
- Cultural Significance: The jackrabbit and the rabbit frequently have a cultural significance in different societies, from folklore to symbols to food customs. Knowing the differences between them can provide insights into different cultural beliefs and practices that are associated with the animals.
- Educational Purposes: The distinction between jackrabbits and rabbits acts as a teaching tool. It aids in the teaching of biology, ecology and zoology by showing the diversity of species as well as showing the evolution of adaptations to different habitats.
- Wildlife Management: Recognizing the different behaviors of wildlife can help in the management and controls. Customizing management strategies to the specific species’ behavior and habitats is crucial to efficient population control and to prevent ecological imbalances.
Understanding the differences between rabbits and Jackrabbits can be crucial to ecological balance conservation efforts and agricultural management, as well as educational programs, cultural appreciation, and the most effective practices for managing wildlife.
Comparison Table of Rabbit and Jackrabbit
Absolutely, here’s a comparison table highlighting the key differences between rabbits and jackrabbits:
| Aspect | Rabbit | Jackrabbit |
|---|---|---|
| Size | Smaller | Larger |
| Body Shape | Compact, rounded | Elongated, slender |
| Ears | Shorter | Longer, more prominent |
| Legs | Shorter, less powerful | Longer, more powerful |
| Habitat | Varied habitats including forests, grasslands, burrows | Open habitats such as deserts, grasslands, scrublands |
| Behavior | More likely to burrow and create warrens | Prefers running; less tendency to burrow |
| Diet | Herbivorous | Herbivorous |
| Running Ability | Slower, less agile | Faster, more agile |
| Geographical Range | Worldwide | Primarily North and Central America |
| Nocturnal Behavior | Often nocturnal | Often crepuscular or diurnal |
| Predator Avoidance | Relies on burrows for safety | Relies on speed and agility for escape |
| Cultural Significance | Often kept as pets, cultural symbols in various societies | Common in folklore and cultural traditions |
| Conservation Status | Various species may have differing conservation statuses | Varies among species, some may face conservation concerns |
This table highlights some of the primary differences between rabbits and jackrabbits, encompassing their physical traits, behaviors, habitats, and cultural significance.
Physical Characteristics of Rabbits and Jackrabbits
Some physical differences between rabbits and jackrabbits include:
Jackrabbits can weigh up to seven kilograms (15 lbs), whereas rabbits typically range from 0.5-2 kg (1-4.5 lbs). Jackrabbit ears can extend six inches (15 centimeters longer), whereas their counterparts have shorter ears of 2-4 inches or 5-10 centimeters in length.
Leg Length: Jackrabbits have longer legs than rabbits, which helps them run faster and jump further. Their tails also stand out more, usually held upright with an exposed black tip at their ends compared to shorter rabbit tails that usually blend in seamlessly into their fur coats.
Fur: Jackrabbits generally possess coarser and sparser coats compared to rabbits; rabbits’ fur usually tends to be soft and fluffy while Jackrabbit fur often takes on darker, brownish-gray tints that differ significantly in colors and patterns from rabbits.
Jackrabbits tend to be more athletic and leaner than traditional rabbits, which have rounder bodies with compact shapes.
