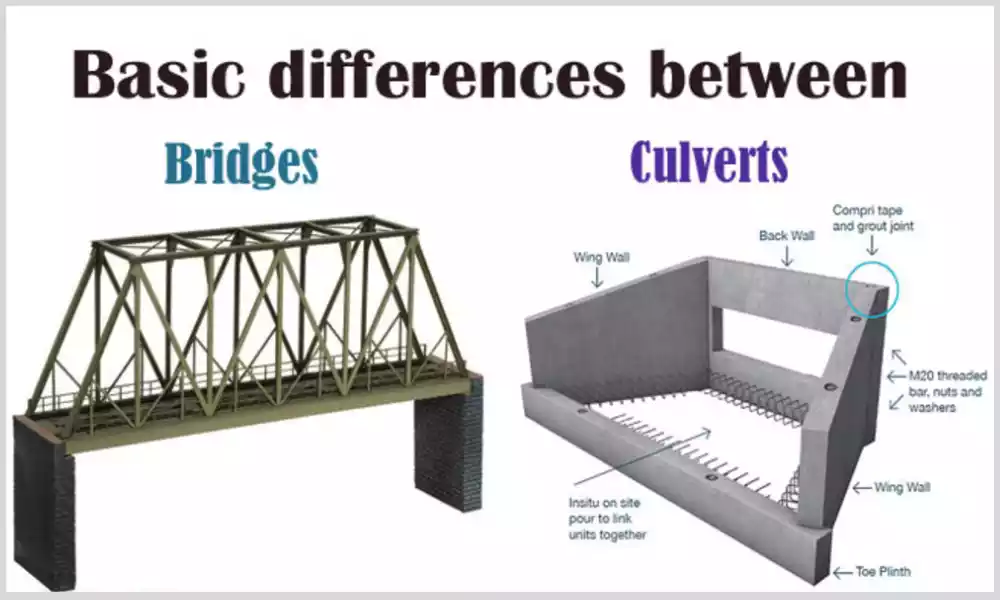
What is bridge and Culvert?
Bridge:
A bridge is a construction that is designed to span an obstruction, like the body of water, valley or a road, to allow access over the obstruction for vehicles, pedestrians or other types of traffic. Bridges are constructed using robust materials like concrete, steel or wood, and are constructed to be able to withstand the forces and weight that the vehicles they transport.Bridges vary in dimensions and shapes, based on the location and function of the structure. They are an Essential part of the Transportation Infrastructure.
Culvert:
A culvert can be described as a structure that permits water to flow underneath the railway, a road or any other physical obstruction like a drainage ditch or small stream. Culverts are usually constructed of robust materials such as concrete, steel or plastic. They are Constructed to be able to Withstand the force and Weight of the Vehicles that pass Through Them.
Culverts are generally rectangular or round and vary in length and size according to the flow of water as well as the size of the obstruction they’re crossing. Culverts are an essential part of drainage infrastructure, assisting to avoid erosion and flooding caused by excessive flow of water.
Bridge vs Culvert
Here’s a comparison table of culverts and bridges:
| Criteria | Bridge | Culvert |
| Scope | In order to allow for the passage of an obstruction | In order to allow water to flow through an obstruction |
| Design | Spanning structure | Tunnel-like structure |
| The typical location | Over bigger bodies of water or more extensive crossings | In smaller bodies of waters or in shallower crossings |
| Type of traffic | It is designed for pedestrian or vehicular traffic | It was designed to facilitate drains and flow |
| Construction | Strong foundation is required and frequent maintenance | It is possible to be buried underground and requires less maintenance |
| Materials | Concrete, steel and wood | Concrete, metal, plastic |
| Size and shape | Variable in size and shape to be able to handle traffic | Typically, rectangular or round |
| Durability and longevity | A longer lifespan, which needs more frequent maintenance | Lengthier and requires less maintenance |
| Effects on the environment | Impacts can be more significant on the area around it | Could have a less significant impact on the area surrounding it |
| Cost | Costlier to build and keep in | It is more economical to build and maintain |
Note The following is a general table of comparison and might not be applicable to all instances of a culvert or bridge. The construction and features of these structures could differ widely based on the particular location, traffic demands as well as environmental concerns.

Specific characteristics of Bridges
Bridges are structures constructed to span an obstruction, like water bodies or a valley an avenue, which allows access to the obstacle for vehicles, pedestrians and other forms of traffic. These are the most common features of bridges:Spanning structures The bridges are built to cross a gap, or obstruction, allowing an easy passage across it.
Built to facilitate traffic: Bridges have been constructed to support pedestrian or vehicular traffic across the obstruction.