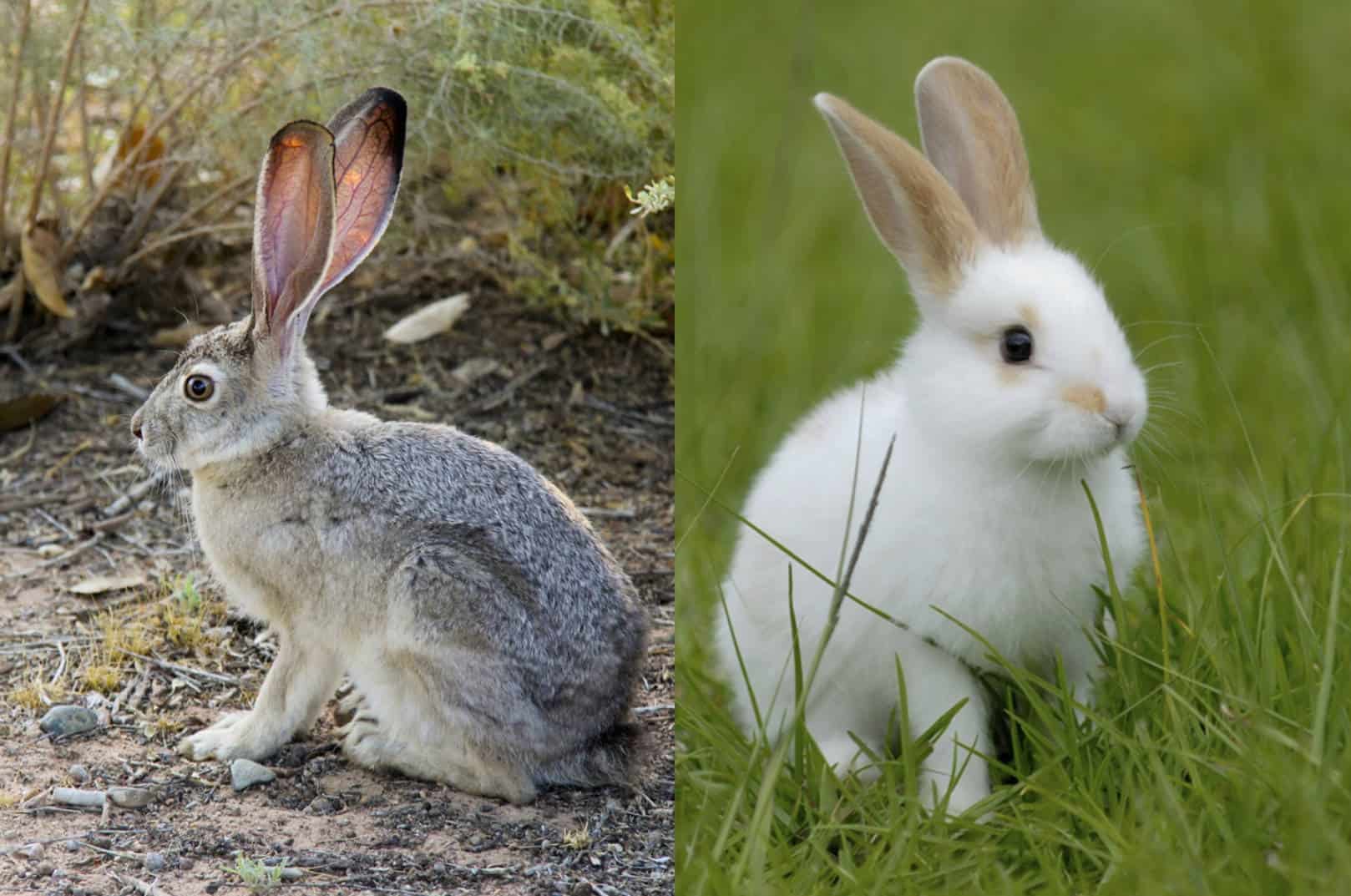

Habitat and Distribution
Certainly! Here’s a breakdown of the habitat and distributional distinctions between jackrabbits and rabbits:
Rabbits:
- Habitat: Rabbits can be adapted and thrive in a variety of conditions. They are found in many habitats like grasslands, forests, meadows deserts, as well as urban zones. They prefer areas with shade to protect themselves and have burrowing possibilities.
- Distribution: Rabbits enjoy a vast distribution throughout the world and are found on continents such as Europe, Africa, Australia as well and the Americas. Different species have evolved to particular regions based on the climate and the availability of food.
Jackrabbits:
- Habitat: Jackrabbits are more focused on their preferred habitats and favor open areas such as deserts, arid grasslands, and scrublands. They’re well-adapted to their environment, using their agility and speed to ensure protection instead of digging.
- Distribution: Most commonly located throughout North as well as Central America, jackrabbits inhabit areas like those in the desert of the American Southwest, the prairies along open grasslands. They’ve evolved to thrive in these semi-arid and desert areas.
The primary distinction is in the habitats they prefer which are rabbits. Rabbits exhibit a wider adaptation to a variety of habitats, including those with more vegetation, whereas jackrabbits prefer desert landscapes that are open and dry using their speed and agility to avoid predators in these environments.
Diet and Nutrition
Certainly! Here’s a look at the diet and food habits of rabbits and jackrabbits.
Rabbits:
- Diet: Rabbits are herbivores that have diets that are mostly comprised of hay, grasses leaves of greens, and other vegetables. They consume a high amount of fiber and require a regular intake of roughage to ensure good digestion.
- Nutrition: The digestive system of humans is designed to break down the cellulose in plant materials. They are coprophagous and consume their own feces, which allows them to re-digest specific nutrients, a process vital to obtaining essential minerals and vitamins.
Jackrabbits:
- A diet: similar to rabbits, jackrabbits are herbivores. They mainly eat the grasses, plants, as well as other plants that they find in their habitats of dryness. They can eat plants that may not be more than other herbivores due to their special digestive system.
- Nutrition: Jackrabbits have evolved to draw water from their food sources, allowing them to live in dry environments. The digestive system of their body efficiently processes the tough desert plants with low nutrients they eat, allowing them to thrive in spite of their limited resources for food.
Both jackrabbits and rabbits are herbivores, however, their diets differ depending on their environment. Rabbits consume a range of greens and grasses while jackrabbits have adjusted to harsher conditions, relying on tougher, less nutritious vegetation that is found in dry areas.
Reproduction and life cycles
Rabbits and jackrabbits differ significantly in terms of life cycles and reproductive strategies, yet both species share similarities in this regard.Rabbits reproduce rapidly. Female rabbits can produce multiple litters per year. Litters of 3-8 young are called kits and typically breed between three and eight months of age.
Rabbits can quickly start reproducing again after birth as their gestation period only lasts 28-31 days! Kits born without hair or vision but quickly gain it once weaned between four and five weeks of age in captivity (or 10 in nature!). Wild populations have lived as long as 10 years! Jackrabbits are more fertile than rabbits; females usually breed once or twice annually and give birth to litters of two to eight young.
Leverets emerge after 41-47 day gestation periods with eyes wide open and fully furred heads; after birth, they can move around freely while feeding themselves as adults and are weaned off their mothers at four weeks; in the wild, these little guys usually last between one to five years before passing into another species’ territory.
Rabbits and Jackrabbits share the ability to produce multiple offspring at one time in one litter; rabbits in particular typically experience shorter gestation periods and can breed more frequently due to predation and environmental pressures; both species ultimately live relatively brief lives in nature due to these threats.
Behavior and social structure
There’s no doubt that there’s a parallel between the social and behavioral structure of jackrabbits and rabbits:
Rabbits:
- Social Structure: Rabbits are typically social animals. They are usually found in groups. They reside in warrens or burrows, and they form colonies that include multiple people. Within these colonies, they create hierarchical structures.
- Behavior: The animals exhibit territorial behavior by in which they mark their territory by releasing scent glands. Rabbits are crepuscular. That means they are active between the dawn and dusk hours. They communicate with different sounds, like tapping their hind legs to send an alarm signal.
Jackrabbits:
- Social Structure: Jackrabbits are typically individuals. They don’t live in burrows or warrens as do rabbits, instead, they have separate places to rest or shelters. They are not as Social and tend to keep their own territory.
- Behavior: Jackrabbits are known for their agility and speed, and they rely on these attributes to elude predators. They are mostly crepuscular or diurnal. They are active in the early morning and late afternoon. They communicate using vocalizations and body language but typically have fewer social interactions than rabbits.
The primary distinction is in their social structure and behaviors: rabbits tend to form groups and create hierarchical structures within colonies, whereas jackrabbits are more of a solitary species that prefer their own territories, without complicated social structures. Furthermore, their patterns of activity and communication methods differ in relation to their social habits.
Conclusion
While jackrabbits and rabbits might appear similar on the surface their differences in the way they interact with each other, their habitat preferences food habits, and adapting to different habitats set them apart.
Understanding these differences can shed light on the many ways that these animals thrive in their natural habitats, highlighting the importance of individualized conservation efforts and the preservation of the environment for these species that are unique.