Structural Materials: Bridges may be Constructed of a variety of Different materials, Including Concrete, steel or even wood, Depending on the strength Required as well as Durability and Aesthetics.
Foundation Bridges require a sturdy foundation that can hold up their weight as well as the load of traffic they transport. The foundation may be made from steel, concrete, or any other material, based on the area and specifications for the design.
Design flexibility Bridges are designed with a variety of sizes and shapes, including arches, beams cables and trusses to meet the needs of different kinds of traffic and environmental concerns.
Maintenance requirements: Bridges require regularly scheduled maintenance, which ensures their security and long-term durability. This Includes Inspection, repair or Replacement of parts that have been Damaged or Worn out.
Lifespan: Bridges generally last longer than culverts or other forms of infrastructure. A well-maintained bridge could last for decades as well as centuries based on the construction and materials employed.All in all bridges are a crucial part of the transportation infrastructure offering a secure and effective means for goods and people to traverse obstacles like waterways and valleys.
Specific characteristics of Culverts
Culverts are structures that allow water to flow over a railway line, a road or other physical obstacle for example, a drainage ditch, or a small stream. These are the most common features of culverts:
Tunnel-like structures Culverts are usually tunnel-like structures that permit water to flow under an obstruction like a road or another.Built for drainage, culverts are designed to permit water to flow through the obstruction, thus preventing erosion and flooding due to the flow of water.
Culverts constructed of structural materials: They are usually constructed of sturdy materials like metal, concrete, or even plastic, depending on the anticipated flow of water as well as the size of the obstruction they’re going to be passing through.
Placement: Culverts are usually installed under smaller bodies of water or on the banks of shallower crossings where bridges aren’t needed.Flexible design Culverts are able to be constructed in various sizes and shapes, such as rectangular or round shapes to suit different types of water flow as well as environmental concerns.
Maintenance requirements: Culverts require regular maintenance to avoid obstructions and to ensure that they are functioning properly. This includes removing the culvert of debris and sediment that has accumulated in the culvert.
Lifespan: Culverts generally have a shorter duration than bridges, however it can differ based on the type of material and design utilized. A well-maintained culvert can last for several decades.In the end, culverts are an essential element of drainage infrastructure. They assist to avoid erosion and flooding caused by water flow. They’re generally less expensive to build and keep up than bridges, and constitute an essential component of the transportation infrastructure in areas with less river channels and more shallow crossings.
Advantages and disadvantages in the use of Bridges and Culverts
Here are some benefits as well as disadvantages to bridges as well as culverts:
Benefits of Bridges:
Clear passageway over physical obstacles, for example, a body waters or valleys.
They can handle heavier traffic loads than culverts.
They can last longer than culverts.
It is possible to design in different sizes and shapes to meet various traffic requirements.
It can be a significant part of the landscape’s visual appeal and contributes to the aesthetics and beauty of a place.
The disadvantages of bridges
It is more expensive to build and maintain than culverts.
It can have a bigger impact on the environment surrounding it and require additional infrastructure, such as access roads or drainage systems.
Are more susceptible to the effects of natural disasters like earthquakes or floods.
The advantages of culverts
Let water flow over the obstruction to prevent erosion and flooding caused by overflowing water.
Typically, bridges are more cost-effective to construct as well as maintain than bridges.
It is possible to design a system that can be able to accommodate various kinds of flow.
Impacts are less on the environment around it.
The disadvantages of Culverts:
They are not able to carry the same traffic as bridges.
They typically have a shorter life span than bridges.
It is possible to get blocked and require frequent maintenance.
Not suitable for large bodies of water or for deeper crossings.
In the end, the decision between a bridge or the culvert will be based on many elements, including the dimensions and depth of the obstacle to be crossed as well as the anticipated traffic loads as well as environmental factors, and budgetary restrictions. Both culverts and bridges are essential components of the transportation infrastructures, allowing secure and reliable passage over or through physical obstacles.
Conclusion
In the end bridges and culverts are two distinct types of structures that are designed to meet diverse needs in transportation infrastructure. Bridges typically allow passage across large areas of lake, a valley and other obstacles while culverts allow water to flow beneath an obstruction or a road which prevents erosion and flooding.
Bridges can be more costly to build as well as maintain than culverts however they can handle heavier traffic and have longer life span. They may also have more impact on the environment around them and are more susceptible to destruction from natural catastrophes.
Culverts tend to be more cost-effective to build as well as maintain than bridges however, they cannot withstand as heavy traffic loads, and usually have a shorter life span. They are essential components of drainage infrastructure. They can be constructed to handle different kinds of flow.
The final decision on a bridge and a culvert is going to depend on a range of elements, such as the dimensions and the thickness of the obstruction being traversed, anticipated traffic load, environmental factors and budgetary restrictions.